An APFS Filesystem flaw could lead macOS losing data under certain conditions
19.2.2018 securityaffairs Apple
The Apple expert Mike Bombich discovered an APFS Filesystem vulnerability that could lead macOS losing data under certain conditions.
A few days ago a ‘text bomb‘ bug was reported for Apple iOS and macOS apps, the issue can crash any Apple iPhone, iPad Or Mac.
Now the Apple expert Mike Bombich discovered an APFS Filesystem vulnerability that could lead macOS losing data under certain conditions.
The bug ties the way the operating system handles APFS sparse disk images formatted in Apple filesystem format APFS.
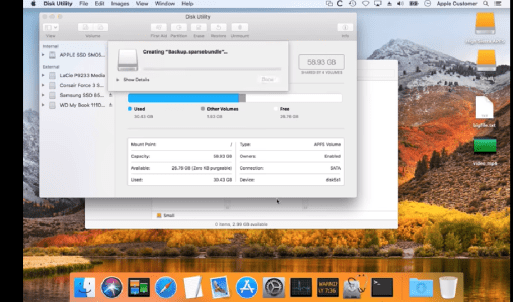
An Apple Disk Image is a disk image commonly used by the macOS operating system is “mounted” as a volume within the Finder. It contains the entire contents and structure of a disk volume, such as USB, CD, DVD, hard disk drive, or network share.
Disk images are commonly used by several Mac apps, for example for backup applications or disk cloning.
The expert discovered that APFS sparse disk images don’t properly manage the volume of the “free disk space” from the sparse disk image, the OS doesn’t correctly report “free disk space” respect the real “free disk space” value.
“Earlier this week I noticed that an APFS-formatted sparsebundle disk image volume showed ample free space, despite that the underlying disk was completely full. Curious, I copied a video file to the disk image volume to see what would happen. The whole file copied without error! I opened the file, verified that the video played back start to finish, checksummed the file – as far as I could tell, the file was intact and whole on the disk image.” wrote Mike Bombich. “When I unmounted and remounted the disk image, however, the video was corrupted. If you’ve ever lost data, you know the kick-in-the-gut feeling that would have ensued. Thankfully, I was just running some tests and the file that disappeared was just test data. Taking a closer look, I discovered two bugs in macOS’s “diskimages-helper” service that lead to this result.”
Bombich explained that data are written into the void because the OS doesn’t warn users that there is no enough space on the underlying hard drive to contain his data.
As described by the expert, the misleading data are still accessible for a short period after the write operation, unfortunately after the next system reboot exceeding files become corrupted and inaccessible.

Bombich is the author of the Mac backup software Carbon Copy Cloner, according to statistics from his software no many users are affected. The expert says that only 7% of all Carbon Copy Cloner users store backups as sparse disk image files and that only 12% of these 7% use APFS-formatted disk images.
The Carbon Copy Cloner software will not support AFPS-formatted sparse disk images until Apple addresses the vulnerability reported by Bombich.
Below a video PoC of the flaw.
“Until Apple resolves this disk images bug, we strongly recommend that people avoid using APFS-formatted sparse disk images for any purpose with any application.” concluded the expert.
Researchers spotted a new malware in the wild, the Saturn Ransomware
19.2.2018 securityaffairs Ransomware
Researchers at the MalwareHunterTeam spotted a new strain of ransomware called Saturn Ransomware, the name derives from the .saturn extension it appends to the name of the encrypted files.
Currently, the malware requests victims of $300 USD payment that doubles after 7 days.
Once infected a system, the Saturn Ransomware checks if it is running in a virtual environment and eventually it halts the execution to avoid being analyzed by researchers.
Then it performs a series of actions to make impossible for the victims restoring the encrypted files, it deletes shadow volume copies, disables Windows startup repair, and to clear the Windows backup catalog.
Below the command executed by the malicious code:
At this point, the Saturn ransomware is ready to encrypt files having certain file types.
The ransomware such as many other threats uses a Tor payment site that is reported in the ransom note dropped on the machine while the Saturn ransomware is encrypting the files.
“While encrypting the computer, Saturn Ransomware will drop ransom notes named #DECRYPT_MY_FILES#.html and #DECRYPT_MY_FILES#.txt and a key file named #KEY-[id].KEY in each folder that it encrypts a file. The key file is used to login to the TOR ransom site, while the ransom note contains brief information on what has happened to the victims files and a link to the TOR payment site at su34pwhpcafeiztt.onion.” wrote Larwrence Abrams from Bleeping Computer.

File encrypted by the Saturn Ransomware (Source Bleeping computer)
The Saturn ransomware also drops a #DECRYPT_MY_FILES#.vbs triggers an audio message to the victims, and it sets your Windows desktop background to #DECRYPT_MY_FILES.BMP.
