Hackers Earn $1 Million for Zero-Day Exploits at Chinese Competition
20.11.2018 securityweek Exploit
White hat hackers earned more than $1 million for exploits disclosed at the Tianfu Cup PWN hacking competition that took place on November 16-17 in Chengdu, the capital of China's Sichuan province.
The contest ran alongside the Tianfu Cup conference and is similar to Zero Day Initiative’s Pwn2Own – they both offer significant prizes and in both cases the demonstrated vulnerabilities are disclosed to their respective vendors. However, at this year’s Pwn2Own events combined – Pwn2Own 2018 and Pwn2Own Tokyo 2018 – hackers earned roughly $600,000.
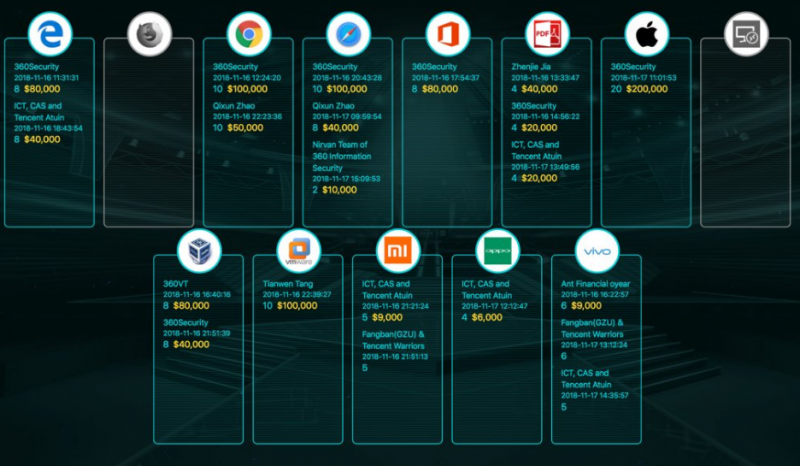
At the Tianfu Cup PWN competition, participants earned a total of $120,000 for two Microsoft Edge exploits that allowed remote code execution. Two Chrome exploit chains earned hackers a total of $150,000.
Three teams received the same amount for Safari vulnerabilities, including $100,000 for an exploit demonstrated on macOS.
The highest single reward, $200,000, was paid out to contestants who demonstrated an iPhone X jailbreak and a remote code execution exploit.
Tianfu Cup organizers told SecurityWeek that this iPhone X exploit involved a type confusion Just-in-Time (JIT) bug in Safari and a use-after-free vulnerability in the iOS kernel. The hackers promised to make details available after Apple pushes a fix.
Researchers also earned $120,000 for two Oracle VirtualBox exploit chains, and $100,000 for hacking VMware Workstation and Fusion.
VMware has confirmed that the vulnerabilities allow an attacker to execute code on the Workstation host from the guest. The company says it’s working on addressing the flaws and promised to publish an advisory.
Earlier this month, VMware informed customers of patches for a critical virtual machine (VM) escape vulnerability disclosed recently by a researcher at the GeekPwn2018 hacking competition in China.
A Microsoft Office exploit chain involving a logical bug and a memory corruption flaw earned researchers $80,000. A total of $80,000 were paid out for three Adobe Reader hacks.
Participants also earned several thousands of dollars for hacking Vivo X23, OPPO R17 and Xiaomi Mi 8 smartphones.
There were also several attempts that did not earn participants any money due to the fact that they involved previously disclosed vulnerabilities.
According to organizers, participants earned $1,024,000 for disclosing 30 vulnerabilities. Of that amount, $620,000 was paid to a team from Chinese cybersecurity firm Qihoo 360. Independent researchers and teams from universities, Tencent, and Ant Financial, one of China's main financial services providers, also took part in the competition.
