CERT-UA Uncovers New Malware Wave Distributing OCEANMAP, MASEPIE, STEELHOOK

CATEGORIE : Virus |
DATE: 29.12.23 |
| WEB : The Hacker News |
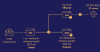
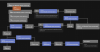
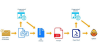
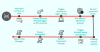
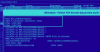
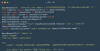
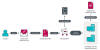
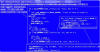
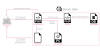
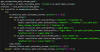
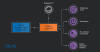
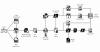
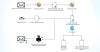
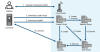
The Computer Emergency Response Team of Ukraine (CERT-UA) has warned of a new phishing campaign orchestrated by the Russia-linked APT28 group to deploy previously undocumented malware such as OCEANMAP, MASEPIE, and STEELHOOK to harvest sensitive information.
The activity, which was detected by the agency between December 15 and 25, 2023, targets government entities with email messages urging recipients to click on a link to view a document.






















































































































_small.png)