The authentication to TOR site is made by uploading the key file, then users will display the Saturn Decryptor page for the victim that includes detailed instructions.
Researchers are still analyzing the Saturn ransomware, even if it is being actively distributed, it is still unclear what distribution vector threat actors are using to spread it.
Further information, including the Indicators of compromise (IoCs), are available in the blog post published by Bleeping Computer.
Prosecutor Robert Mueller indicted 13 Russians for a massive operation aimed to influence Presidential election
19.2.2018 securityaffairs BigBrothers
The special prosecutor Robert Mueller has accused thirteen Russian nationals of tampering with the 2016 presidential election and charged them with conspiring against the United States.
Thirteen Russian nationals and three Russian entities have been indicted for a massive operation aimed to influence the 2016 Presidential election.
The special prosecutor Robert Mueller has accused the defendants of tampering with the 2016 US presidential election and charged them with conspiring against the United States.
According to the results of the investigation conducted by the prosecutor, the Internet Research Agency, a Russian organization, and the 13 Russians began targeting the United States back in 2014.
Russian nationals used stolen American identities and local computer infrastructure to influence the 2016 Presidential election, the group deliberately denigrate the candidate Clinton to support Trump.
“Certain Defendants traveled to the United States under false pretenses for the purpose of
collecting intelligence to inform Defendants’ operations. Defendants also procured and used
computer infrastructure, based partly in the United States, to hide the Russian origin of their
activities and to avoid detection by U.S. regulators and law enforcement.” reads the Mueller’s indictment.
“Defendant ORGANIZATION had a strategic goal to sow discord in the U.S. political
system, including the 2016 U.S. presidential election. Defendants posted derogatory information
about a number of candidates, and by early to mid-2016, Defendants’ operations included
supporting the presidential campaign of then-candidate Donald J. Trump (“Trump Campaign”) and
disparaging Hillary Clinton.”
The indictment states the Russian organization since April 2014 created a specific section focused on the US population that acted to influence the sentiment of citizens on the candidates through social media platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and YouTube. By 2014,
The group used VPN services to connect from Russia to the US and manage their network of social media accounts.
The organization would use email addresses such as staceyredneck@gmail.com during its activities.
16 Feb
kadhim (^ー^)ノ
✔
@kadhimshubber
Replying to @kadhimshubber
In September 2017, people apparently continue to write emails in which they say: "the FBI busted our activity (not a joke). So, I got preoccupied with covering tracks together with the colleagues" https://www.justice.gov/file/1035477/download … pic.twitter.com/jZCaq61ork
kadhim (^ー^)ノ
✔
@kadhimshubber
Email addresses the Russians allegedly used with their PayPal accounts include: "staceyredneck@gmail.com" and "wokeaztec@outlook.com" https://www.justice.gov/file/1035477/download … pic.twitter.com/7A6pbdM42I
7:23 PM - Feb 16, 2018
View image on Twitter
2
See kadhim (^ー^)ノ's other Tweets
The Russian propaganda machine created and controlled numerous social media accounts, one of them is the Twitter account “Tennessee GOP,” which used the
handle @TEN_GOP.
“The @TEN_GOP account falsely claimed to be controlled by a U.S. state
political party. Over time, the @TEN_GOP account attracted more than 100,000 online followers.” continues the Indictment.
The group used stolen identities of US citizens to buy political advertisements on social media, they also recruited Americans to spread derogatory information.
We are facing with a powerful and efficient propaganda machine. defendants and their conspirators
constantly monitored their campaign over social media. They measured the
size of the online U.S. audiences reached by their actions and the types of engagement with the
posts.
The activity of the organization was very active in 2016, when defendants posing as American citizens and communicating with Americans began to gather intelligence to better target their campaign.
“In order to carry out their activities to interfere in US political and electoral processes without detection of their Russian affiliation, the Defendants conspired to obstruct the lawful functions of the United States government through fraud and deceit, including by making expenditures in connection with the 2016 US presidential election without proper regulatory disclosure; failing to register as foreign agents carrying out political activities within the United States; and obtaining visas through false and fraudulent statements,” the indictment reads.
Social media giants Facebook and Twitter are both accused of running ads and promoted content for the groups operated by the Organization.
Twitter has admitted the involvement of thousands of bot accounts in Russian propaganda, the company has deleted 200,000 tweets posted by army of trolls used by the Kremlin.
Effective Tips for Internet Safety for Kids You Must Read
19.2.2018 securityaffairs Safety
Online safety for your kids is very important. However, that doesn’t necessarily mean that it needs to be hard work.
The key thing is to learn how to get parental controls set up properly so that you won’t have to worry as much about online safety when your kids start to use the internet for both school projects and entertainment.
