Deadglyph: New Advanced Backdoor with Distinctive Malware Tactics
CATEGORIE : Virus |
DATE: 24.9.23 |
| WEB : The Hacker News |
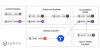
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a previously undocumented advanced backdoor dubbed Deadglyph employed by a threat actor known as Stealth Falcon as part of a cyber espionage campaign.
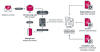
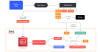
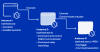
"Deadglyph's architecture is unusual as it consists of cooperating components – one a native x64 binary, the other a .NET assembly," ESET said in a new report shared with The Hacker News.