Third-Party Patch Released for Windows Zero-Day
31.8.18 securityweek Vulnerebility
A patch is available for a Windows zero-day that became public knowledge earlier this week, but it’s not from Microsoft.
Instead, the fix comes from 0patch, a community project that aims at addressing software vulnerabilities by delivering tiny fixes to users worldwide. The patches are indeed tiny, usually less than 30 bytes in size.
The fix for this week’s vulnerability is also very small, at only 13 bytes. It was released within 24 hours after the bug was ousted on Twitter on Monday, and, already validated and verified, it is now rolling out to users.
@0patch
· Aug 29, 18
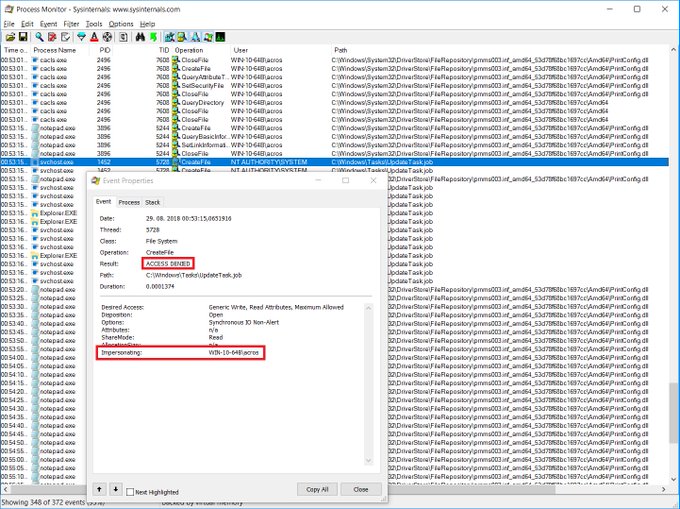
Okay people, 24 hours after the 0day was published we have a micropatch candidate for @SandboxEscaper's LPE in Task Scheduler. As you can see, scheduler's access to user-controlled hardlink is impersonating the user and gets ACCESS DENIED. pic.twitter.com/3kHcXdY42H
View image on Twitter
0patch
@0patch
Validated and verified, our micropatch for @SandboxEscaper's LPE in Task Scheduler is now published and freely available for everyone to use. It currently applies only to fully updated 64bit Windows 10 1803. We welcome requests for ports to other versions at support@0patch.com. pic.twitter.com/9pNufwUehU
2:19 PM - Aug 30, 18
39 people are talking about this
Twitter Ads info and privacy
The vulnerability was discovered in the Windows Task Scheduler’s Advanced Local Procedure Call (ALPC) interface and was confirmed to impact at least Windows 10 64-bit machines. CERT/CC issued an alert soon after details on the bug were posted online along with proof-of-concept (PoC) code.
“As the researcher's POC demonstrates, one can use this vulnerability to replace a system executable file and wait for a privileged process to execute it. In particular, it was shown that a printing-related DLL could be replaced and then executed by triggering the Print Spooler Service to load it,” 0patch points out in a blog post.
The issue resides in Task Scheduler's SchRpcSetSecurity method, which is externally accessible via ALPC. The method can be called by any local process and sets a desired security descriptor (sddl) on a task or folder.
Because the method “fails to impersonate the requesting client when setting the security descriptor,” Task Scheduler changes the access control list of the chosen file or folder as Local System user for all users, even low-privileged ones.
While the micropatch fully addresses the issue, preventing even variations of the exploit to trigger the vulnerability, users are advised to apply a Microsoft-supplied fix as soon as one becomes available. The unofficial fix might also cause unexpected errors, 0patch warns.
Microsoft’s next set of patches is expected to arrive on September 11 and an official fix for this 0-day is highly likely to be delivered then.