There are many ways that the version of the internet that your kids see can be fine-tuned. One option is to use a free content filter that is offered by all of the major providers.
There are also sophisticated software that is available for sale that you can invest in if you feel the need for a more advanced solution.
In order to determine which is best for you, we will be covering some of the major parental control options that are available to you.
In this article, we will be discussing various parent control options that are available to you. However, keep in mind, that although there are some very useful parental control tools that are available – it is still important for you to watch what your children are doing when they are online as much as you can. There is no substitute when it comes to parental supervision of children.
Content filters
All of the major UK broadband providers, including EE, Virgin Media, TalkTalk, Sky, and BT offer content filters as a standard feature.
They block off sites that contain material that is inappropriate for children, like self-harming, pornography, and other nasty material. Access to sites that are known to contain malware and viruses are also restricted. The best internet packages will have this as standard nowadays.
Which broadband providers offer the best security?
You will need to decide whether or not you want to use the filters when you are getting your broadband first set up. The settings can be changed at any time by simply logging into your account. So you can always change your mind on whether you want to use the filters or not.
Software
Some broadband providers offer parental control software as part of their broadband packages. This type of software is widely available. Content filters are network-level filters and are applied to anyone who uses the connection.
By contrast, parental control software affects only the device that it is installed on. So for example, if you install parent control software on your desktop computer, it will not affect what your children are doing when they are using their tablets and phones.
In addition to filtering inappropriate content out, like gambling-related, violent and pornographic sites, some of this software also lets you monitor the online activity of your children and even restrict what times of days certain websites can be used.
This can definitely come in handy. You will finally have a way of keeping them off of sites like Facebook and YouTube when they are supposed to be doing their homework.
In general, any device that is able to access the internet has its own onboard parental control sets that can be tinkered with before allowing your children to use it.
That is particularly helpful if the broadband company provides you with the software that is the kind that applies to just one device at a time.
For example, Apple’s iPad and iPhone, have a broad range of restrictions, and you cause the settings menu to easily access them. You can lock them in place and protect them using a password.
Those devices, in addition to many others, also allow you to disable paid transactions inside of games and apps. That way your kids can run up any bills without you knowing about it!
There is no such thing as a flawless system. That is why it is a very good idea to make use of all of the different tools that are available to you.
When you place restrictions on the way devices can be used and also install software, it makes it double unlikely that your children will be exposed to any unsuitable or harmful material while they are online.
This will help to put your mind at ease, which is so important these days with all of the dangers lurking online.
Web browsers
At times your web browser, which is the program that is used for browsing the internet, allows you to block out certain kinds of websites.
Those settings may be used in conjunction with whatever software you have installed on your computer already which provides you with an added layer of protection.
For example, when the Google Chrome browser is used – which is a free download that is available to use – it includes a feature that allows you to set up different account profiles for managers and supervised users, which gives you full control of how your children can use the internet when they are online.
Once again it is best to use these features of the browser in combination with other parental controls, especially since the settings apply only to the Chrome browser. More tech-savvy, older children can quickly discover a workaround, such as downloading another web browser other than Google Chrome.
Websites
On certain internet platforms and websites, like iTunes, YouTube, and Google, there is a family-friendly filter that can be switched on that should block out any content that isn’t suited for children to see.
Once again, keep in mind that there is no such thing as a flawless system so that is why it makes sense to use these features in combination with other kinds of parental controls.
This is only really effective to use with very young children since older kids can figure out how the filter can be turned off if they get curious enough and want to look at things that they know they aren’t allowed to.
General advice on how to get safe online
Get Safe Online, an internet safety initiative has provided the advice below. We hope you find it helpful to manage your children’s experiences online.
Set some boundaries even before your child gets their first internet connected device – whether it is a console, laptop, tablet, or mobile device. After they have their device, it might be harder to change the settings or how they use it.
Network-level parental controls are offered by all major providers. When you switch to a different broadband package, you will have an option for turning content filtering on, so that adult material is blocked.
Keep in mind that doesn’t mean all bad stuff will be blocked – there is no such thing as a fully effective filter. You will need to stay vigilant and supervise your children.
Have a discussion with your children about what is appropriate and safe to share and post online.
All videos, photos, and comments are part of a person’s ‘digital footprint’ and may be seen by anybody and be available forever on the internet.
Speak with your children about the type of content they view online, along with the precautions they need to take when they are communicating with others online – for example, to never share personal information with strangers.
Keep in mind that services such as YouTube and Facebook have a reason for having minimum age limits of 13 years old. Don’t cave in to pressure – speak with your child’s school and other parents to be sure everyone is on the same page.
Explain to your children that being online doesn’t provide them with protection or anonymity. Make sure that you clearly tell them that they shouldn’t do anything over the internet that they wouldn’t feel completely comfortable doing in real life.