5.4.24 Phishing The Hacker News

New Phishing Campaign Targets Oil & Gas with Evolved Data-Stealing Malware
5.4.24 Phishing The Hacker News
An updated version of an information-stealing malware called Rhadamanthys is being used in phishing campaigns targeting the oil and gas sector.
"The phishing emails use a unique vehicle incident lure and, in later stages of the infection chain, spoof the Federal Bureau of Transportation in a PDF that mentions a significant fine for the incident," Cofense researcher Dylan Duncan said.
The email message comes with a malicious link that leverages an open redirect flaw to take the recipients to a link hosting a supposed PDF document, but, in reality, is an image that, upon clicking, downloads a ZIP archive with the stealer payload.
Written in C++, Rhadamanthys is designed to establish connections with a command-and-control (C2) server in order to harvest sensitive data from the compromised hosts.
"This campaign appeared within days of the law enforcement takedown of the LockBit ransomware group," Duncan said. "While this could be a coincidence, Trend Micro revealed in August 2023 a Rhadamanthys variant that came bundled with a leaked LockBit payload, alongside a clipper malware and cryptocurrency miner.

"The threat actors added a combination of an information stealer and a LockBit ransomware variant in a single Rhadamanthys bundle, possibly indicating the continued evolution of the malware," the company noted.
The development comes amid a steady stream of new stealer malware families like Sync-Scheduler and Mighty Stealer, even as existing strains like StrelaStealer are evolving with improved obfuscation and anti-analysis techniques.
It also follows the emergence of a malspam campaign targeting Indonesia that employs banking-related lures to propagate the Agent Tesla malware to plunder sensitive information such as login credentials, financial data, and personal documents.
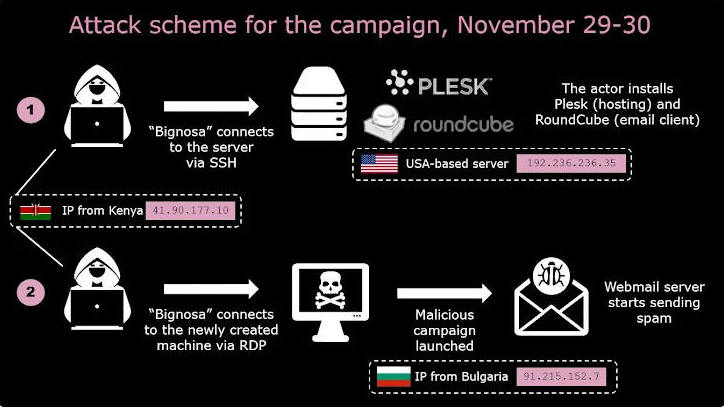
Agent Tesla phishing campaigns observed in November 2023 have also set their sights on Australia and the U.S., according to Check Point, which attributed the operations to two African-origin threat actors tracked as Bignosa (aka Nosakhare Godson and Andrei Ivan) and Gods (aka GODINHO or Kmarshal or Kingsley Fredrick), the latter of whom works as a web designer.
"The main actor [Bignosa] appears to be a part of a group operating malware and phishing campaigns, targeting organizations, which is testified by the US and Australian email business databases, as well as individuals," the Israeli cybersecurity company said.
The Agent Tesla malware distributed via these attack chains have been found to be secured by the Cassandra Protector, which helps protect software programs against reverse-engineering or modification efforts. The messages are sent via an open-source webmail tool called RoundCube.
"As seen from the description of these threat actors' actions, no rocket science degree is required to conduct the cyber crime operations behind one of the most prevalent malware families in the last several years," Check Point said.
"It's an unfortunate course of events caused by the low-entry level threshold so that anyone willing to provoke victims to launch the malware via spam campaigns can do so."