Most Sophisticated iPhone Hack Ever Exploited Apple's Hidden Hardware Feature

CATEGORIE : Apple |
DATE: 28.12.23 |
| WEB : The Hacker News |
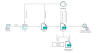
The Operation Triangulation spyware attacks targeting Apple iOS devices leveraged never-before-seen exploits that made it possible to even bypass pivotal hardware-based security protections erected by the company.
Russian cybersecurity firm Kaspersky, which discovered the campaign at the beginning of 2023 after becoming one of the targets, described it as the "most sophisticated attack chain" it has ever observed to date. The campaign is believed to have been active since 2019.